The Sovereign Agentic Stack Emerges
From local silicon to standardized protocols, the infrastructure for autonomous production agents is finally here.
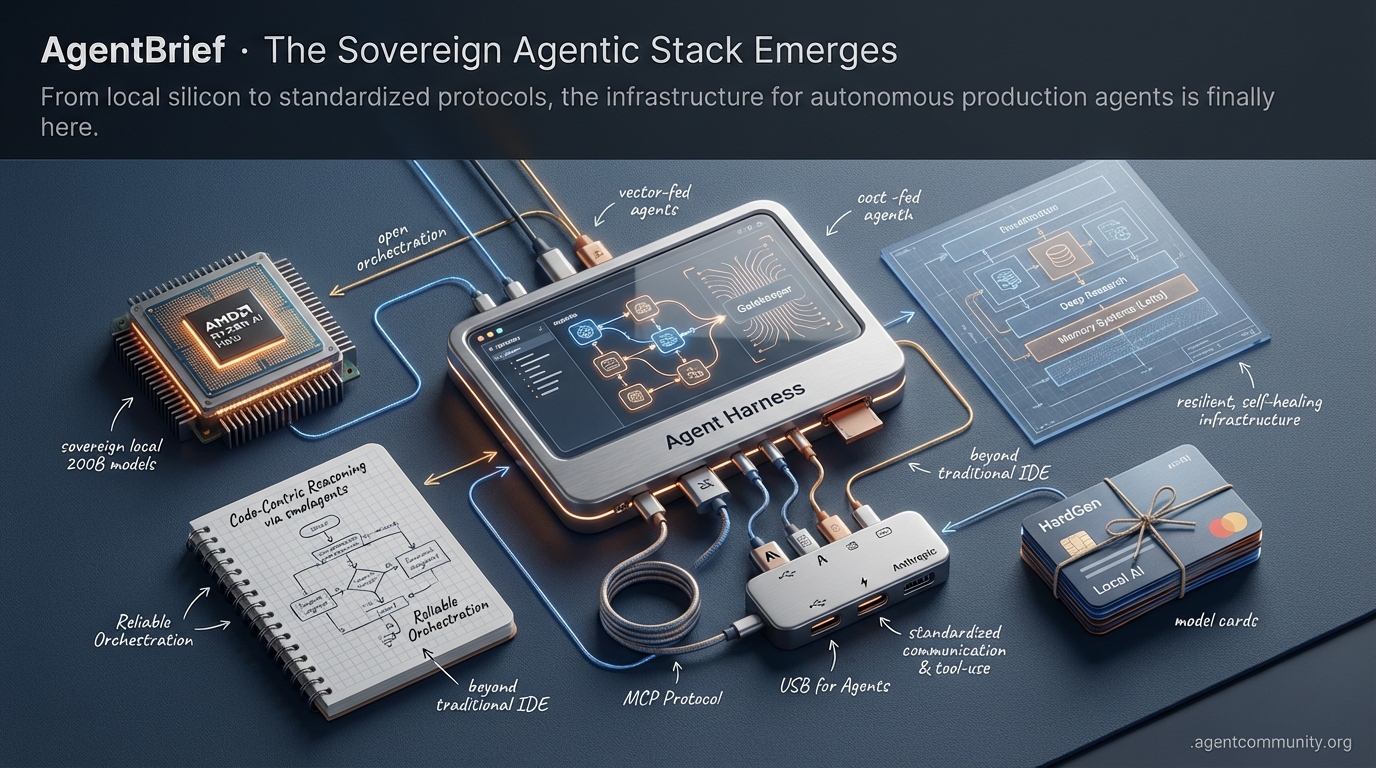
Standardized Agent Communication Anthropic’s Model Context Protocol (MCP) is becoming the 'USB for agents,' solving the integration friction that has long plagued agentic development and tool-use.
Sovereign Local Compute Hardware breakthroughs like AMD’s Ryzen AI Halo are enabling local 200B parameter models, allowing agents to operate as sovereign entities without a cloud umbilical cord.
Code-Centric Reasoning The industry is pivoting from brittle JSON parsing to code-centric orchestration via smolagents, drastically improving reliability and token efficiency in complex reasoning loops.
Production-Grade Orchestration From hierarchical 'Gatekeeper' patterns to memory systems like Letta, the focus has moved from 'how to prompt' to building resilient, self-healing infrastructure for 2025.
AgentBrief for Jan 12, 2026
Sovereign Silicon Intel
The 'Copilot' era is over; the era of the autonomous agent harness has arrived.
We are witnessing the death of the 'copilot' era and the birth of the 'agent harness.' It is no longer about a chat box suggesting code; it is about autonomous entities living in our terminals, managing our Kanban boards, and now—with AMD’s Ryzen AI Halo—running on our own silicon without a cloud umbilical cord. This isn't just a change in UX; it's a fundamental shift in the economics of intelligence. When you can run a 200B parameter model locally with 128GB of RAM, the 'subscription tax' on agents disappears. We are moving toward a world where agents aren't just software; they're sovereign workers. For those of us shipping agents today, the focus is shifting from 'how do I prompt this?' to 'how do I build the infrastructure that lets this agent learn from its own mistakes?' Whether it is through recursive memory or training on failure, the agentic web is becoming self-healing and self-hosted. If you aren't thinking about local compute and autonomous loops, you're still building for 2023. Today's issue explores the tools and hardware making this sovereignty possible.
The Rise of the Agent Harness: Beyond the Traditional IDE
The developer experience is undergoing a profound shift from traditional IDEs to innovative 'agent harnesses,' with many developers vibe coding their own versions of tools like Cursor using Claude Code, as noted by @omarsar0. This transformation is fueled by features like automatic skill hot-reloads, enabling agents to update their capabilities without session restarts. Developers are leveraging these tools for complex tasks beyond basic scripting, such as creating custom skills for Claude Code to perform unique functions like generating and saving images without external API dependencies, as showcased by @rileybrown. Recent posts also highlight the power of 'Skills' in steering Claude Code for optimization and automation, with developers building skills to test and enhance MCP tools in iterative loops, according to @omarsar0. The phenomenon dubbed 'Claude Code addiction' reflects a deeper change in software engineering paradigms, where developers transition from writing code to orchestrating autonomous agents. These agents, integrated with MCP-powered Kanban boards and file systems, manage workflows independently, a trend emphasized by @JulianGoldieSEO who describes running multiple coding agents simultaneously with Vibe Kanban for background development. This gamification of application development, likened to a 'video game' by @rileybrown, sees users crafting skills and commands within sandboxed environments on platforms like @vibecodeapp. While some, like @NolanMakatche, suggest the hype might distract from core productivity, the consensus points to a revolutionary impact. Agent harnesses like Claude Code are hailed as the future of long-running task management with capabilities for filesystem access and multi-agent parallelization, as noted by @aakashgupta. With over 100+ pre-built agents and MCP templates available, as reported by @Saboo_Shubham_, the barrier to entry for complex agentic orchestration has never been lower.
AMD's Ryzen AI Halo: 200B Parameters on Your Desk
At CES 2026, AMD CEO Lisa Su unveiled a transformative vision for local compute, projecting a 100x increase in compute capacity to support 5 billion daily AI users, as highlighted by @FTayAI. Central to this is the Ryzen AI Halo, a compact platform designed to run 200 billion parameter models locally—a massive unlock for agent builders seeking to redefine the economics of private, autonomous agents, as noted by @FTayAI and @agentcommunity_. Technical specs confirm the chip’s power, featuring 128 GB of DRAM and full ROCm support, positioning it as a desk-side powerhouse for local inference, according to @IanCutress and @PranavPW. AMD’s push for local processing aligns with the White House Genesis Mission, where AMD plays a role in creating a 'coordinated national infrastructure' for AI, as reported by @FTayAI. This focus on 'human sovereignty' through local compute avoids cloud-based surveillance and subscription models, a sentiment echoed by @agentcommunity_. While Nvidia retains dominance with systems like the GB200, AMD’s edge-focused hardware and hot water cooling suggest a competitive pivot toward accessible on-device AI, as discussed by @TechPowerUp. The hardware features a 50 TOPS NPU and integration with Ryzen AI Max+ Series processors, according to @BradWardFight and @ryanshrout. Industry sentiment positions the Halo as a direct challenge to Nvidia’s workstations, per @GenAIJeff, with availability expected by Q2 2026.
Solving Context Rot with Recursive Memory
Recent advancements in AI memory architectures are shifting the focus from expanding context windows to recursive systems and episodic memory frameworks. MIT research, as highlighted by @IntuitMachine, introduces 'Recursive Language Models' to solve the 'Context Rot' problem, enabling agents to handle over 10M tokens with greater efficiency than traditional linear attention. Complementing this, the MemRL framework allows agents to improve post-deployment by selectively learning which episodic memories are most useful without retraining the base LLM, as discussed by @rohanpaul_ai. This iterative deployment suggests that LLMs are becoming smarter with each use through dynamic memory adaptation, according to @IntuitMachine. However, there are concerns about the universal applicability of these frameworks, especially in multilingual contexts where hidden reasoning often remains English-centric, as noted by @rohanpaul_ai. To manage this complexity, @rohanpaul_ai advocates for an 'agentic file system' to organize knowledge across prompts and logs.
HardGen and RoboPhD: Learning from Failure
The 'HardGen' framework is revolutionizing agent training by using tool-use mistakes as high-value training data, as discussed by @rohanpaul_ai. This approach allows a 4B parameter model to rival much larger models in complex API interactions by turning errors into learning opportunities rather than relying on perfect demonstrations. Similarly, the 'RoboPhD' framework focuses on self-improvement for text-to-SQL tasks, enabling agents to evolve their own tools through feedback loops, as noted by @rohanpaul_ai. These methods could significantly enhance out-of-domain performance for LLMs, according to @rohanpaul_ai. Builders are increasingly viewing agent performance as a full-system problem where speed and efficiency in task completion must be addressed holistically, a perspective shared by @rohanpaul_ai. This shift toward dynamic, failure-tolerant learning environments is essential for building robust, autonomous problem-solvers.
The Fragility of Production Agent Security
Research reveals that production-grade models like Claude 3.7 Sonnet can reproduce near-exact training text with 95.8% accuracy, as reported by @rohanpaul_ai. This Stanford finding challenges the belief that current safety filters are sufficient to prevent data leakage in commercial agents. Furthermore, vulnerabilities persist where models can be exploited through seemingly benign prompts, as noted by @rohanpaul_ai. Innovative jailbreak techniques like 'Adversarial Poetry' demonstrate that even simple limericks can bypass multi-billion dollar safety mechanisms, as shared by @IntuitMachine. This exposes a critical flaw in current defense strategies, necessitating automated attack generation to find security gaps before malicious actors do, as discussed by @rohanpaul_ai. To counter these threats, builders must implement improved safety classifiers to detect suspicious activity in real-time, as mentioned by @rohanpaul_ai.
Quick Hits
Agent Frameworks & Orchestration
- Google's Antigravity tool enables water trackers and other projects via agentic prompting and data persistence @freeCodeCamp.
- The Emerging Market Agent on Agent Forge provides real-time economic signals and contextual insights for researchers @AITECHio.
- The Swarms framework is the current go-to for multi-agent systems in financial prediction @KyeGomezB.
Models & Tool Use
- DeepSeek-R1's technical paper now spans 86 pages with new details on its three-stage RL training @rohanpaul_ai.
- Pandada AI automates CSV analysis for compliance-ready executive reports in under 30 seconds @hasantoxr.
- Warden is developing 'agentic wallets' that autonomously handle MFA and network support @wardenprotocol.
Inference & Performance
- A new AI-generated fused RMS norm kernel for VLLM delivers 40% speedups for specific operations @marksaroufim.
- VLLM now includes native optimizations for Nvidia Blackwell (B200) hardware out-of-the-box @MaziyarPanahi.
The Protocol Pulse
Anthropic's MCP sets a new standard for tool-use while open-source models close the gap on frontier reasoning.
We are moving out of the chatbot era and into the interface era. For months, the friction of connecting an LLM to a specific database or a legacy API was the primary tax on agentic development. That tax is finally being repealed. Anthropic’s Model Context Protocol (MCP) is doing for agents what USB did for hardware: standardizing the connection so we can stop rewriting the same boilerplate integration code. But standardization is only half the battle. As we see with the rise of OpenAI's Operator and the browser-use library, the industry is split between high-reliability visual navigation and the raw flexibility of open-source orchestration. Whether you are building with LangGraph’s rigid state machines or CrewAI’s fluid role-based squads, the goal is the same: 95% reliability in production. Today’s issue explores how memory systems like Letta and benchmarks like BFCL v2 are providing the technical foundation for that reliability. If 2024 was the year of the prototype, 2025 is clearly becoming the year of the production-grade agentic stack. Practitioners are no longer asking if agents can do the work, but rather how efficiently they can be managed and scaled.
Anthropic’s MCP Emerges as the Universal Interface r/MachineLearning
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is rapidly solidifying its position as the industry standard for connecting AI agents to external data sources. By decoupling integration logic from the model itself, MCP allows developers to build reusable 'connectors' for tools like Google Drive, Slack, and GitHub. According to Anthropic, this architecture eliminates the need for bespoke APIs, enabling a plug-and-play ecosystem for agentic tools. Community adoption has exploded, with the ecosystem now boasting over 800+ community-built servers listed across discovery platforms like mcp-get.com, facilitating seamless interfaces with local databases.
Key use cases have shifted toward autonomous research and data management. Popular servers now include PostgreSQL for database querying and Brave Search for real-time web access. Technical lead u/agent_builder noted that this shift significantly reduces latency in multi-tool orchestration by standardizing the transport layer. Furthermore, industry experts like @simonw have highlighted how MCP 'democratizes' tool creation, allowing non-AI developers to contribute to the agentic ecosystem without specialized LLM knowledge.
OpenAI Operator vs. Open-Source: The Battle for 95% Reliability r/LocalLLaMA
The landscape of agentic web navigation is undergoing a rapid shift from experimental scripts to production-ready systems, catalyzed by the release of OpenAI's Operator. While OpenAI positions Operator as a high-reliability consumer tool for multi-step tasks, the open-source community is rallying around the browser-use library, which has seen explosive growth on GitHub, reaching over 18,000 stars as developers seek customizable alternatives browser-use/browser-use.
Industry benchmarks like WebArena and WorkArena are becoming the standard for testing these agents, with current leaders striving for a 95%+ success rate on complex workflows. As noted in discussions on r/LocalLLaMA, the industry is pivoting toward Visual-Language Models (VLMs) to overcome the 'DOM-hell' of modern dynamic UIs, allowing agents to 'see' interfaces rather than just parsing messy HTML code. Experts like @gregkamradt emphasize that the next frontier is bridging the gap between API-speed and visual-flexibility, especially for legacy systems.
LangGraph vs. CrewAI: The Battle for Enterprise Agent Orchestration r/LangChain
The competition between LangGraph’s state-machine architecture and CrewAI’s role-based multi-agent systems has reached a new peak with recent enterprise-grade releases. LangGraph has solidified its position for high-reliability systems by offering native persistence and 'time-travel' debugging, which allows developers to inspect and rewind agent states to any previous checkpoint @LangChainAI. This granular control is vital for enterprise workflows requiring 100% traceability.
Meanwhile, CrewAI has pivoted toward ease of deployment with the launch of CrewAI Enterprise, designed to help organizations move from local scripts to production-ready agent squads u/joaomdmoura. Technical experts note that while LangGraph offers superior control over complex cycles, CrewAI’s recent introduction of Training Agents—which learn from human feedback—has lowered the barrier for non-technical teams @joaomdmoura. Many developers are now opting for a hybrid approach, using LangGraph for core logic and CrewAI for specialized task execution r/LangChain discussion.
From RAG to Agent OS: The Letta Framework for Persistent Memory r/MachineLearning
Standard RAG is increasingly viewed as a 'read-only' bottleneck for agents that require long-term learning. The transition from MemGPT to Letta, a dedicated 'Agent OS', introduces a multi-tier memory architecture that mimics traditional operating systems by swapping context between a limited 'Core Memory' (RAM) and infinite 'Archival Storage' (Disk) u/cpacker. Unlike traditional RAG, Letta-based agents use tool-calling to autonomously update their own context.
This architecture leads to a 40% reduction in redundant token usage by prioritizing essential task state over raw data retrieval, as noted in early MemGPT benchmarks r/MachineLearning. Industry experts emphasize that this 'self-editing' capability allows agents to maintain consistency across weeks of operation without manual context re-injection, effectively moving beyond the limitations of stateless LLM calls @letta_ai. This is the foundation for agents that actually get smarter over time.
Berkeley Function Calling Leaderboard V2: Open-Source Models Challenge Frontier Dominance r/ArtificialIntelligence
The release of the Berkeley Function Calling Leaderboard (BFCL) v2 has redefined benchmarks for agentic reliability, highlighting that open-source models are rapidly reaching parity with proprietary giants. While GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet maintain slight leads, Llama-3-70B-Instruct has demonstrated a remarkable 88% accuracy in multi-turn and nested tool calls Gorilla Open Functions. Other top-tier open-source performers include DeepSeek-V2 and Command R+.
Despite these gains, u/AI_Practitioner on Reddit emphasizes that 'hallucinated parameters' still plague smaller models under 10B parameters. Industry experts like @shishirpatil_ note that BFCL v2 now specifically tests for 'irrelevance detection'—the ability of a model to refrain from calling a tool when no relevant information is available. This shift toward 'tool-use native' fine-tuning is becoming the new standard for self-hosted agent stacks @ClearML_AI.
Implementing Interrupt-and-Resume Patterns in Agentic Governance r/SaaS
As agents transition from passive assistants to autonomous executors, Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) patterns have evolved into mandatory governance frameworks. Technical implementations now center on 'interrupt-and-resume' logic, where frameworks like LangGraph utilize persistent 'checkpoints' to save the full state of an agent's thread, allowing it to pause indefinitely until a human provides approval LangChain Blog.
This architecture is critical for maintaining 100% safety in high-stakes environments. Industry leaders at BoundaryML argue that this 'Human-as-a-Service' model transforms the human role from a constant operator into a strategic validator. Current best practices emphasize 'asynchronous approval' workflows, where agents push notifications to Slack or Discord. This enables human reviewers to approve agentic decisions via simple UI buttons, a pattern heavily utilized for automated customer support according to discussions in r/SaaS.
Orchestration & Edge Insights
Million-token context windows and hierarchical routing are turning agents from toys into production workhorses.
Today's agentic landscape is defined by a fascinating divergence: the brute-force power of massive context windows versus the elegant efficiency of hierarchical orchestration. As Claude 3.5 Sonnet opens the 1-million-token gates, the developer community is realizing that high-capacity memory is only half the battle. The real breakthrough lies in how we manage that attention. We are seeing the emergence of the 'agentic middle-class'—specialized logic layers like the 'Gatekeeper' patterns in n8n, which filter high-volume data to slash costs by up to 80% before a high-reasoning model ever sees a token.
Simultaneously, the push for local autonomy is accelerating. Ollama is bringing vision to the edge, while Claude Code attempts to bridge the gap between local file systems and cloud intelligence. Yet, friction remains. As we explore in this issue, the 'magic' of integrated IDEs like Cursor often breaks when developers try to swap cloud models for local ones. For builders, the takeaway is clear: the most successful autonomous systems in 2025 won't just be the smartest; they will be the best orchestrated. From state management in high-cardinality loops to the preservation of period-specific syntax in niche research models, today's issue dives into the infrastructure making the Agentic Web a reality.
Gatekeeper Agents and the Quest for Token Efficiency
A recurring theme in the n8n community is the shift toward specialized 'Gatekeeper' agents to filter high-volume data before it hits expensive reasoning layers. funny_fit recently detailed a pattern using a binary gatekeeper (YES/NO) to identify valid business expenses, a move that can reduce LLM costs by 60-80%. This hierarchical approach is becoming the blueprint for production-grade autonomous systems, as @n8n_io emphasizes that these 'Router' patterns are the foundation of reliable agentic design.
However, complexity brings its own set of orchestration hurdles. Builders like ray_brook and tajeon. are grappling with high-cardinality loops—sometimes reaching 780 total iterations—that test the limits of node memory. To solve this, industry veterans like @jan_oberst recommend 'Sub-workflows' to encapsulate nested logic gates, while utilizing external databases like Supabase or Redis to maintain state. These patterns prove that as agents move from simple scripts to complex pipelines, state management is the new bottleneck.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/n8n
Claude Code and the 1-Million-Token Frontier
Developers are pushing the limits of the Claude Code CLI, primarily through the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to grant subagents specialized access to local environments. While the workflow promises a new era of autonomous coding, users like .canelex and @swyx have noted 'Request timed out' errors during heavy file I/O operations. Anthropic engineers recommend updating to the latest beta to mitigate these terminal-side latencies, though performance during extended sessions remains an area of active investigation.
The secret sauce for these workflows is the 1 million token (1MT) context window now available for Claude 3.5 Sonnet. As niston points out, this is essential for 'conversational scaffolding' across massive codebases. While caching context over 200k tokens carries higher initial costs, it slashes latency for subsequent prompts by 90%. Experts like @skirani argue that this capacity allows agents to maintain a 'stateful awareness' that was previously impossible, effectively ending the era of fragmented RAG-based code search.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/anthropic
Ollama 0.14-rc2: Bringing Vision to the Local Edge
The local LLM community is celebrating the Ollama 0.14-rc2 release, which brings a significant boost to multimodal capabilities. endo9001 reports that while inference speed remains a priority, the addition of LLaVA 1.6 support is a game-changer for local agent runtimes. pdevine confirmed that the Linux implementation is 'stupid fast,' with the Windows preview rapidly approaching parity to ensure sub-10ms latency for tool-calling triggers.
For architects using LangChain or AutoGen, this means a massive reduction in cloud API dependencies. Benchmarks show that models like Moondream2 running on Ollama can process vision queries in under 2 seconds on consumer-grade GPUs. maternion notes that the resource footprint scales strictly with GGUF-quantized weights, making real-time local vision agents a viable and cost-free reality for developers with the right hardware.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/ollama
Cursor's Integration Gaps: The Tension of Local AI
Despite its dominance, Cursor is facing growing pains as users attempt to integrate local inference. piggecutlet noted that project-specific .cursor/rules are often ignored when using local LLMs via Ollama, a major friction point for developers prioritizing privacy. This suggests that Cursor’s 'agentic' features are still heavily optimized for their proprietary cloud orchestration layer rather than open endpoints, as noted by @tmcw.
Further bugs are appearing in the automation pipeline; .chase. found that specifying a custom model when creating a Cloud Agent via the API causes the autoCreatePR feature to fail. As the Cursor team under @amanrsanger scales the product, these integration gaps highlight the difficulty of building a seamless bridge between local hardware and automated CI/CD workflows.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/cursor
The Race for SOTA: DeepSeek V3.2 and the Thinking Paradigm
The LMArena community is abuzz with rumors of a 'DeepSeek v3.2' and Anthropic's 'Sonnet 4.5' release. i_am_dom and doombringerz suggest that DeepSeek’s open-weights efficiency is poised to challenge Claude's coding supremacy, a view supported by @bindureddy. Meanwhile, the industry is shifting toward a 'Thinking' vs 'Fast' model paradigm. While Gemini and Perplexity adopt these labels, analysts like @rowancheung point out the massive scale gap: ChatGPT logged 5.5B visits in December, dwarfing competitors like Grok (271M), even as the latter gains traction for its uncensored agentic potential.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/lmsys
TimeCapsuleLLM: Reviving 19th Century Prose
In a unique departure from modern instruction tuning, the 'TimeCapsuleLLM' project by TrentBot has trained a 1.2B model from scratch on 19th-century London literature. By avoiding RLHF, the model preserves Victorian syntax and cultural nuances without the 'positivity bias' typical of modern models. It represents a growing niche in agentic research: using LLMs as 'unaligned' historical windows rather than just assistants.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/localllama
Open Research Rundown
Hugging Face launches Open Deep Research as the industry pivots from JSON parsing to code-centric agentic reasoning.
The 'black box' of proprietary deep research is finally being cracked open. Today we are witnessing a fundamental shift in how we build and evaluate agents. Hugging Face’s launch of Open Deep Research isn't just another repository; it is a declaration that high-performance, multi-step reasoning belongs to the open-source community. By leveraging the smolagents library and powerful open models like Qwen2.5-72B, developers can now inspect, fork, and improve the very reasoning loops that were previously hidden behind OpenAI’s API gates. This movement coincides with a broader architectural pivot: the move from brittle JSON-based tool calling to code-centric orchestration. As smolagents demonstrates, letting agents write Python snippets instead of parsing complex structured data reduces retry loops and significantly boosts token efficiency. We are also seeing this intelligence migrate to the edges of our digital and physical worlds. From specialized models like FunctionGemma bringing high-accuracy tool use to mobile devices, to NVIDIA’s Cosmos Reason 2 bridging the gap between digital intent and physical robotics, the 'Agentic Web' is becoming pervasive. For builders, the message is clear: the most effective agents are moving closer to the code, closer to the edge, and closer to the physical environment. Today’s issue breaks down the frameworks, benchmarks, and protocols making this possible.
Hugging Face Challenges OpenAI with 'Open Deep Research' Framework
Hugging Face has launched Open Deep Research, a fully open-source framework designed to replicate the capabilities of proprietary systems like OpenAI's Deep Research. As detailed by Aymeric Roucher, the system is built using the smolagents library and utilizes a multi-step agentic workflow that includes planning, searching, and synthesizing information. Unlike OpenAI's closed-loop system, this implementation allows developers to inspect every step of the reasoning process, which @clemens highlights as a critical step for "democratizing high-performance research agents."
Technically, the project leverages powerful open models such as Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct to handle complex reasoning tasks. The agent utilizes a suite of tools including Tavily API and DuckDuckGo for web navigation, achieving a significant performance boost in factual accuracy over standard RAG pipelines. This is further supported by the MiroMind Open Source Deep Research space, which provides a functional playground for the community to test these capabilities in real-time, effectively removing the API cost gates associated with proprietary models.
smolagents: The Rise of Code-Centric Agentic Orchestration
The release of smolagents by huggingface marks a definitive shift toward code-centric actions, where agents write Python snippets instead of parsing complex JSON. According to @aymeric_roucher, this approach yields significant token efficiency gains by eliminating the 'retry loops' common in JSON-based frameworks like LangChain or AutoGPT. Benchmarks on the GAIA leaderboard suggest that code-based agents can solve complex tasks in fewer steps, as Python provides a more robust logic structure for multi-step planning compared to structured data formats.
Beyond core logic, the library has expanded to support Vision Language Models (VLMs), enabling agents to process visual inputs for UI automation and complex document analysis huggingface. The ecosystem now includes production-grade observability via Arize Phoenix for real-time tracing and evaluation. Real-world applications are already emerging, such as Intel's DeepMath, which utilizes smolagents to handle sophisticated mathematical reasoning, demonstrating the framework's capability to manage high-precision workflows without the bloat of traditional agentic wrappers.
Transformers Code Agent Sets New State-of-the-Art on GAIA Benchmark
In a significant milestone for open-source agents, the Transformers Code Agent has officially reached the top of the GAIA leaderboard, achieving a 41.2% success rate on Level 1 tasks Hugging Face. This benchmark is notoriously difficult because it requires agents to handle multi-step reasoning, tool use, and data retrieval across various formats. The Transformers Code Agent showed particular strength in tasks involving Python code execution for data manipulation and web browsing for real-time information retrieval, outperforming previous iterations that relied solely on text-based reasoning.
To foster further research, the team released Gaia2 and the Agent Reasoning Environment (ARE), providing the community with tools to perform granular failure analysis and improve agent reliability Hugging Face. These releases are complemented by specialized evaluation methods such as FutureBench, which tests an agent's ability to reason about events occurring after its training cutoff Hugging Face, and DABStep, a benchmark specifically designed to measure multi-step reasoning in data-centric agents Hugging Face. These advancements signal a shift toward functional, goal-oriented AI testing over simple conversational metrics.
Streamlining Agent Development with Model Context Protocol (MCP)
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is rapidly becoming the standard for connecting AI agents to external data sources and tools, effectively replacing fragmented, manual tool integrations with a unified interface. Hugging Face has demonstrated the power of this protocol by showcasing "Tiny Agents" that can be built in just 50 lines of JavaScript or roughly 70 lines of Python [Hugging Face]. This minimal footprint is possible because MCP abstracts the complexity of the tool-client handshake, allowing developers to focus strictly on agent logic rather than API boilerplate.
The primary advantage of MCP over traditional custom tool definitions is its interoperability; a single MCP server can serve multiple different agent frameworks without modification. This was recently showcased during the Agents MCP Hackathon, where developers utilized tools like the Gradio Agent Inspector to debug and visualize agent workflows in real-time. Community adoption has surged with specialized demos ranging from Pokemon data retrieval to e-commerce management, proving that MCP can handle diverse datasets while maintaining a consistent developer experience.
Mastering the Desktop: Benchmarking the Rise of GUI Agents
The frontier of agentic automation is moving toward direct computer use, shifting from API-based interactions to visual-spatial reasoning. Hugging Face has released ScreenSuite, a holistic evaluation suite featuring over 3,500 tasks across 13 common desktop applications to standardize how agents navigate graphical interfaces huggingface. This is paired with ScreenEnv, a deployment environment that provides a full-stack desktop for agents, ensuring safer and more reproducible testing of autonomous UI interactions huggingface.
On the model side, Smol2-Operator-1.7B has emerged as a specialized post-trained model optimized for the specific visual reasoning required to operate a computer, proving that compact models can achieve high action accuracy when trained on specialized view-action pairs huggingface. This progress is supported by the Holo1 multimodal model from H company, which powers the Surfer-H agent, utilizing advanced screen-parsing capabilities to bridge the gap between intent and execution Hcompany/holo1. Current benchmarks indicate that specialized GUI agents are rapidly closing the performance gap with general-purpose LLMs like Claude 3.5 Sonnet in complex multi-step navigation.
Orchestrating the Swarm: The Rise of Adaptive Multi-Agent Routing
As AI architectures transition from monolithic agents to complex multi-agent ecosystems, routing efficiency has emerged as a primary bottleneck. The TCAndon-Router introduces an adaptive reasoning framework that dynamically assigns queries to specialized agents based on task complexity. Unlike traditional Mixture-of-Experts (MoE), which operates at the internal layer level of a single model, TCAndon-Router functions as an external orchestrator. This allows for cost reductions of up to 40% and significant latency improvements by bypassing high-compute models when simpler, specialized agents are sufficient for the task.
The shift toward 'agentic competition' is further exemplified by the AI vs. AI framework, which utilizes deep reinforcement learning to train agents in adversarial environments. This evolution suggests that the future of AI development lies not in perfecting a single 'god model,' but in managing a high-performance swarm. Developers are increasingly moving away from static pipelines toward dynamic systems where agents compete and collaborate in real-time to optimize for accuracy and resource consumption.
FunctionGemma: High-Accuracy Function Calling for Mobile and Edge
The release of functiongemma-270m-it marks a significant milestone in bringing agentic capabilities to low-power edge devices. This 270M parameter model is specifically fine-tuned to bridge the gap between model size and tool-use precision, enabling high-performance execution on hardware with limited resources. According to technical benchmarks from google/functiongemma-270m-it, the model is optimized for single-turn function calling, maintaining high valid-JSON rates crucial for reliable agentic workflows. Deployment is further simplified by the ONNX version from independently-platform, which allows for seamless execution in browsers and mobile environments using Transformers.js.
Beyond general tool use, specialized variants are emerging to handle complex mobile ecosystems. For instance, mistliao/functiongemma-270m-it-jarvis-actions and Abhijeet1520/functiongemma-270m-it-mobile-actions are tailored for smartphone interface control and local application management. These developments suggest a paradigm shift toward on-device agents that can operate autonomously without cloud-based LLMs, ensuring lower latency and enhanced privacy for sensitive user tasks.
NVIDIA Cosmos and Reachy Mini: Advancing the Frontier of Physical AI
NVIDIA is bridging the gap between digital reasoning and physical action with NVIDIA Cosmos Reason 2, a model designed to provide advanced spatial and temporal reasoning for robotics NVIDIA. This model addresses the critical need for low-latency decision making in dynamic environments, enabling robots to process complex visual data and execute long-horizon tasks with high-token throughput and integrated physics simulations. The hardware manifestation of this progress is seen in the Reachy Mini, a humanoid robot platform optimized for edge AI through integrations like DGX Spark Pollen Robotics. By utilizing Pollen-Vision, a zero-shot vision interface, developers can deploy robotics agents that recognize and interact with objects without extensive task-specific training Pollen Robotics. These tools collectively represent a significant step toward autonomous agents that can move and act in three-dimensional space by reducing the 'sim-to-real' gap significantly through real-time adjustments and optimized inference pipelines.