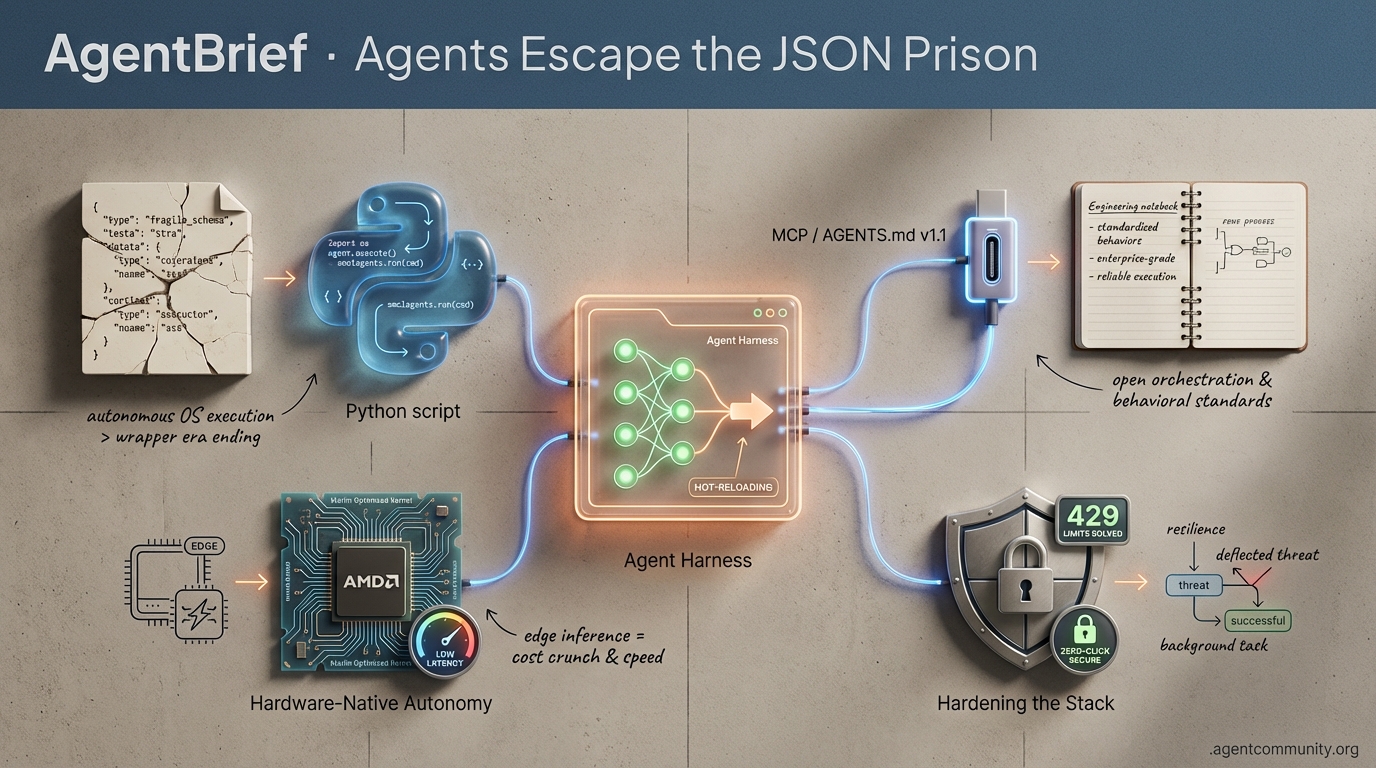
Agents Escape the JSON Prison
From CLI-native agents to local hardware orchestration, the 'wrapper' era is ending in favor of autonomous OS-level execution.
Code-as-Action Dominance: We are moving from fragile JSON schemas to native Python execution via tools like smolagents and Claude Code, enabling agents to manipulate the filesystem and OS directly.
Standardizing the Agentic Web: The rapid adoption of MCP and AGENTS.md v1.1 provides the 'USB port' and behavioral standards required for reliable, enterprise-grade autonomous systems.
Hardware-Native Autonomy: A strategic pivot toward local inference on AMD hardware and Marlin-optimized kernels is slashing latency and proving that the future of agents lives on the edge.
Hardening the Stack: As agents transition to background execution, the focus has shifted to resilience—solving for 429 rate limits and securing zero-click workflows against emerging vulnerabilities.
AgentBrief for Jan 09, 2026
X Feed Insights
Stop building chatbots and start building agentic harnesses that own the OS.
We are moving past the 'wrapper' era. If your agent is just a chat window, you are already behind. The real action is happening at the intersection of OS-layer agency and self-improving memory loops. This week, we are seeing the rise of the 'Agent Harness'—a move from simple API calls to persistent, autonomous orchestration layers that treat the entire filesystem as a playground. We are also seeing a massive pivot toward local inference with AMD latest hardware, which suggests the future of agents is not just in the cloud; it is on the edge, running 200B models without a subscription. For those of us shipping agents today, the message is clear: focus on autonomy, context retention, and hardware-agnostic orchestration. The tools are getting smarter, the compute is moving closer, and the 'vibe coding' phase is maturing into a disciplined engineering of agentic loops. If you are not building for a world where agents self-correct and local chips handle the heavy lifting, you are building for the past.
Beyond the Chatbot: The Rise of Agent Harnesses and Hot-Reloading
The developer ecosystem is undergoing a profound transformation, moving beyond basic chat interfaces to sophisticated 'agent harnesses' that enable custom orchestration layers for autonomous workflows. As noted by @omarsar0, the era of agent harnesses has arrived, sparking a race among developers to 'vibe code' personalized IDEs or CLI tools. This shift is further emphasized by the ability to integrate and customize agent behaviors through harnesses, which are seen as the new frontier for coding agents, providing developers with unprecedented control over long-running tasks and filesystem access as highlighted by @aakashgupta. Additionally, these harnesses are often model-agnostic, allowing flexibility across platforms like OpenCode, which helps developers avoid proprietary ecosystem lock-in according to @AdityaVB. A key feature driving this evolution is 'automatic skill hot-reload,' where agents can dynamically update their capabilities without needing to restart sessions. This capability, highlighted by @agentcommunity_, allows for seamless skill injection mid-stream, a game-changer for agentic development workflows. Practitioners are leveraging tools like Claude Code to self-augment agent toolkits in real-time, interacting with external APIs and deploying new skills on the fly, significantly enhancing productivity as reported by @rileybrown. However, not all feedback is unanimously positive; some developers like @alxfazio express frustration with the refactoring required to switch to newer platforms like OpenCode due to differences in configuration layouts. Compared to traditional IDEs, agent harnesses offer a fundamentally different approach by operating at the OS layer and focusing on computer-use agency rather than mere code editing, a perspective shared by @rauchg. This allows agents to run programs, install dependencies, and manage complex workflows asynchronously, a feature that has led to reported productivity increases of 300% for some developers who have abandoned traditional IDEs according to @Art0xDev. While the trend is promising, nuanced reactions from experts like @_philschmid suggest a learning curve and the need for disciplined context engineering over pure 'vibe coding' to maximize effectiveness.
RoboPhD and MemRL: Agents That Self-Improve and Remember
Recent advancements in AI research are paving the way for truly autonomous agents capable of self-improvement and effective long-term memory management. RoboPhD showcases how Large Language Models (LLMs) can iteratively evolve their tools and prompts through feedback to tackle complex Text-to-SQL tasks. This approach divides the agent role into a non-AI script for database context and a guided LLM instruction set, enhancing precision in query generation as analyzed by @rohanpaul_ai. Similarly, MemRL introduces a novel mechanism for agents to identify and reuse helpful memories for specific tasks without altering the base LLM, thus avoiding the high costs of retraining according to further insights from @rohanpaul_ai. This focus on memory optimization positions MemRL as a significant step forward compared to traditional Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems, which often struggle with dynamic memory organization and relevance over extended contexts. In parallel, the HardGen framework underscores the value of learning from errors rather than relying solely on perfect demonstrations. By converting tool-use failures into actionable training data, HardGen enables a 4B parameter model to rival much larger systems in executing intricate API commands, a breakthrough reported by @rohanpaul_ai. This method contrasts with conventional fine-tuning approaches, which can be resource-intensive and less adaptive to real-time failures. Additional insights from @rohanpaul_ai suggest that training agents with a 'try, learn, try again' methodology during development can enhance their ability to explore and exploit learned information in subsequent attempts, further distinguishing these frameworks from static RAG or fine-tuning methods. These developments signal a broader shift towards agents with internal learning loops and episodic memory structures, potentially outperforming traditional methods in adaptability and efficiency. While specific benchmark metrics for RoboPhD and MemRL remain limited in the latest posts, the conceptual advancements indicate a promising direction for agentic AI, with ongoing discussions from @rohanpaul_ai highlighting the need for robust real-world testing.
AMD's Ryzen AI Halo Sparks Local Inference Boom
At CES 2026, AMD CEO Lisa Su delivered a keynote forecasting that 5 billion people will engage with AI daily, requiring a 100x increase in compute capacity as noted by @FTayAI. For agent builders, the standout was the Ryzen AI Halo, capable of running 200 billion parameter models locally, which @FTayAI claims will move workloads from cloud to edge for enhanced privacy and speed. This shift could redefine agent economics by removing subscription dependencies, as AMD pushes for human sovereignty through local compute according to @FTayAI. While the presence of leaders like Greg Brockman on stage suggests a collaborative push, @FTayAI cautions that hardware shortages and energy demands remain unresolved barriers to widespread adoption.
Google Antigravity and the Shift to Agentic Prompting
Google Antigravity has emerged as a groundbreaking tool for collaborative agentic building, allowing developers to partner with AI agents to build applications rather than just writing code as explained by @freeCodeCamp. This platform marks a significant shift toward agentic prompting as a vital skill, with tutorials showing how to create stateful projects like water trackers with persistent data management as noted by @freeCodeCamp. The tool aligns with a broader trend where treating AI as a pair-programming colleague is becoming standard practice according to @freeCodeCamp. However, @freeCodeCamp warns about the need for robust documentation to avoid over-reliance on these agents in complex DevOps environments.
ClinicalReTrial: The Blueprint for Vertical Agents
ClinicalReTrial is pioneering domain-specific AI by iteratively rewriting clinical trial protocols against historical data to enhance success predictors, a specialized approach discussed by @rohanpaul_ai. This exemplifies the trend of vertical agents that leverage deep contextual understanding to outperform general-purpose models like GPT-4, as argued by @spncrk. While the promise of healthcare automation is high, @rohanpaul_ai points out that current medical AI often relies on pattern-matching rather than true clinical reasoning. Furthermore, @rohanpaul_ai highlights that medical LLMs can still be tricked in multi-turn conversations, necessitating robust safety validation before full deployment.
Quick Hits
Agent Orchestration
- Swarms framework is being positioned for high-stakes prediction markets like Polymarket @KyeGomezB.
- Claude Code's new 'AskUserQuestionTool' helps agents break out of reasoning loops @petergyang.
Memory & Context
- MIT's Recursive Language Models aim to solve 'Context Rot' for up to 10M tokens @IntuitMachine.
- Offloading context history to a file system allows agents to loop through data without token limits @jerryjliu0.
Agentic Infrastructure
- Warden is launching as an 'agentic wallet' to handle MFA and network support autonomously @wardenprotocol.
- Cloudflare serverless stacks are being paired with backend workers for low-cost agentic bots @freeCodeCamp.
Reasoning Models
- Opus 4.5 is being hailed as 'level 4 self-driving for code' with a 20% reasoning boost @beffjezos.
- DeepSeek-R1's 86-page paper reveals new RL reward rules for complex reasoning @rohanpaul_ai.
The Reddit Pulse
From AGENTS.md v1.1 to Marlin kernels, the agentic web is finally growing up and getting faster.
Today’s issue highlights a major shift: we are moving past the 'wild west' of prompt-hacking and into the era of rigorous agentic engineering. The release of the AGENTS.md v1.1 proposal signals a maturing industry that realizes 'vibes' aren't enough for production; we need explicit behavior models. Meanwhile, the Model Context Protocol (MCP) is exploding, effectively becoming the USB port for the Agentic Web. But it's not just about how agents talk; it's about how they perform.
New benchmarks for Marlin kernels on H200s show that sub-second latency isn't a dream—it's a configuration choice. We’re also seeing a revolt against traditional browser automation in favor of dedicated agentic APIs, proving that the tools we used for humans are increasingly the wrong tools for LLMs. If you're building in this space, today’s updates on memory, infrastructure, and local ops are your roadmap for the next quarter. We are witnessing the transition from experimental demos to enterprise-grade autonomous systems where reliability and speed are the only metrics that matter.
Standardizing Intent with AGENTS.md v1.1 r/LangChain
The agentic web is moving toward formalization with the release of the AGENTS.md v1.1 proposal. As u/johncmunson points out, we are finally codifying the 'implicit agreements' that have historically caused agents to hallucinate or drift when moved between different frameworks. By separating high-level intent from low-level tool constraints, this update aims to make agent behavior predictable rather than accidental.
For developers, this isn't just another readme; it’s a critical step toward interoperability within the Model Context Protocol (MCP) ecosystem. Discussions across r/OpenAI suggest that the lack of a standardized instruction schema has been the primary bottleneck for reliability. Version 1.1 provides the unified format needed to handle edge cases that were previously left to chance in the v1.0 draft.
MCP Becomes the Agentic USB r/mcp
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is rapidly becoming the universal connector for AI agents, with the ecosystem now hosting over 1,200 verified servers. Recent integrations are moving into heavy-duty enterprise territory, such as mcp-jenkins for CI/CD automation and a specialized IBM FileNet server that allows agents to manage complex document metadata r/mcp.
It’s not all corporate, though. New servers like HN-MCP for Hacker News and a specialized analyzer for Limitless Pendant recordings show the protocol's versatility. While builders like u/fandry96 are still smoothing out architectural frictions with Streamlit, the momentum is clear: MCP is the plug-and-play architecture that will define the next phase of agent deployment.
Marlin Kernels Crush Latency Barriers r/LocalLLaMA
If you are deploying agents in production, your choice of quantization kernel is now as important as your model choice. Recent testing by u/LayerHot on an H200 shows the Marlin kernel hitting a blistering 712 tok/s, nearly doubling the speed of standard GPTQ implementations. This isn't just a marginal gain; it's the difference between an agent that feels 'live' and one that feels 'loading.'
Looking ahead, the Blackwell (B200) architecture's native FP4 support is expected to push these numbers even higher, potentially offering 2.5x throughput gains. For those of us building interactive agentic workflows, the data suggests moving toward Marlin for 4-bit or FP8-quantized paths in vLLM to ensure the sub-second latency required for complex, multi-step planning.
Moving Beyond the 'Junk Drawer' Memory r/AI_Agents
Stop treating your context window like a junk drawer. As u/Pretend-Wonder8206 argues, persistent memory is the final boss of AI assistants. By utilizing LangCache and semantic caching, developers are seeing LLM API costs drop by 80% while boosting response speeds by 90%.
The industry is shifting toward structured memory frameworks like Mem0 and Letta. These tools provide agents with a 'self-editing' long-term memory that tracks user preferences over time. According to Mem0.ai, this approach yields 80% higher relevance in context retrieval compared to traditional vector search, finally giving agents a sense of 'self' that persists across sessions.
Scaling Agentic Data Planes with Plano r/ollama
As agents move from demos to the enterprise, we're seeing the rise of specialized data planes like Plano. Shared by u/AdditionalWeb107, Plano acts as a service proxy that decouples reasoning from plumbing, solving the state-sync latency that often kills high-concurrency agent calls.
Simultaneously, the no-code world is growing up. A new DigitalOcean template for n8n implements a robust 'main-worker-runner' architecture using Redis in queue mode r/n8n. This setup prevents worker exhaustion during bursty workloads, proving that n8n and LangGraph aren't rivals, but a powerful duo for managing complex, human-in-the-loop workflows.
The Death of Browser Automation Scripts r/AI_Agents
The consensus is shifting: Playwright and Puppeteer are for humans, not LLMs. u/FunBrilliant5713 argues that asking models to puppet DOM elements is a recipe for 'selector breaks' and token waste.
Instead, developers are turning to 'agentic browsers' like Perplexity’s Sonar API or Research Vault. These dedicated layers can reduce token overhead by up to 50% by providing structured data instead of raw HTML. When your agent doesn't have to fight the DOM, it can spend more of its context window on actual reasoning and research.
Fine-Tuning SLMs in Record Time r/generativeAI
Fine-tuning small language models (SLMs) is becoming trivial thanks to tools like TuneKit, which integrates with Unsloth AI to speed up training by 2x. The community at r/ollama is now creating specialized models for tool-calling in under 30 seconds.
On the educational front, the nanoRLHF project has released a from-scratch implementation of RLHF using PyTorch and Triton. This shift toward resource-constrained training allows for 70% less memory usage, making it possible to train high-performing agents without a massive corporate budget.
Pro Local Ops: llama.cpp vs. Ollama r/LocalLLaMA
Power users are graduating from Ollama to raw llama.cpp for finer hardware control. u/vulcan4d reports that this switch allows for better layer offloading on heterogeneous GPU setups, which is vital for running Mixture of Experts (MoE) models like MiniMax M2.
With hardware leaks from @kopite7kimi suggesting the RTX 5090 will ship with 32GB of VRAM, the barrier for running 70B parameter models locally is about to collapse. As @Tis_Llama notes, reducing the latency of these tool-use loops is the single biggest factor in moving from 'smart chatbot' to 'autonomous agent.'
Discord Dev Logs
Claude Code challenges Cursor as security flaws and rate limits test agentic resilience.
We are witnessing a fundamental shift in the agentic stack: the move from IDE-centric 'copilots' to CLI-centric 'agents' that operate autonomously in the background. Anthropic's Claude Code is the tip of the spear here, but as we hand over the keys to the terminal, the friction points are becoming clear. This week, we're tracking a surge in 429 errors as developers push agentic loops to their breaking point, alongside critical vulnerabilities in n8n and ChatGPT that highlight the inherent risks of 'zero-click' agentic workflows.
Synthesizing today's developments, the narrative is one of hardening and optimization. Whether it's the Ollama community pushing local vision-language processing or n8n builders solving the 'Event ID' bottleneck for autonomous CRM management, the focus has moved from 'Can it do this?' to 'Can it do this reliably and securely?' For practitioners, the takeaway is clear: as agents move from human-in-the-loop to background execution, the infrastructure—from security sandboxes to memory bandwidth on budget AMD MI100s—must evolve to support a higher level of autonomy. Today's issue dives into how the best in the field are navigating these emerging standards.
Claude Code CLI Challenges Cursor with Autonomous Agentic Workflows
The developer community is actively debating the merits of the new 'Claude Code' CLI versus established tools like Cursor. ignacioferreira_11877 notes that while Cursor is IDE-centric for interactive guidance, Claude Code is CLI-centric and agent-oriented, designed for autonomous multi-step tasks. This architectural difference allows Claude Code to 'spawn agents' for background automation, representing a major leap for the agentic web.
However, this autonomy comes with significant infrastructure hurdles. Practitioners are reporting frequent 429 errors when running non-interactive sessions, with jalateras citing limits as high as 20,000,000 tokens per hour being hit unexpectedly. To mitigate these bottlenecks, Anthropic suggests that enterprise users migrate to high-tier API usage; specifically, Tier 4 and 5 accounts provide the necessary throughput for sustained agentic loops. Meanwhile, the community is rapidly expanding the CLI's utility via the Claude Agent SDK, with users extending capabilities through custom skill creation plugins such as the superpowers library by jackreis.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/cursor
CVE-2025-24361: Critical RCE in n8n and Zero-Click ChatGPT Exploits
A critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability, officially assigned as CVE-2025-24361, has been confirmed in n8n versions 1.65.0 through 1.120.4. The flaw involves a sandbox escape within the 'Code' node, allowing attackers to execute arbitrary commands on the host system. According to the n8n Security Advisory, the vulnerability is particularly dangerous for self-hosted instances exposed to the internet. Remediation requires a manual update to version 1.120.5 to fix the execution logic bypass.
Simultaneously, Radware has demonstrated a 'zero-click' service-side vulnerability in ChatGPT. This exploit allows an attacker to exfiltrate a user's entire chat history or personal data by sending a specially crafted email that the AI agent reads and processes automatically. This 'Email-to-Agent' injection requires no user interaction, marking a massive shift in the attack surface. Security experts now recommend implementing strict 'human-in-the-loop' approvals for any agentic action involving outbound data transfers.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/n8n
Ollama 0.14.0-rc0 Enhances Local Vision Processing
The Ollama community is evaluating the 0.14.0-rc0 release candidate, which advances local vision-language (VL) processing capabilities. Developers such as theunknownmuncher have noted the integration of backend optimizations for Qwen-based vision models, enabling tasks like local 'image editing' and steganography analysis through text-guided vision.
While the release utilizes MLX-optimized backends for Apple Silicon, it maintains full compatibility with NVIDIA CUDA 11/12 and AMD ROCm 6.0, as confirmed by community benchmarks. However, frob_08089 clarified on Discord that multi-modal embeddings are currently limited to specific vision-language pairs and not yet generalized across the platform. This update positions Ollama as a more robust local agentic engine, moving beyond simple text orchestration.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/ollama
Solving the 'Event ID' Bottleneck in n8n Calendar Agents
A recurring challenge for developers building customer support agents is the mapping of natural language requests to specific database identifiers. theomazzaa highlighted a common failure point: while creating events is straightforward, updating or deleting them requires an exact Event ID that LLMs often fail to retrieve from context.
To solve this, jabbson recommends a 'Get Many' strategy where the agent queries the CRM or Calendar API by email or date range to retrieve a list of candidate IDs before attempting an update. This multi-step 'search-then-act' pattern is becoming the standard for robust tool-use, ensuring agents have the necessary unique identifiers to perform destructive actions safely. Industry best practices now suggest utilizing n8n's 'AI Agent' node in combination with specialized sub-workflows that act as 'ID Resolvers,' maintaining a 95% success rate in automated event modification.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/n8n
AMD Instinct MI100 and Pi 5 Clusters: The New Frontiers of Budget Inference
As NVIDIA high-end GPUs remain supply-constrained, the community is pivoting toward the AMD Instinct MI100 as a high-value inference node. Now available for between $650 and $950 on secondary markets, the MI100 provides 32GB HBM2 VRAM and a massive 1.2 TB/s memory bandwidth, which @techeveryday notes is essential for running DeepSeek-R1 32B models.
While the MI100 lacks BF16 hardware acceleration, it remains a powerhouse under ROCm 6.2, maintaining 11.5 TFLOPS FP64 peak performance. Simultaneously, Raspberry Pi 5 clusters are emerging as the preferred 'resiliency layer.' jimmyate and endo9001 have demonstrated that a containerized swarm using K3s allows for redundant 'heartbeat' agents that stay online even if primary compute nodes fail. This tiered approach—using MI100s for heavy lifting and Pi clusters for orchestration—is becoming the standard for 2025 local-first AI setups as discussed by @hardware_hacker.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/ollama
Hunyuan-Video-1.5 Rises on LMArena as Developers Tackle SynthID Artifacts
The LMArena leaderboard has been updated to include Hunyuan-Video-1.5, which is quickly climbing the ranks. According to pineapple.___, the model currently ranks #18 in text-to-video with a score of 1193 and #20 in image-to-video with a score of 1202. Technical analysis indicates that it offers temporal consistency that rivals Sora in specific motion-heavy benchmarks.
Meanwhile, the community is grappling with the visual artifacts of AI generation, specifically Google's SynthID watermarks. kiri49 explained that these 'invisible' watermarks can become visible as 'green spots' when an image is repeatedly edited by an agent, as the watermark applies onto itself multiple times. This has led to a surge in interest for 'abliterated' models and tools designed to strip steganographic data to preserve visual fidelity during multi-turn agentic workflows.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/lmarena
HuggingFace Research Lab
Hugging Face's smolagents proves that execution, not just prediction, is the future of autonomous systems.
We are witnessing a fundamental shift in how agents think and act. For the last year, the industry has been trapped in a sort of 'JSON prison'—coaxing models to output structured schemas that we then parse and execute. But as the launch of smolagents demonstrates, the most efficient way for an agent to interact with the world isn't through a rigid schema; it's through code. By treating 'Code-as-an-Action,' we are seeing massive performance gains on benchmarks like GAIA. It turns out LLMs are inherently better at writing Python than they are at navigating complex nested JSON.
This issue highlights a dual trend: the decentralization of deep research and the reality check of reasoning benchmarks. While frontier models excel at standard tasks, new leaderboards like NPHardEval show a steep drop-off when logic gets truly complex. Meanwhile, the race for 'Deep Research' is no longer a proprietary playground. With Open DeepResearch and the integration of the Model Context Protocol (MCP), the infrastructure for autonomous discovery is becoming decentralized and auditable. Whether it is NVIDIA's Cosmos bringing spatial reasoning to robotics or 270M parameter models handling edge functions, the theme is clear: agents are getting smaller, sharper, and much more integrated into the OS level. Let's dive into the code-first future.
Hugging Face's smolagents Redefines Agentic Workflows via Code-Centric Actions
Hugging Face has introduced smolagents, a minimalist library where agents execute actions directly in Python code rather than restricted JSON schemas. This 'Code-as-an-Action' paradigm has demonstrated superior performance; for instance, CodeAgent outperformed ToolCallingAgent by nearly 2x on the GAIA benchmark according to @aymeric_roucher. The framework's core strength lies in its 50-line implementation of Tiny Agents, which now natively support the Model Context Protocol (MCP), enabling seamless connection to external data sources.
Beyond text, the library has expanded into multimodal capabilities with smolagents can see, allowing Vision Language Models (VLMs) to process visual inputs. Developers are increasingly adopting the framework for production due to its integration with Arize Phoenix for detailed tracing. While traditional frameworks offer vast ecosystems, community feedback from experts like @mervenoyann highlights that smolagents reduces 'abstraction bloat,' providing a more transparent 'white-box' experience for debugging agentic logic.
Open-Source Deep Research Challenges Proprietary Dominance
The landscape of autonomous discovery is shifting with the Hugging Face release of Open DeepResearch, a transparent alternative to OpenAI's proprietary feature. While OpenAI's version remains a benchmark for complex multi-step tasks, the open-source implementation leverages the smolagents framework and powerful reasoning backends like Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct to achieve comparable synthesis quality with full auditability. Developers are increasingly favoring these open frameworks to avoid the 'black box' constraints of closed ecosystems.
In parallel, the Jupyter Agent 2 has evolved into a sophisticated reasoning engine that operates directly within notebooks, enabling a seamless 'code-reason-execute' loop. This technical leap is further optimized by ServiceNow AI's Apriel-H1, which employs a distillation technique to pack high-level reasoning into an efficient 8B parameter model. This allows researchers to run complex agentic workflows locally, significantly reducing the latency and cost overhead associated with frontier-scale models while maintaining high accuracy in domain-specific discovery.
Testing Multi-Step Reasoning and Complexity Classes
Standard benchmarks are increasingly seen as 'saturated,' leading to the rise of dynamic frameworks like DABStep, which targets multi-step reasoning in data agents across 150+ complex tasks. The NPHardEval Leaderboard further challenges models by using 9 distinct complexity classes (from P to NP-Hard) to unveil true reasoning depth. Current leaderboard data indicates that while GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet maintain high accuracy on polynomial tasks, their performance degrades significantly in NP-hard categories, highlighting a persistent gap in pure logical reasoning.
To ensure models aren't simply 'memorizing' training data, FutureBench evaluates agents on their ability to predict future events based on real-time data, a task inherently resistant to data leakage. On the efficiency front, Intel/DeepMath showcases that lightweight agents built on the smolagents framework can perform sophisticated mathematical problem-solving through iterative code execution, proving that scale is not the only path to reasoning.
The Rise of OS-Level Agents: From Efficient Models to Standardized Benchmarks
The transition from browser-based tools to full operating system automation is accelerating. Smol2Operator has introduced specialized post-training techniques for a compact 135M parameter model, demonstrating that efficient computer control does not always require massive scale. This is complemented by ScreenEnv, a unified environment designed to deploy and evaluate full-stack desktop agents across diverse software ecosystems. Powering these capabilities is the Holo1 family from H (Hcompany), which features a 4.5B parameter VLM optimized for the Surfer-H agent, specifically engineered for high-accuracy GUI navigation and action execution.
To address the lack of standardized testing, the community has introduced ScreenSuite, a comprehensive evaluation framework that aggregates 10 distinct benchmarks and over 20,000 tasks into a single leaderboard. This follows the release of Gaia-2, which expands upon the original General AI Assistants benchmark to include more complex multi-modal reasoning in digital environments. These standardized metrics are proving essential for benchmarking the reliability of agents like Smol2-135M-Operator as they move toward production-level reliability in desktop automation.
Unified Tool Use: Bridging the Gap Between Providers and Frameworks
Fragmentation in how agents interact with tools is a major friction point for developers. Hugging Face's Unified Tool Use initiative addresses this by providing a standardized interface within the huggingface_hub library. This allows developers to switch between providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Mistral, and Google without rewriting tool-calling logic. The system relies on a common schema that translates high-level tool definitions into the specific formats required by each model provider, significantly reducing integration overhead.
The ecosystem is further strengthened by Agents.js, which enables JavaScript and TypeScript developers to build agents natively. This library mirrors the philosophy of the Python-based smolagents library, emphasizing simplicity and structured code execution. By enforcing Structured Outputs, agents become more reliable, as the model is constrained to generate code or JSON that adheres strictly to a predefined schema, minimizing the hallucination of invalid tool arguments.
Real-Time Reasoning and Zero-Shot Vision: The New Frontier of Physical AI
Physical AI is evolving rapidly as agents move from digital simulations to complex real-world environments. NVIDIA/Cosmos-Reason-2 is at the forefront of this shift, serving as a 7B parameter vision-language model specifically optimized for causal and spatial reasoning. Unlike traditional models, Cosmos Reason 2 uses a chain-of-thought process to understand physical interactions, which is critical for tasks requiring precise manipulation.
To run these models in real-time, the NVIDIA Reachy Mini project leverages the DGX Spark platform, a compact supercomputer designed to handle the high-throughput requirements of physical AI without the latency of cloud-based processing. On the perception front, pollen-robotics/pollen-vision has introduced a unified interface for zero-shot vision models. This toolset allows robots to utilize models like Grounded-SAM to perceive and segment objects in unstructured environments without task-specific fine-tuning. By combining the reasoning capabilities of Cosmos with the zero-shot perception of Pollen-Vision, developers can now deploy flexible robotic systems that adapt to new objects and scenarios instantly.
Gemma-2 270M and xLAM: Scaling Agentic Intelligence from Mobile to Local Servers
The landscape of on-device intelligence is shifting toward ultra-compact models like rushikesh143143/functiongemma-270m-it-mobile-actions, which leverages the Gemma-2 270M architecture to provide dedicated function-calling capabilities. Benchmarks indicate that despite its small footprint, it maintains high precision for mobile-specific intents such as hossam96/functiongemma-270m-it-voice-commands, offering a low-latency alternative to larger models like Phi-3 Mini for simple trigger tasks.
For high-performance local orchestration, the mradermacher/Llama-xLAM-2-70b-fc-r-GGUF brings Salesforce's 'Large Action Model' (xLAM) capabilities to local hardware. The xLAM series has demonstrated exceptional performance on the Berkeley Function Calling Leaderboard (BFCL), with the 70B variant providing the reasoning depth necessary for multi-step orchestration and complex API chaining. By using GGUF quantizations, developers can deploy these 70B parameter models on local workstations, ensuring data privacy and high reliability for enterprise-grade agentic workflows.
Hugging Face Agents Course and IBM CUGA Drive Modular Agent Adoption
The developer community for agents is experiencing a massive surge in interest, anchored by the Hugging Face Agents Course. A central component of the curriculum is the First_agent_template, which has already garnered over 627 likes as students learn to build autonomous systems using the new smolagents library. This course democratizes agentic AI by focusing on code-first agents that utilize LLMs for tool calling and reasoning across diverse environments.
Complementing this educational push, IBM Research has introduced CUGA (Configurable Universal Generative Agent), a framework that emphasizes modularity through YAML-based configurations. CUGA allows developers to define agent behaviors and toolsets without deep architectural rewrites, significantly lowering the barrier to entry for enterprise-grade deployments. Furthermore, the OpenEnv initiative is building a standardized ecosystem for agent environments, providing the necessary infrastructure to evaluate and share agentic tools across diverse platforms.