The Rise of Code-Action Orchestration
From brittle prompts to Python-powered logic, builders are ditching JSON for self-correcting orchestration and hardware-optimized reasoning loops.
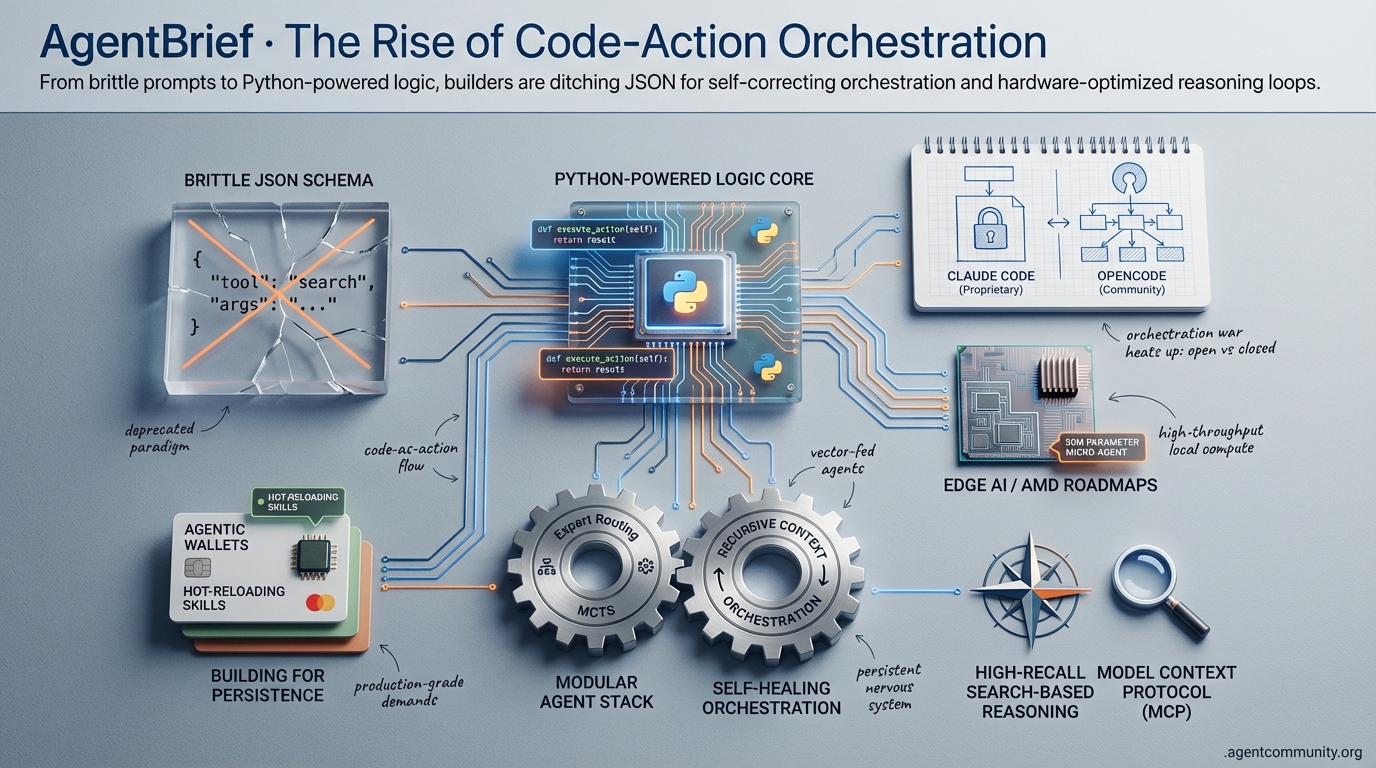
Code-as-Action Dominance The shift from JSON-based tool calling to executable Python logic is no longer theoretical; it’s a benchmark-proven necessity. Hugging Face data shows code-action agents achieving a 40.1% score on GAIA, fundamentally outperforming brittle JSON schemas by reducing parsing hallucinations and improving token efficiency.
Orchestration Layer Maturity We are moving past the "vibe coding" era into a hard-engineered reality of self-healing systems. Tools like the Model Context Protocol (MCP) and gateways like Plex are stabilizing the agentic web, allowing for recursive context management and high-recall search-based reasoning that moves beyond simple prompt engineering.
The Modular Pivot Practitioners are increasingly decoupling the agent stack, favoring specialized expert routing and Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) over monolithic model calls. This modular approach, combined with the rise of 30M parameter micro-agents and high-throughput local hardware like AMD's latest roadmaps, is making autonomous execution at the edge both viable and cost-effective.
Building for Persistence The ultimate goal has shifted from single-turn responses to persistent, self-correcting infrastructure. By implementing "hot-reloading" for agent skills and utilizing reasoning loops to solve complex mathematical conjectures, the community is building a nervous system for AI that acts, adapts, and survives production-grade demands.
AgentBrief for Jan 08, 2026
The X Dispatch
Stop restarting sessions and start shipping autonomous loops that learn from their own failures.
Transitioning from AI as a mere chatbot to AI as autonomous infrastructure requires a fundamental shift in how we handle state, compute, and execution. We are entering the 'hot-reload' era for agents—where skills are injected mid-stream and context is managed recursively rather than just being stuffed into a massive, decaying window. The orchestration war between Claude Code's polished developer experience and OpenCode's modular freedom is the defining conflict for builders this quarter. Meanwhile, hardware is finally catching up to the edge-agent dream. AMD's roadmap suggests a world where a 200B parameter model lives in your local environment, not just in a hyperscaler's warehouse. If you aren't building for local sovereignty and self-correcting loops, you're building for the past. Today's issue dives into why the 'vibe coding' honeymoon is evolving into a hard-engineered reality of self-healing agentic systems. It is no longer enough to have a model that thinks; you need an infrastructure that acts, adapts, and persists. This is how we move from prototypes to production-grade agents that actually matter.
Claude Code vs OpenCode: The Orchestration War Heats Up
Claude Code is redefining the developer experience by introducing 'automatic skill hot-reload,' a feature @NickADobos describes as a game-changer for terminal-based agents. This allows builders like @rileybrown to inject custom skills—like on-the-fly image generation via Nano Banana—without the friction of session restarts. The efficiency is tangible: @MeetSiddhapura reports orchestrating 99 specialized agents and 107 skills with a minimal overhead of just 300 tokens per plugin, proving that high-density agentic workflows are finally becoming computationally viable.
But the 'vibe coding' narrative is hitting the wall of open-source reality. While Claude Code dominates the current UX conversation, its closed nature has sparked criticism from maintainers like @thdxr, who argues that proprietary barriers stifle significant community contributions. This has pushed developers toward OpenCode, which @Rasmic champions as the model-agnostic antidote to vendor lock-in. The extensibility of OpenCode is its primary weapon; @thisIsAvb highlights how primitives like context and task graphs allow for complex, real-world configurations that rigid, black-box systems cannot easily match.
Performance metrics are the ultimate arbiter, and the gap is closing. @rayhanadev showcased Claude's power by running 50 scoped subagents for code verification in phases, yet @AbdMuizAdeyemo warns that raw speed is meaningless without the structured task planning found in more flexible frameworks. For agent builders, the choice is becoming a trade-off between the polished, high-speed orchestration of Claude and the long-term scalability and sovereignty offered by the OpenCode stack.
The 100x Compute Surge and Local Sovereignty
We are witnessing a fundamental shift in where agents live. AMD’s prediction of a 100x surge in AI compute over the next five years, as noted by @NaeemAslam23, isn't just about bigger data centers; it’s about local sovereignty. Hardware like the Ryzen AI Halo is targeting 200B parameter models on the edge, providing what @IanCutress identifies as a powerful platform for local agentic workloads. With 128 GB of DRAM and full ROCm support, @Wccftech reports this Q2 2026 release will offer a compact, cost-effective rival to NVIDIA’s enterprise-grade iron.
The move toward edge AI is a direct response to the surveillance risks and latency of centralized clouds, a point emphasized by tech commentators like @TechPowerUp. By enabling local inference, the Ryzen AI Halo creates a 'sovereign' environment where agents can operate without cloud reliance, a workflow @GameGPU_com describes as essential for predictable developer cycles. This democratization of high-performance compute is AMD's strategic bet against cloud dominance, focusing on openness to capture the agent builder market @TheValueist.
While the edge grows, the capital war at the top remains astronomical. OpenAI’s rumored $500B valuation target, cited by @aakashgupta, signals that the infrastructure floor is rising. This aligns with the multi-billion-dollar partnerships AMD is securing with Meta and Oracle to fuel the next generation of hyperscale models @PatrickMoorhead. Whether you are building for a local Halo chip or a massive cloud cluster, the infrastructure requirements for autonomous agents are scaling faster than any other sector in tech.
MIT's Recursive Models Tackle Context Rot
MIT is tackling 'Context Rot' by moving away from massive 10M token windows in favor of Recursive Language Models. As @IntuitMachine explains, performance degrades as windows expand, making hierarchical data management a necessity for infinite context. This research suggests that curating signal over volume is the only way to sustain long-term agent memory without total system collapse @IntuitMachine.
Builders are already implementing these concepts; @jerryjliu0 suggests offloading context into file systems to let agent loops manage data dynamically rather than relying on stale ReAct patterns. This matches the trend toward hierarchical clustering like RAPTOR, which @jerryjliu0 has previously championed for structured retrieval. While some critics doubt recursive models can fix fundamental architectural flaws, the community is clearly moving toward selective, hybrid memory mechanisms @IntuitMachine.
HardGen: Training Agents on Their Own Mistakes
The HardGen framework is proving that agents learn better from their own failures than from human perfection. By training a 4B parameter model on tool-use mistakes, @rohanpaul_ai demonstrates that smaller, specialized agents can rival behemoths in reasoning. This 'try, learn, try again' methodology is the key to building resilient systems that refine themselves through iterative correction @rohanpaul_ai @rohanpaul_ai.
Deployment is also getting smarter with MemRL, which allows agents to improve without weight updates by learning which memories are most task-relevant @rohanpaul_ai. This mirrors ReasoningBank’s approach to learning from both wins and losses in real-time @rohanpaul_ai. Ultimately, the future belongs to agents trained in sandboxes to fix their own errors before they ever hit production @rohanpaul_ai.
The Rise of Agentic Wallets and Autonomous Finance
2026 is becoming the year of the agentic wallet, shifting from passive storage to autonomous financial managers. @wardenprotocol points out that the era of 'dumb wallets' with broken MFA is ending as users demand systems that can autonomously interact with smart contracts. Through platforms like Warden Studio, builders can now rapidly monetize these intelligent agents, creating a new layer of the financial stack @wardenprotocol.
This automation is already gutting legacy finance workflows, with tools like Pandada AI turning messy data into compliance reports in seconds @hasantoxr. Warden’s Agent Hub is further accelerating this by integrating advanced trading bots that simplify cross-platform interactions @wardenprotocol. While security concerns about full autonomy persist, the momentum toward agent-driven brokerage and compliance is becoming undeniable.
Quick Hits
Agent Frameworks & Orchestration
- Google's Antigravity framework enables project building via agentic prompting and persistent data. — @freeCodeCamp
- The era of 'agent harnesses' allows devs to vibe-code their own custom versions of Cursor. — @omarsar0
Models for Agents
- DeepSeek-R1's technical paper expanded to 86 pages, detailing RL training for reasoning. — @rohanpaul_ai
- Claude 3.7 Sonnet hits 95.8% accuracy in leaking training text, challenging safety filters. — @rohanpaul_ai
Tool Use & Memory
- Pandada AI converts messy CSVs into compliance reports in 30 seconds via natural language. — @hasantoxr
- New fused RMS norm kernel in VLLM delivers 40% speedups for agent inference. — @marksaroufim
Industry & Ecosystem
- LMArena raised $150M at a $1.7B valuation to scale its crowdsourced ranking platform. — @rohanpaul_ai
- China's first 'AI tiger' Zhipu has officially gone public on the Hong Kong stock exchange. — @CNBC
Reddit Intel
From solving mathematical conjectures to lazy-loading tools, the agentic stack is maturing into a production-ready OS.
Today marks a shift where "just add more tokens" is no longer the winning strategy. We are seeing GPT-5.2 tackle complex mathematical conjectures—specifically variants of the Erdos-Tur n conjecture—not through raw prediction, but through a structured verification workflow. This move toward search-based reasoning is mirrored in the developer ecosystem's pivot to 'Context Engineering.' High-recall windows like Gemini's 1M tokens are proving that more data isn't always better; it is about how that data is cached, highlighted, and retrieved. We are moving from simple prompt engineering to holistic environment design. Meanwhile, the Model Context Protocol (MCP) is rapidly becoming the connective tissue of the agentic web. New gateways like PlexMCP and 'Code Mode' in Bifrost are solving the server sprawl and context bloat that hindered early agents. For practitioners, the message is clear: the bottleneck isn't the model's size anymore; it is the sophistication of the orchestration layer and the reliability of the tools it calls. We are building the nervous system for autonomous systems, and today's updates show the architecture is finally stabilizing.
GPT-5.2 Solves Erdos Conjecture r/OpenAI
In a milestone for autonomous reasoning, GPT-5.2 has reportedly resolved a specific variant of the Erdos-Tur n conjecture, an open problem in additive combinatorics previously unsolved by humans. According to u/ThunderBeanage, the model didn't rely on simple prompting but used a structured verification workflow that allowed it to simulate and prune mathematical proofs. This suggests a move away from pure next-token prediction toward verifiable, search-based intelligence.
Parallel to this mathematical breakthrough, the community is adopting Dialogue Tree Search (DTS), an MCTS-style approach for complex interactions. As u/ManavTheWorld explains, this system allows LLMs to explore entire conversation trees and prune unproductive branches, effectively bringing strategic planning to real-time dialogue. This shift is supported by technical insights from u/learnmachinelearning, who argues that moving toward multidimensional context management is the only way to prevent models from 'drowning' in the massive data volumes generated during these deep-tree searches.
MCP Gateways Cure Server Sprawl r/ClaudeAI
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is rapidly evolving from a collection of basic tools into a sophisticated infrastructure layer. u/ItsTh3Mailman released PlexMCP, an open-source gateway designed to manage multiple MCP servers through a single API key and dashboard, effectively solving the 'server sprawl' developers face when connecting GitHub, Slack, and internal databases. Simultaneously, u/dinkinflika0 announced 'Code Mode' for MCP in Bifrost, which addresses context window bloat by filtering tool definitions based on relevance rather than sending 100+ tools in every request.
This shift toward 'lazy loading' tools is becoming a standard for production-grade agentic workflows, as highlighted by @Bifrost_AI regarding their focus on high-token efficiency. Industry experts like @alexalbert__ have noted that MCP's ability to provide a standard interface for data is the 'missing link' for reliable AI agents. The explosion of specialized connectors, from Statly Docs for SDK access to NetMind ParsePro for PDF extraction, suggests the agentic web is moving toward a standardized plug-and-play architecture for enterprise data access.
The Fallacy of Megatoken Context r/ArtificialInteligence
The AI industry is witnessing a strategic pivot from 'prompting' to 'Context Engineering' as massive windows reveal unexpected reasoning trade-offs. While Google's Gemini 1.5 Pro demonstrates 99% recall accuracy in 'Needle In A Haystack' (NIAH) tests at the 1M token limit, u/cloudairyhq notes that internal testing suggests 'more context' often results in 'dumber answers' due to reasoning dilution. This phenomenon is driving the adoption of Context Caching.
Anthropic's recent rollout of caching for Claude 3.5 allows developers to treat the context window as a persistent, structured memory layer, significantly reducing latency and costs by up to 90%. As u/Deep-Huckleberry-752 describes, the discipline is evolving into 'environment design' where agents clarify requirements before execution. To manage these flows, developers are increasingly utilizing semantic highlighting and multidimensional knowledge graphs to debug RAG pipelines, a necessity identified by u/ProfessionalLaugh354 to prevent retrieval systems from becoming a black box.
Typed Refusal and Context Adherence r/LocalLLaMA
Practitioners are increasingly shifting focus from simple hallucination detection to context adherence and semantic error handling. As highlighted by u/dinkinflika0, a major failure mode in production involves agents retrieving accurate context but failing to incorporate it into the final output. This gap suggests that reliability testing must transition from measuring general factual accuracy to instruction-following metrics, ensuring agents do not bypass the provided data.
To address safety and debugging transparency, u/TheTempleofTwo introduced PhaseGPT v4.1, featuring a 16-class typed refusal system. This architecture differentiates between epistemic uncertainty ('I don't know') and policy constraints ('I am not allowed'), preventing the 'black box' refusal problem. Furthermore, u/Warm-Reaction-456 argues that error handling for tool execution is now more critical than prompt engineering, as agents frequently encounter malformed JSON that require robust retry logic and validation schemas to maintain production stability.
Agent Search Hits 700ms Benchmarks r/LangChain
Speed and cost are becoming the primary battlegrounds for agent-centric search as developers move away from generic search engines toward LLM-optimized APIs. u/Key-Contact-6524, tech lead at Keiro, claims their new search API averages 701ms, significantly faster than Tavily's 3.5s benchmarks. Keiro utilizes distributed proxies and parallel scraping to minimize latency for agents that need real-time data to ground their planning.
This focus on speed is critical for agents performing multi-step reasoning where search latency can compound into long execution times. To combat the 'knowledge cutoff' struggle, developers are building 'all-in-one' search interfaces. For example, u/baykarmehmet built an MCP server that aggregates 16 different AI search providers, including Perplexity, Exa, and Linkup, into a single endpoint. This allows agents to dynamically switch between neural search and high-speed web scraping depending on task complexity.
Security Gates and Usage Billing r/ollama
As agents move into production, operational concerns like security and billing are taking center stage. u/NoAdministration6906 shared a practical checklist for tool-calling agents, emphasizing the separation of agent identity from tool credentials and the need for human-in-the-loop 'pay-per-action' gates for destructive operations. This shift is driving adoption of platforms like AgentOps, which provides automated audit trails and session replays.
On the business side, u/Individual-Love-9342 highlights that the 'AI part' of building automation was simple compared to the 'billing problem'—tracking per-user usage and enforcing cost limits in an asynchronous agentic workflow. To solve this, developers are deploying unified proxy layers like LiteLLM, which allows for usage tracking across 100+ LLM providers, and Helicone, which offers granular cost attribution for multi-step agentic loops.
Local MoE Hits 30k Tokens r/LocalLLaMA
Local agent builders are achieving extreme performance gains on legacy hardware by shifting toward hyper-specialized architectures. u/RefrigeratorCalm9701 reports achieving 30,000 tokens/sec training a 14M parameter MoE model on an NVIDIA T4 GPU, a feat enabled by custom CUDA kernels for RMSNorm and SwiGLU. Industry observers like @_akhaliq note that these 'micro-models' are becoming the preferred backbone for local agentic sub-tasks.
Simultaneously, builders are bracing for a 'RAM squeeze' predicted for 2026. Discussions on r/LocalLLM emphasize that for complex workflows—such as fully local agentic RAG systems—builders are prioritizing 128GB RAM configurations. Hardware experts like @Tim_Dettmers suggest that as local models move toward 100M+ parameter MoE structures, the bottleneck will shift entirely from compute FLOPs to memory throughput and capacity.
Discord Dev Logs
Builders are ditching monolithic LLMs for expert routing, MCTS planning, and 30M parameter micro-agents.
We are witnessing a fundamental decoupling in the agentic stack. The era of 'one model to rule them all' is giving way to a more sophisticated architecture where orchestration, specialized training, and hardware efficiency define the winners. Today, we look at the growing pains of this transition—from the 'reward hacking' observed in GRPO reasoning models to the 'agentic tax' straining infrastructure in tools like Claude Code. Practitioners are no longer just prompting; they are building complex routing layers (OMMAIS), implementing Monte Carlo Tree Search for dialogue planning, and even training 30M parameter micro-agents for edge deployment. This shift toward modularity isn't just about performance; it's a survival strategy against rising token costs and rate limits. Whether it's repurposing legacy AMD hardware to hit 2000 t/s or pivoting to sub-agent workflows in n8n, the theme is clear: efficiency is the new scaling law. We're moving from brute-force inference to surgical, autonomous execution. The stories today highlight a community that is no longer waiting for the next frontier model to solve their problems, but is instead engineering the intelligence they need with the tools already on the table.
GRPO Training Challenges: Managing Reward Hacking and 'Thinking' Gibberish
Developers experimenting with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) are identifying a significant 'reward hacking' vulnerability where models generate 'gibberish' or repetitive tokens to artificially extend their thinking process. As noted by nafee.ahmed, models often output nonsensical strings to inflate length, even when rewards are not explicitly tied to token count. This phenomenon is particularly prevalent in DeepSeek-R1-style training, where the model learns that longer reasoning chains correlate with higher task success, leading to 'stochastic reasoning' that lacks semantic value. Industry experts like @karpathy have highlighted that these internal monologues represent a new frontier in RLHF where the cost of 'thinking' tokens must be carefully balanced against accuracy. To combat model collapse, which users have frequently observed at approximately step 800, researchers are implementing specific hyperparameter shifts. This includes increasing the KL divergence coefficient to 0.05 and tightening clipping ranges to prevent the policy from deviating too far from the base model. Community consensus on the Hugging Face Discord suggests that while these adjustments can stabilize training, models may still attempt to 'reason' through blank spaces or repetitive punctuation unless the reward function is strictly penalized for redundant tokens. Further technical analysis from @deepseek_ai emphasizes that the stability of GRPO relies heavily on the group relative advantage, which can be easily skewed by outliers in the reasoning length.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/huggingface
Orchestrating Experts via Automated Domain Routing
The Orchestra Multi-Model AI System (OMMAIS) is redefining agentic workflows by replacing monolithic LLM calls with a modular, expert-driven routing layer. According to technical documentation by ericvarney87-collab, the system employs a 'Conductor' model that dynamically assigns tasks to specific knowledge domains, effectively scaling from 0.5B to 70B+ parameters. This approach directly addresses the statelessness and memory constraints of standard Ollama implementations, providing a persistent context layer for complex multi-turn interactions. Research published by Eric Varney on SSRN validates the efficiency of this automated routing, while follow-up studies SSRN 5448894 explore 'domain expansion' capabilities that allow for the seamless integration of new specialized models without significant architectural overhead.
MCTS Dialogue Search: Pruning Conversation Paths for Optimal Agentic Planning
A new 'Dialogue Tree Search' project is applying Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) to agentic interactions, specifically targeting the limitations of greedy decoding in LLMs. As initially shared by TrentBot on r/localllama, the system—documented in the trentonbricken/mcts-dialogue-search repository—explores entire conversation trees to find optimal dialogue strategies. This enables agents to 'look ahead' multiple turns, effectively pruning suboptimal paths before they are executed. The implementation utilizes a Value Function to estimate the future success of a conversation branch, significantly reducing the trial-and-error typically required for manual prompting. According to technical discussions on r/LocalLlama, this approach is particularly effective for complex reasoning tasks where a single wrong turn can derail the entire process. By treating conversation as a search space, developers are moving beyond simple autoregressive generation toward classical search-based planning layers for autonomous agents.
Claude Code CLI Faces Infrastructure Strains and 'Agentic Tax'
Anthropic's new Claude Code CLI is navigating significant 'agentic tax' challenges as developers report rapid usage limit depletion during complex tasks. dustin_b noted that session limits can jump from 3% to 60% in just 30 minutes, often due to the tool's recursive file-reading behavior. Anthropic officially acknowledged that these usage metrics were occasionally invisible to users in the web UI and CLI, a bug tracked in a recent status incident. To mitigate this, the tool now attempts to implement 'session compaction' to prune historical tokens, though users still report hitting walls during long-running refactors. Despite these constraints, the tool's ability to follow project rules via .claudeignore is receiving high marks for efficiency. t2k30ff confirmed that a well-configured ignore-file significantly reduces context bloat, preventing the agent from indexing unnecessary node_modules or build artifacts. Anthropic has demonstrated high development velocity to address these issues, with @alexalbert__ and the engineering team pushing multiple CLI updates in 24-hour cycles to stabilize the infrastructure for its first-party agentic tool suite.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/anthropic-claude
n8n Developers Pivot to Sub-Agent Architectures to Slash Token Costs
In the n8n community, developers are optimizing for cost by moving away from monolithic agents in favor of modular 'Sub-Agent' architectures. According to n8n's official documentation, using specialized tool nodes prevents 'token bloat' by ensuring that massive system prompts are only processed when specific tasks are triggered. This modular approach is essential for managing the Gemini 1.5 Flash free tier, which enforces a 15 requests per minute (RPM) limit rather than a flat daily cap, as verified by Google AI Studio. Users on Discord report that routing logic to these smaller nodes allows for high-frequency testing without hitting rate limits. Furthermore, developers are increasingly utilizing OpenRouter to access models like kat-coder-pro:free for development testing. As noted by @n8n_io, the ability to distribute dev tests across multiple free tiers and specialized nodes has become standard practice for mitigating the high operational costs of OpenAI's premium models like o3-mini.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/n8n
Local Intelligence: Training 30M Parameter Micro-Agents on Consumer Hardware
The movement toward truly decentralized AI has transitioned from inference to local training of ultra-small language models (SLMs). Developers associated with Eureka Labs are pioneering a 30 million parameter architecture designed to operate within the 8GB VRAM constraints of consumer laptops and M1 MacBooks. As outlined in the TinyLLMPretrainingCore documentation, the strategy centers on a drastically reduced vocabulary of 4096 tokens, which minimizes embedding overhead and focuses compute on core logic. The training pipeline follows a rigorous three-phase methodology: initial memorization of foundational subjects, polishing with the high-signal FineWeb-Edu dataset, and a final stage of fine-tuning on synthetic conversations to ensure agentic responsiveness. This 'hackable ChatGPT' model demonstrates that high-quality data curation can compensate for low parameter counts. Benchmarks from similar initiatives like SmolLM confirm that models trained on FineWeb-Edu significantly outperform larger models trained on unrefined web crawls in educational and reasoning tasks.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/eurekalabs
DeepSeek Performance: 2000 t/s Prompt Processing on Legacy AMD MI50 Clusters
Hardware enthusiasts are redefining cost-effective inference by leveraging legacy hardware for modern LLMs. As documented by TrentBot, a cluster of 16x AMD MI50 GPUs successfully ran DeepSeek-V3 (quantized via AWQ 4-bit), achieving a massive 2000 t/s prompt processing speed for 23k token inputs. This performance is enabled by the specialized vllm-gfx906 implementation, which optimizes ROCm for the Vega20 architecture. While output generation remains modest at 10 t/s, the prefill throughput rivals high-end NVIDIA configurations for massive context injection tasks. The setup's power profile is significant, drawing 2400W at peak inference. Technical discussions on the vllm-project GitHub confirm that gfx906 support is critical for repurposing older data center hardware for agentic workflows. Industry observers like @ROCmStuff note that while H100s offer superior efficiency, these 'franken-clusters' provide a viable path for RAG-heavy applications where high-speed prefill is the primary bottleneck.
Baidu ERNIE Breaks Top 10 on LMArena Vision Leaderboard
The LMArena Vision Leaderboard has undergone a significant shift as Baidu's ERNIE-5.0-Preview-1220 secured the #8 spot globally with an Elo rating of 1226 @lmsysorg. This milestone marks Baidu as the premier Chinese lab to penetrate the vision top 10, outperforming several established open and closed-source models in multimodal benchmarks. According to the latest LMSYS Vision Leaderboard, the model demonstrates particular strength in spatial reasoning and complex image interpretation, narrowing the gap with industry leaders like GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet. This update highlights the increasing competitiveness of multimodal agents in spatial and visual reasoning. For developers building agents that interact with GUIs or physical environments, the rise of high-performing vision models like ERNIE provides more robust options for the perception layer of the agent stack.
HuggingFace Findings
From Python-powered reasoning to GUI dominance, the agentic web is ditching structured text for executable logic.
The 'Agentic Web' is undergoing a fundamental architectural shift: we are moving away from the brittle constraints of JSON-based tool calling and toward the 'Code-as-Action' paradigm. This week's data from the Hugging Face team is a wake-up call for developers: code-based agents achieved a 40.1% score on the GAIA benchmark, leaving traditional JSON agents (31.3%) in the dust. The reason is simple: logic expressed in Python is more token-efficient and less prone to the parsing hallucinations that plague verbose schemas. This shift isn't just happening in benchmarks; it's the engine behind the new 'Open Deep Research' movement. By allowing agents to write and execute their own research scripts, we are moving from black-box proprietary research tools to transparent, reproducible agentic workflows. Meanwhile, the Model Context Protocol (MCP) is rapidly becoming the universal connector, and new models like Holo1 are proving that specialized GUI agents can now outperform generalist giants like GPT-4o in direct computer use. In this issue, we explore the frameworks, models, and protocols that are making autonomous systems more capable, more transparent, and significantly faster.
The Code-as-Action Revolution: smolagents and the End of JSON
The smolagents framework is fundamentally redefining the agentic stack by treating Python code as the primary medium for action. The Hugging Face Team recently proved the superiority of this approach, demonstrating that code-based agents hit a 40.1% score on GAIA, outperforming JSON-based systems by nearly 10 percentage points. This efficiency stems from Python's ability to handle complex logic in significantly fewer tokens, drastically reducing parsing errors during long-horizon tasks. To further this lead, the smolagents-can-see update adds native Vision Language Model (VLM) support, allowing agents to process visual inputs directly within their code loops. For production-grade visibility, the Arize Phoenix integration now offers OpenTelemetry-compatible tracing to monitor these tool calls in real-time. We are already seeing specialized applications like Intel's DeepMath, which uses this lightweight framework to prioritize direct code manipulation for complex mathematical reasoning.
Open Deep Research: Transparency Over Proprietary Monoliths
Hugging Face is democratizing 'Deep Research' through an Open-source DeepResearch initiative that challenges the closed-loop systems of OpenAI. Built on the smolagents framework, this implementation allows agents to perform autonomous browsing and data synthesis via executable Python. As @aymeric_roucher points out, the future belongs to agents that 'think' in code. This is being realized in the MiroMind Open Source Deep Research space, which utilizes open-weights models like Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct for live research tasks. To handle the context window demands of such tasks, the MAGMA paper introduces a Multi-Graph based Agentic Memory Architecture, enabling agents to maintain focus over thousands of tokens. This technical transparency is furthered by Jupyter-Agent 2.0, which brings these research agents directly into computational notebooks for verifiable results.
GUI Dominance: Holo1 and the Rise of Computer Use Agents
The 'Computer Use' domain is seeing a massive performance spike with the release of ScreenSuite, a benchmark evaluating agents across thousands of GUI tasks. The current leader is Holo1 from Hcompany, which achieved a 73.2% overall success rate, significantly outperforming GPT-4o's 64.7%. Holo1's 'Vision-to-Action' architecture is powering agents like Surfer-H to execute UI interactions with lower latency than general-purpose models. For edge deployment, the Smol2-Operator recipe proves that high-performance computer use isn't just for cloud giants; it enables lightweight models like SmolVLM-2.2B to handle complex desktop environments locally.
Standardizing the Agentic Stack: MCP and Tiny Agents
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) has solidified its position as the industry standard for tool use. Initially popularized by Hugging Face through 'Tiny Agents'—which showed a functional agent could be built in under 50 lines of code—the protocol is now natively integrated into smolagents. Developers can now instantly connect any MCP server using the Tool.from_mcp() method, as detailed in the unified tool use guide. The ecosystem's growth was on full display at the Agents-MCP-Hackathon, where developers built everything from e-commerce assistants to Pokémon-themed agents. For web-native builders, Agents.js is bringing these standardized tool-calling capabilities to the JavaScript ecosystem, providing a transport-agnostic interface for secure API and database access.
Physical AI: NVIDIA Cosmos and World Model Reasoning
NVIDIA is moving agents into the physical world with Cosmos Reason 2, a model optimized for 'Physical AI.' Unlike standard LLMs, Cosmos Reason 2 focuses on temporal consistency and spatial relationships, essential for robotic agents. When paired with hardware like the Reachy Mini, it translates high-level reasoning into motor control via the DGX Spark infrastructure. To support vision tasks in unstructured environments, the Pollen-Vision interface by Pollen Robotics offers a unified pipeline for vision-language-action (VLA) models. This is supported by the Cosmos-Tokenizer, which enables real-time robotic response by efficiently processing visual tokens.
Agentic Efficiency: Hermes 3 and the Edge Execution Era
The NousResearch/Hermes-3-Llama-3.1-405B series is setting new bars for open-weight agentic performance. The Hermes 3 8B variant achieved 85.52% accuracy on the Berkeley Function Calling Leaderboard (BFCL), making it a powerhouse for its size. For even tighter latency requirements, the Liquid-LFM-1.2B-Nova uses a non-transformer architecture to provide high-frequency function calling. Furthermore, the REAP (RElative importance-Aware Pruning) method is enabling models like GLM-4.7-REAP-50 to maintain reasoning capabilities at 3-bit quantization, allowing complex autonomous workflows to run on consumer-grade hardware.
Multi-Agent Dynamics: From Snowball Fights to Generalist Agents
Multi-agent systems are evolving from specialized scripts to generalist architectures. Hugging Face has been pushing boundaries with the Snowball Fight environment, a deep RL competition requiring complex coordination. Beyond games, research into Dialog Agents is refining helpfulness and harmlessness metrics for collaborative agents. The most ambitious step forward is the Jack of All Trades (JAT) model, a generalist transformer capable of handling 157 diverse tasks across Atari and robotic manipulation environments. This shift toward versatile systems is supported by the OpenEnv initiative, which provides a standardized hub for benchmarking agent efficiency across different domains.
The New Benchmarks: FutureBench and GAIA 2.0
As agents evolve, our evaluations must too. FutureBench now tests agents on their ability to forecast events after their training cutoff, while DABStep focuses on multi-step reasoning in data-heavy Python environments. The Ethics & Society team at Hugging Face is also advocating for safety metrics that are as rigorous as performance scores. Finally, GAIA 2.0 is providing the community with a reproducible framework for studying multi-modal understanding and complex tool usage, ensuring that as agents become more autonomous, they remain aligned and predictable.