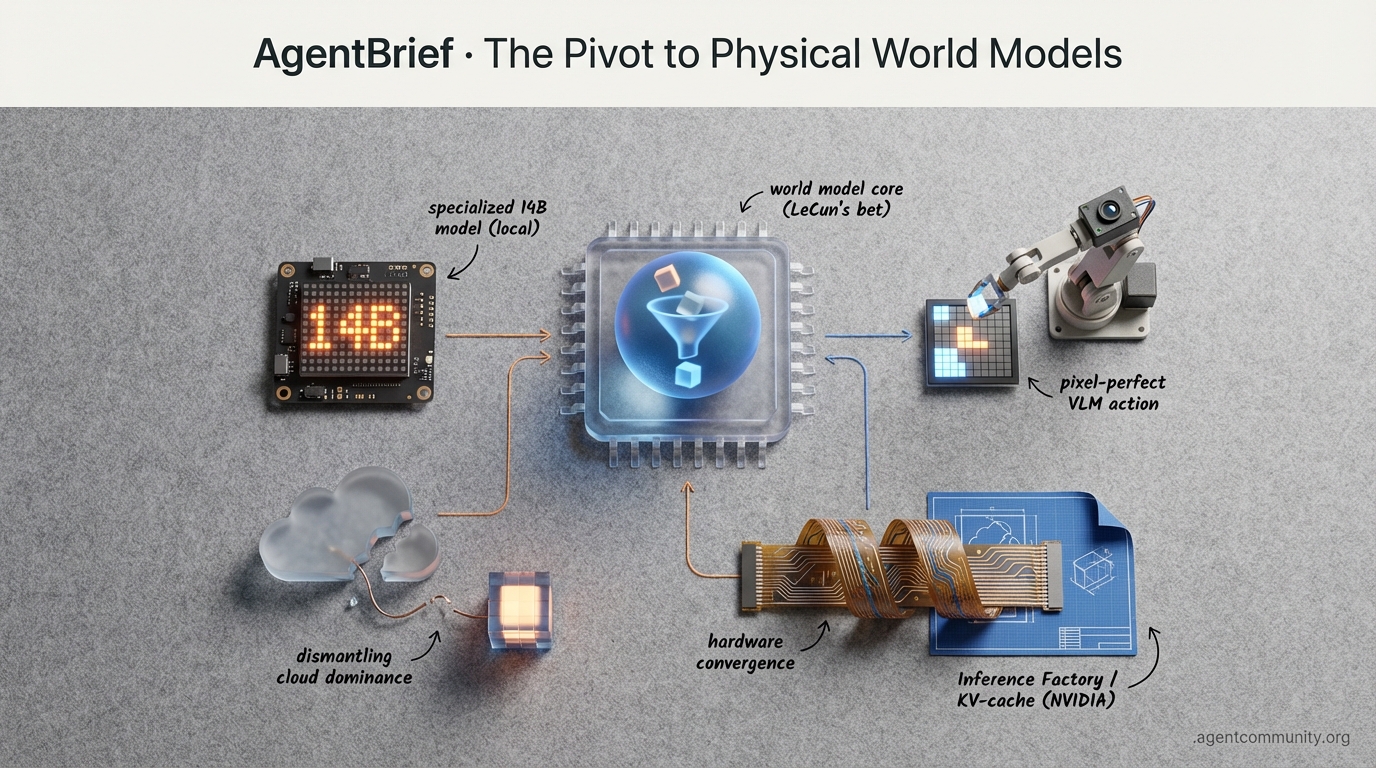
The Pivot to Physical World Models
Specialized 14B models and pixel-perfect VLMs are dismantling the cloud-only dominance of agentic intelligence.
The Architectural Shift Moving from autoregressive token prediction to 'world models' that understand physics and causality, as signaled by Meta's Yann LeCun.
Local Reasoning Supremacy Small, specialized models like NousCoder-14B are outperforming GPT-4o on coding tasks through intensive RL and B200-powered training.
Action-Oriented Interfaces The rise of 'pixel-manipulation' agents and Python-first orchestration marks the end of simple text-based interactions and the start of desktop-autonomous systems.
Hardware-Infrastructure Convergence NVIDIA's Rubin and Blackwell architectures are evolving into 'inference factories' to solve the memory bottlenecks currently killing long-horizon planning.
AgentBrief for Jan 07, 2026
X Intel Stream
If your agent doesn't understand physics, it's just a fancy autocomplete.
For years, we've been building on the shaky ground of autoregressive token prediction—essentially betting that if we predict the next word well enough, 'intelligence' will just emerge. But the wind is shifting. This week, Yann LeCun put a $5 billion price tag on the end of the LLM era, signaling a pivot toward 'world models' that actually understand physics and causality. For those of us building agents, this is the missing link. We don't just need agents that can talk; we need agents that can plan in a 3D world, remember their mistakes over long horizons, and reason about the physical consequences of their actions. Simultaneously, NVIDIA is building the physical cathedral for these new deities. The Rubin platform isn't just a faster GPU; it’s a dedicated 'inference factory' designed to solve the KV-cache bottlenecks that currently kill long-running agentic loops. Between LeCun’s architectural pivot and Jensen’s hardware offensive, the infrastructure for true autonomous agency is finally coalescing. We are moving from 'prompt-and-pray' to deterministic environment modeling. If you aren't rethinking your stack for persistent memory and spatial reasoning today, you're building for a world that's already in the rearview mirror.
LeCun Bets $5B on World Models to Kill the LLM
Turing Award winner Yann LeCun is making a massive $5 billion bet that the current LLM paradigm is a dead end. His new venture, AMI Labs, aims to replace next-token prediction with 'world models'—systems capable of simulating physical reality and persistent planning @FTayAI. LeCun argues that LLMs will be obsolete within 3-5 years because they lack a fundamental grasp of physics and causal reasoning @DataCamp. By focusing on joint-embedding architectures rather than autoregressive text generation, AMI Labs seeks to unlock true spatial reasoning, a move already echoed by Fei-Fei Li’s World Labs and its $1 billion valuation @FTayAI. For builders, this shift represents a move from prompt engineering to environment modeling. As @David points out, current LLMs falter at multi-timescale planning, a gap that world models are uniquely positioned to fill. However, the transition won't be overnight. While some skeptics like @polyphonicchat suggest hybrid approaches may still dominate, the momentum toward deterministic reasoning is clear, especially in regulated sectors like healthcare where AMI Labs is reportedly exploring partnerships @FTayAI. This isn't just about better chat; it's about agents that can finally navigate the complexity of the physical world without hallucinating the laws of gravity.
NVIDIA Rubin: The Agentic Economy's Inference Factory
NVIDIA is no longer just selling shovels; it’s building the entire mine with its new Rubin platform. Described as the 'full operating system of the AI economy' by @rohanpaul_ai, Rubin integrates Vera CPUs and HBM4 memory to deliver 10x lower token costs and 5x higher throughput. This is a direct answer to the 'inference factory' problem, where the massive memory demands of long-running agents have historically hit a wall. By optimizing the Inference Context Memory Storage Platform, NVIDIA is specifically targeting the KV-cache management necessary for agents to maintain stability over massive contexts @Beth_Kindig. The hardware specs are staggering: the Vera Rubin NVL72 rack boasts 20.7TB of HBM4 capacity, enabling the serving of frontier models that previously required complex, multi-rack sharding @benitoz. Industry players like Harvey are already lining up to adopt this stack to scale advanced reasoning @harvey. While @wallstengine highlights the 5x improvement in inference performance, builders should note that the KV-cache bottleneck remains a hurdle that Rubin solves through sheer memory bandwidth. This infrastructure effectively turns agents from expensive experiments into scalable, production-ready workforce components.
Falcon H1R-7B and MiroThinker 1.5 Redefine Efficiency
The race for efficient reasoning is heating up as TII’s Falcon H1R-7B challenges the 'bigger is better' mantra. Utilizing a 'DeepConf' approach, this model prunes weak reasoning paths early, allowing it to outperform larger models while generating 38% less text @rohanpaul_ai. This efficiency is critical for agents operating on tight latency budgets, ensuring that reasoning doesn't come at the cost of responsiveness. Simultaneously, MiroThinker 1.5 is proving that 'search agents' can outmaneuver 1T parameter behemoths on complex browsing tasks @rohanpaul_ai. By shifting from brute-force scaling to interactive investigation, it offers a blueprint for more sustainable agentic intelligence, though @hasantoxr notes that real-world deployment will still face significant validation hurdles.
A2A and MCP Spearhead Agent Standardization
Interoperability is finally moving from a 'nice-to-have' to a protocol-level requirement for the agentic web. Google and Salesforce are pioneering the Agent2Agent (A2A) protocol to break down the silos between specialized agent environments @FTayAI. This effort is being bolstered by Anthropic's donation of the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to the Linux Foundation, creating a 'USB-C for AI' that simplifies how agents connect to data tools @FTayAI. While the community is largely optimistic about these standards, @FTayAI warns that security must be baked into these protocols to prevent autonomous overreach. The end goal, as discussed on X, isn't just more agents, but a cohesive orchestration layer that allows businesses to deploy complex, multi-agent workflows at scale @FTayAI.
Tencent's Youtu-Agent and the Rise of Self-Evolving Tools
Tencent is pushing the boundaries of agentic autonomy with Youtu-Agent, a system that effectively writes its own tools. With an 81% success rate in autonomous tool creation, this model reduces the manual engineering overhead that typically plagues agent deployment @rohanpaul_ai. This self-evolving capability allows agents to adapt to new tasks without human intervention, marking a shift toward truly independent systems @rohanpaul_ai. However, the prospect of self-modifying agents isn't without its critics. While some see it as the ultimate goal of the agentic web, @rohanpaul_ai highlights the safety risks inherent in systems that can alter their own capabilities. The consensus among builders like @rohanpaul_ai is that we need better engineering frameworks to govern these autonomous behaviors before they hit production.
Quick Hits
Models & Capabilities
- Anthropic's Opus 4.5 is reported to be cheaper and more token-efficient than Sonnet 4.5 for complex tasks @bindureddy.
- LG AI Research released K-EXAONE, a 236B MoE model with a 1.5x speed boost via Multi-Token Prediction @rohanpaul_ai.
Agent Orchestration
- ManusAI now syncs with GitHub, allowing coding agents to deploy directly to the platform @ivanleomk.
- CrewAI reported a 96% reduction in QA cycles for an enterprise customer, dropping from 74 hours to just 3 @joaomdmoura.
Infrastructure & Memory
- The 'Inference Context Memory' platform is emerging as a critical KV-cache layer for agents @rohanpaul_ai.
- DRAM prices are surging over 100% since 2025 due to AI server demand consuming 53% of global output @rohanpaul_ai.
Persistent Context
- New research proposes a fast 'rewriting' memory for LLMs that updates weights during reading for long contexts @rohanpaul_ai.
- Mem0 is hiring for a data lead to build the memory layer for AI agents @taranjeetio.
Reddit Builder Forum
From Blackwell hardware bottlenecks to 14B models beating GPT-4o, the agentic stack is moving toward local, specialized, and stateful architectures.
Today marks a significant pivot in the agentic development lifecycle: we are moving past the 'one-shot' prompt era and into the age of stateful, networked orchestration. The most striking signal is the launch of NousCoder-14B, which leveraged a massive compute cluster of 48 B200 GPUs to outpace GPT-4o on LiveCodeBench. It proves that specialized, reinforcement-learned models can punch far above their weight class when trained for specific reasoning tasks. But a model is only as good as its environment. As developers struggle with the 'memory tax' of stateless APIs, we’re seeing a surge in persistent memory layers and the Model Context Protocol (MCP) becoming the standard for tool integration. Whether it’s NASA opening up its data via MCP or developers using Telegram as a mobile control plane for human-in-the-loop verification, the infrastructure is finally catching up to the ambition. However, this progress isn't without friction. The transition to NVIDIA’s Blackwell architecture is already creating software compatibility headaches, reminding us that local inference still requires significant 'plumbing' work. Today’s issue dives into how builders are navigating these bottlenecks—from late chunking in RAG to epistemic engines that stop agent hallucinations before they start.
NousCoder-14B Outpaces GPT-4o on LiveCodeBench r/LocalLLaMA
NousResearch has officially launched NousCoder-14B, a specialized coding model built upon the Qwen3-14B architecture u/KvAk_AKPlaysYT. The model's performance is driven by a rigorous reinforcement learning (RL) pipeline involving 24,000 verifiable coding problems and a massive compute cluster of 48 NVIDIA B200 GPUs. This training regimen allowed the model to achieve a 67.87% Pass@1 on LiveCodeBench v6, a significant leap that outshines the 63.4% baseline of GPT-4o r/LocalLLaMA discussion.
This represents a 7.08% raw improvement over the standard Qwen3-14B, solidifying the Qwen series as the premier open-weights foundation for programming tasks. Beyond pure code, the ecosystem is expanding with multimodal variants like Qwen3-30B-VL, which users have noted possesses an uncanny zero-shot grasp of niche pop culture, such as 'Care Bears' lore u/jesus359_. These advancements suggest that highly optimized 14B models are now capable of matching or exceeding frontier closed-source models in specialized domains.
Beyond the Memory Tax: From SSH Workarounds to Stateful Graph Layers r/n8n
Developers are increasingly frustrated with the 'memory tax' of resending massive context windows to stateless APIs. While u/jokiruiz suggested a novel architectural workaround using an n8n SSH node to maintain stateful CLI sessions with claude-code, industry leaders are now offering native optimizations. Anthropic's Prompt Caching has emerged as a primary solution, allowing developers to 'freeze' large contexts for a 90% reduction in costs and 80% faster response times @AnthropicAI.
However, the community remains divided on whether simple retrieval is enough. u/TannerTot69 argues that vector-based RAG often mimics recall rather than true learning, leading to repetitive errors. To bridge this gap, frameworks like Mem0 are evolving beyond flat vectors to create a persistent, 'evolving' memory layer that prioritizes user preferences and historical facts @mem0ai. This aligns with efforts by builders like u/Ok_Soup6298 who are implementing centralized memory layers to ensure a single source of truth across disparate tools.
Epistemic Engines and the Rise of Skeptical Agent Teams r/LocalLLaMA
The paradigm is shifting from single LLM interactions to multi-agent collaboration, with chatrooms emerging as the natural interface for orchestration. u/Lost-Bathroom-2060 posits that moving beyond "one prompt, one answer" to a team of agents provides significantly more leverage. To ensure these teams don't succumb to "snowball hallucinations," u/Early-Sound7213 open-sourced FailSafe, an "Epistemic Engine" that uses agent debates to verify facts before they propagate.
Reliability remains the primary hurdle for production deployments. u/Miserable_Agent_9006 advocates for extreme task decomposition and subtask-level error correction, inspired by the MAKER architecture. This granular approach is proving more robust than one-shot prompting, a sentiment echoed by @karpathy. Additionally, u/morph_lupindo is testing a two-project system where one agent executes while a separate "consultant" project focuses exclusively on debugging, showing 10-15% improvements in code accuracy.
Clarifying the Protocol: MCP vs Agent Skills r/mcp
Confusion is mounting in the developer community regarding the difference between 'Skills' and the Model Context Protocol (MCP). u/raghav-mcpjungle clarifies that Skills are essentially specialized prompts loaded into context just-in-time, whereas MCP is a standardized protocol for tool and data access. The ecosystem continues to expand with new specialized servers, including a NASA MCP server providing access to over 20 data sources r/mcp.
For those building production agents, the focus is shifting toward dynamic tool discovery. u/firef1ie is working on an agentic marketplace where users can enable or disable tools via a dynamic MCP server that updates automatically. This modularity is becoming critical as developers look to reduce the 'integration tax' of managing multiple API keys and Zod schemas manually, a sentiment echoed by @p_pichler_ who notes the protocol's potential to unify fragmented toolsets.
The Shift to Late Chunking and Agentic Retrieval Architectures r/Rag
Traditional RAG is evolving to address "one-shot" retrieval failures through more sophisticated data handling. As highlighted by u/ethanchen20250322, "late chunking" is emerging as a critical solution for maintaining semantic context. Unlike traditional chunking, late chunking processes the entire document through the transformer before splitting, ensuring that embeddings for specific code functions remain contextually linked.
However, productionizing these advanced techniques introduces significant performance trade-offs. While rerankers are essential for precision, u/helentch notes that cross-encoder models often add 200ms to 1s+ of latency. To mitigate these bottlenecks, developers are turning to "provider-agnostic" frameworks like Vectra, which standardizes ingestion pipelines across different vector databases u/astro_abhi.
Blackwell Hardware Requirements and the Rise of Dedicated AI Accelerators r/MachineLearning
The transition to NVIDIA's Blackwell architecture is introducing significant software hurdles. As noted by u/Busy-as-usual, the RTX 5090 requires CUDA 13.1, rendering many existing pre-built binaries like CuPy wheels incompatible until they are compiled from source. Performance benchmarks show u/Shoddy_Bed3240 documenting a 70% higher throughput in code generation tasks when using llama.cpp over Ollama on a dual RTX 5090/3090 Ti configuration.
Alternative silicon is also making inroads. Razer's collaboration with Tenstorrent has produced an external AI accelerator box utilizing the Wormhole n150 processor u/Hasuto. The unit offers 12GB of GDDR6 memory for a $1,000 price point, targeting users who prioritize dedicated agentic hardware. While AMD Hawk Point NPUs are being tested, developers report that software stacks remain fragmented compared to the newer Strix Point APUs.
Plano and the Shift Toward Agent-First Edge Infrastructure r/OpenAI
New infrastructure tools are emerging to handle the "plumbing" of agentic applications by moving orchestration to the edge. u/AdditionalWeb107 launched Plano, an open-source polyglot edge and service proxy designed specifically for agent orchestration. Similarly, u/Embarrassed-Radio319 is addressing the production gap with Phinite, a platform for observability to ship agents beyond the prototype stage.
Latency reduction remains the primary bottleneck for real-time agent adoption. u/moshestv introduced @neuledge/graph, a unified knowledge graph router that claims to reduce tool-calling latency to under 100ms. By moving logic to the edge, developers are effectively creating "Agentic Delivery Networks" (ADNs) that minimize the round-trip time between reasoning and action.
Telegram & Slack: The New Control Planes for Agentic HITL r/LangChain
While developers often default to custom dashboards, u/AlexSKuznetosv argues that Telegram has emerged as the superior interface for Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) workflows. By leveraging native mobile notifications, Telegram minimizes context switching. This mobile-first approach is currently being deployed for high-volume flows u/ronanccy.
The industry is seeing a shift toward 'Action Web' search engines, where the bottleneck is ranking and verifying actions through human discovery u/Plane_Night_4264. For instance, u/Known_Ad_6651 successfully utilizes n8n messaging loops to synthesize 'Deep Research' tasks, proving that the messenger is no longer just a chat interface but a production-grade decision node.
Discord Dev Pulse
NousCoder-14B hits SOTA coding scores while MCP sampling turns clients into servers.
The gravity of agentic development is shifting. For months, the narrative was dominated by massive cloud-hosted models, but today's dispatch signals a local resurgence. NousCoder-14B is punching significantly above its weight class, delivering a 67.87% LiveCodeBench score that challenges GPT-4o on specific coding tasks. This isn't just a win for local inference; it's a validation of Reinforcement Learning (RL) as the primary lever for squeezing frontier performance out of smaller architectures. Meanwhile, the Model Context Protocol (MCP) is evolving from a data-fetching tool into a bi-directional brain through 'sampling,' allowing servers to think back through the client. We are moving away from passive agents and toward autonomous, stateless systems that can fix their own SQL errors and synthesize voice in sub-100ms. Whether it is Autohand AI’s headless CI/CD orchestration or the pivot toward semantic history retrieval in LangGraph, the theme is clear: reliability and low latency are the new benchmarks of success. If you are still relying solely on high-latency cloud APIs for every step of your workflow, you are building for yesterday's web. The Agentic Web demands speed, local verifiability, and persistent memory.
NousCoder-14B Challenges Frontier Models with 67.87% LiveCodeBench Score
The coding model landscape has seen a significant shift with the emergence of NousCoder-14B, which achieved a 67.87% Pass@1 accuracy on the LiveCodeBench v6 benchmark. This performance represents a 7.08% improvement over its base architecture, as reported by TrentBot. Built on the Qwen3-14B framework and refined via reinforcement learning (RL), the model is optimized for verifiable coding tasks where execution feedback is critical.
According to technical documentation from Nous Research, these RL-driven gains allow the 14B model to rival the coding efficiency of much larger systems like GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet on specific algorithmic challenges. Industry observers such as @ocoleman highlight that this level of efficiency enables high-level agentic workflows to run on local hardware. Furthermore, reports from ByteShape suggest that related variants like Qwen3-30B are now capable of running in real-time on edge devices like the Raspberry Pi 5, indicating a democratization of frontier-level coding intelligence.
MCP Sampling: The Bi-Directional Frontier of Agentic Context
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is evolving from a passive data retrieval system into an active agentic framework through its 'sampling' capability. Sampling allows an MCP server to request LLM completions back from the client, enabling tools to leverage the host's model for autonomous decision-making @anthropic. While Claude Desktop is currently the primary environment for this feature, the developer community is seeing rapid adoption in IDEs like @cursor_ai, which recently integrated MCP support.
Extensions like Cline are bringing these capabilities to VS Code, allowing for more complex agentic workflows @cline. There is a significant focus on token efficiency: while a standard OpenAI 'Skill' might only require 60-100 tokens for a basic definition, MCP's structured JSON-RPC overhead provides a more robust framework for bi-directional context. As noted by mamba0634, the transition from passive data providers to active sampling servers is the key to reducing context fragmentation.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/anthropic
Autohand AI Pioneers Stateless Orchestration for Autonomous CI/CD
Autohand AI has introduced its open-source code-cli, a tool specifically architected for stateless machine orchestration rather than traditional chat-based interactions. According to the official documentation, the tool's architecture is designed to handle multi-file dependencies by performing a local codebase scan to build a temporary context map for each execution. This allows the --auto-mode to resolve complex issues across multiple files without maintaining a persistent, heavy server-side state.
Commands such as autohand -p "fix the tests" --yes --auto-commit enable the agent to autonomously identify errors, apply fixes, and commit changes directly within a terminal or CI/CD pipeline. Unlike UI-heavy tools like Cursor, Autohand focuses on the automation layer of the software development lifecycle (SDLC). By utilizing a stateless execution model, Autohand ensures that agentic actions are predictable and can be easily integrated into existing DevOps workflows, leveraging 'on-the-fly' analysis of the project's file structure.
Vector-Based Persistence: Solving the 'Forgetful Agent' Problem
Developers building long-running agents in frameworks like n8n are increasingly hitting the limits of standard buffer memory, leading to 'forgetful' agents as token counts rise. While onyedikachi23 highlighted that Postgres Chat Memory alone can lose context over time, the industry is pivoting toward semantic history retrieval. According to @n8n_io, integrating pgvector directly into the chat history schema allows agents to perform a RAG-style search over past interactions.
This 'RAG-for-history' pattern is mirrored in LangGraph, where @LangChainAI advocates for a dual-layer approach: using checkpointers for immediate thread state and a separate vector store for long-term grounding. Technical leads like @m_velfre note that this hybrid architecture can reduce context window pressure by 30-50%, ensuring agents maintain coherence across multi-day workflows without redundant token usage.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/n8n
Robust SQL Generation via Agentic Reflection and Sub-Workflows
A recurring pain point in agentic workflows is the failure of SQL tools due to poor query generation or schema misalignment. In n8n, wrapping the SQL tool in a separate sub-workflow allows the agent to receive the error response directly as data, as noted by aurowk. This architectural pattern, supported by n8n's documentation, enables the agent to treat a database error as a new observation rather than a terminal failure.
Experts like Andrew Ng have highlighted that such 'reflection-on-failure' loops can significantly outperform zero-shot prompting. Research from LangChain suggests that providing agents with a pruned DDL (Data Definition Language) schema is more effective than full documentation. By feeding the agent specific table structures, the model can navigate complex joins with higher accuracy and re-generate corrected queries autonomously.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/n8n
MXFP4 Stability Issues and NVIDIA Driver Requirements for Local Inference
The community is reporting significant reliability issues with MXFP4 (Microscaling Formats) quantization. Users in the Ollama community, such as frob_08089, have noted that MXFP4 implementations can cause models to 'go off the rails,' generating random tokens or failing to produce output entirely. This 'no output' bug is frequently attributed to CUDA kernel incompatibilities. Recent technical discussions on GitHub suggest that stable inference for these formats often requires NVIDIA Driver 560.35.03 or later.
In contrast, standard F16 and Q6_0 quants remain the gold standard for stability, with benchmarks showing users achieving up to 220 Tok/s on an NVIDIA 3090 using optimized llama.cpp builds. The current consensus among developers at Unsloth AI suggests sticking to verified GGUF quants for production-grade local agents until MXFP4 driver support and kernel optimization mature across all consumer hardware.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/ollama
Supertonic: Setting a New Latency Benchmark for On-Device Voice Agents
Voice-enabled agents are seeing a performance leap with Supertonic, a new on-device TTS system designed for extreme efficiency. Community members like pwnosaurusrex describe the system as 'wicked fast' even on standard CPUs, reportedly outperforming Kokoro-TTS in synthesis speed. Supertonic is easily deployable via uvx supertonic, offering a streamlined alternative to heavy environments.
While some Kokoro-82M implementations can swell to 22GB due to CUDA dependencies, Supertonic maintains a minimal footprint, ideal for resource-constrained environments as detailed in the Supertone documentation. Developers are pivoting to Supertonic for 'embodied agents' where sub-100ms latency is non-negotiable, offering a better balance between phonetic accuracy and computational overhead than the aging Piper TTS standard.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/ollama
Memory Bandwidth and the NPU Frontier: Solving the Local LLM Bottleneck
As local LLM usage grows, the focus is shifting from raw GPU power to memory bandwidth. Discussions in the Ollama community emphasize that for AI workloads, DDR5-6000 can offer up to a 50% performance increase over DDR4. kukunah noted that a dedicated PCIe NPU with high memory capacity would be a game-changer for AI enthusiasts, as current consumer hardware often forces a trade-off between VRAM and cost.
While integrated NPUs like Intel's NPU 3700 are gaining traction, mainstream support in libraries like llama.cpp is still in the experimental stages compared to CUDA or ROCm. For developers deploying agents on the edge, optimizing the hardware stack is as important as the model choice, as memory bandwidth directly dictates the responsiveness of multi-agent systems where multiple models may be loaded simultaneously.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/ollama
HuggingFace Open Source
From desktop-controlling VLMs to GRPO-optimized tool routers, agents are finally moving beyond the text box.
Today marks a decisive shift in the agentic landscape: we are moving from agents that talk about tasks to agents that execute them through code and raw pixel manipulation. The release of ScreenEnv and the Holo1 VLM family highlights a future where the desktop GUI is just another API for autonomous systems. Meanwhile, the 'smolagents' movement is proving that Python is the superior language for agentic reasoning, outperforming traditional JSON-heavy orchestration on benchmarks like GAIA. But it's not just about the 'how'; it's about the efficiency of the 'why'. The adoption of Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) is a technical game-changer for developers. By eliminating the need for a memory-intensive critic model, we can now train 1B-parameter models to handle complex tool routing with the precision of much larger systems. Whether it's running on a high-end server or a 270M-parameter model on a mobile device, the goal is the same: low-latency, high-reliability autonomous action. This issue dives into the protocols, frameworks, and training techniques that are turning LLMs into truly functional operators.
Smolagents Proves Code is the Best Action Language
The 'smolagents' library has emerged as a significant shift in agent orchestration, prioritizing code-based actions over traditional JSON-based tool calling. By allowing agents to write and execute Python snippets, the framework achieves higher success rates on complex tasks, notably beating the GAIA benchmark with a score of 0.43 on the leaderboard as reported by Hugging Face. This approach simplifies the interaction between the LLM and its environment, reducing the overhead of structured output parsing and allowing for complex logic like loops and conditionals to be expressed natively.
Extension of the 'smol' philosophy includes support for Vision Language Models (VLMs) Hugging Face and enhanced observability through Arize Phoenix, which provides open-source tracing for agentic workflows. To address security concerns, smolagents utilizes a secure local sandboxed interpreter to execute Python code safely, though it also integrates with external sandboxing solutions like E2B for production-grade isolation.
From Browsers to Desktops: The Rise of Specialized GUI VLMs
The landscape of autonomous assistants is shifting from browser-based tasks to full-stack desktop automation, driven by the release of ScreenEnv, a comprehensive framework that allows agents to interact with entire operating systems as OpenAI Gym-like environments. Central to this transition is the Holo1 family of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) by H. These models, particularly the Holo1-Multi (8B), are specifically optimized for visual-action loops, achieving a success rate of 81.2% on ScreenSpot and 54.5% on Mind2Web.
To standardize evaluation in this rapidly evolving field, ScreenSuite has emerged as a critical benchmark, aggregating over 3,500 tasks across 14 different GUI environments. Unlike general-purpose LLMs, these specialized agents are trained to interpret raw pixel data and coordinate precise mouse movements, effectively turning the desktop GUI into a programmable API. Researchers are also focusing on efficiency through projects like Smol2Operator, enabling small-scale models to execute complex computer commands.
Distillation and GRPO: The New Efficiency Frontier
Training models to 'think' before they act is moving beyond simple prompt engineering to fundamental reinforcement learning (RL) optimizations. ServiceNow's Apriel-H1 demonstrates that distilling reasoning capabilities from larger models allows smaller variants to mimic complex logical depth efficiently. This shift is accelerated by the adoption of Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), a technique popularized by DeepSeek-R1. Unlike traditional PPO, GRPO eliminates the need for a memory-intensive 'critic' model, enabling the training of models like the Llama-1B-Tool-Router to achieve high accuracy in complex function selection.
Specialized environments are further refining these capabilities. Jupyter Agent 2.0 focuses on training LLMs to reason within stateful computational notebooks, while research from Intel DeepMath highlights how RL can be applied to formal mathematical reasoning. Industry analysis suggests that GRPO is particularly advantageous for tool-use agents because it facilitates iterative refinement based on direct execution feedback.
Model Context Protocol Gains Open Ecosystem Momentum
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is rapidly becoming the connective tissue for agentic tools, with new implementations like Hugging Face demonstrating how to build MCP-powered agents in as few as 50 lines of code. The OpenEnv initiative is pushing for a shared ecosystem where agents can seamlessly discover and use tools across platforms, bolstered by a directory of over 20+ official and community-driven servers for Google Search, GitHub, and Slack.
Community projects like the Coffee Robot illustrate how standardized protocols bridge the gap between digital reasoning and physical API-driven actions. Recent adoption trends show major frameworks like LangChain and LlamaIndex integrating MCP support, while developers are leveraging the Python Tiny Agents framework to create portable, tool-augmented assistants.
High-Speed Agentic Workflows Move to the Edge
The push for local intelligence is accelerating with highly optimized small models. Intel has demonstrated the acceleration of Qwen3-8B agents on Ultra processors using depth-pruned draft models. On the extreme edge, the FunctionGemma-270M-it-mobile-actions series is being fine-tuned for UI control, reaching speeds of over 150 tokens per second on modern mobile chipsets. Projects like Orchestrix are bringing these capabilities to Flutter, enabling on-device function calling for privacy-centric applications.
Beyond Static Tests: DABStep and FutureBench Redefine Evaluation
Evaluation frameworks are evolving to measure multi-step logic and domain-specific performance. The DABStep benchmark focuses on data agents, where Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct has emerged as a leading open-weights model. Similarly, FutureBench tests an agent's ability to predict future events. These metrics are critical as the community moves away from static knowledge tests toward dynamic evaluations. Furthermore, the GAIA 2.0 project and AI vs. AI competitions are providing standardized environments via the Agentic Reasoning Environment (ARE).
Hugging Face and LangChain Standardize Agentic Tool Use
The fragmentation of agent frameworks is being addressed through the new langchain-huggingface partner package Hugging Face, introducing the ChatHuggingFace class for optimized tool-calling. This is powered by the Unified Tool Use initiative, which standardizes tool definitions via the chat_template field in Transformers. For the JavaScript ecosystem, Agents.js Hugging Face provides a robust framework for web-native agents, focusing on a 'tools-first' approach in the browser or Node.js.
From Code to Context: The Rise of Specialized Agent Spaces
The 'Agents Course' First_agent_template has sparked a massive influx of practical demos, with over 100,000 students enrolled. Specialized tools like QSARion-smolagents for chemistry and the EHR Navigator for medical data showcase the versatility of the smolagents library. Industry experts like @m_f_v_m note that code-based actions are significantly reducing production latency, with tools like PythonInterpreterTool appearing in over 80% of trending projects.