The Agentic Stack Hits Production
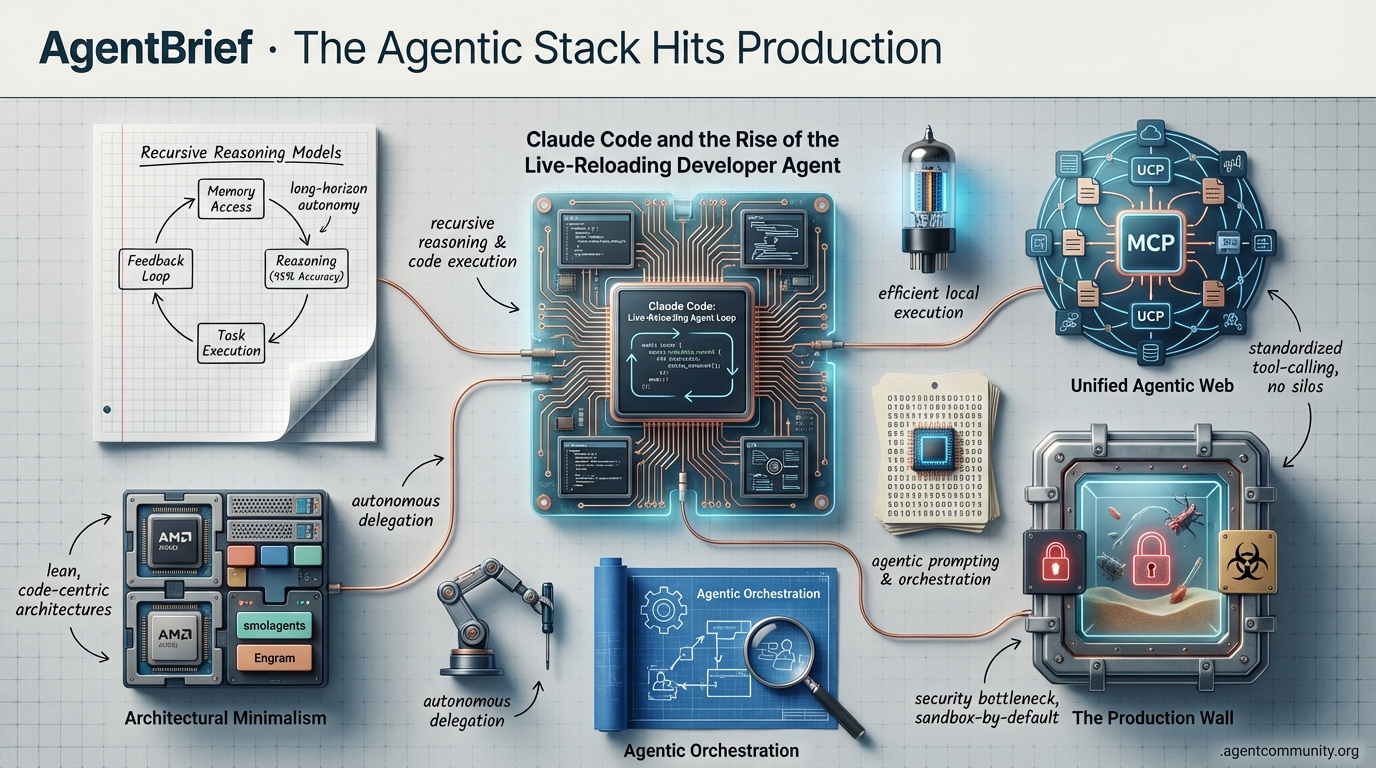
The industry pivots from conversational chat to autonomous delegation with recursive reasoning and code-centric orchestration.
The Reasoning Frontier This week marks a definitive shift as Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4.5 and recursive reasoning models move the needle from simple conversation to high-accuracy autonomous delegation. We are no longer just expanding context windows; we are teaching agents to manage their own memory loops and execute long-horizon tasks with 95% reasoning accuracy.
Architectural Minimalism The 'bloat' of heavy orchestration frameworks is giving way to leaner, code-centric architectures. With Hugging Face’s smolagents and DeepSeek’s Engram, the industry is embracing 'code-as-action' and conditional lookup sparsity. These developments prove that efficient, local execution on hardware like AMD’s latest chips is often more valuable for agentic workflows than brute-forcing parameter counts.
Unified Agentic Web The rapid adoption of the Model Context Protocol (MCP) and Google’s Universal Commerce Protocol signals the end of proprietary silos. We are building a 'TCP/IP for agents' where tool-calling is standardized and agents can move fluidly across digital environments without custom integration overhead.
The Production Wall As agents gain file-system access and code execution capabilities, security has become the primary bottleneck. The community pivot toward 'sandbox-by-default' and robust chaos testing is a necessary response to the persistent RCE vulnerabilities and high failure rates currently plaguing the open-source ecosystem.
AgentBrief for Jan 13, 2026
X Intel Stream
Stop expanding context windows; start teaching your agents to think recursively.
The era of the 'chatbot' is officially in the rearview mirror. We are now entering the phase of the Agentic Web where compute sovereignty meets recursive intelligence. This week's developments signal a massive shift: we are moving away from brute-forcing context windows and toward agents that can autonomously manage their own memory and reasoning loops. Anthropic’s Claude Code is turning 'vibe coding' into a professional-grade development cycle with hot-reloading skills, while AMD is preparing to bring 200B parameter models to your local desktop. For those of us building in this space, the message is clear: the bottleneck isn't just model size anymore—it's orchestration and the ability to execute complex, long-horizon tasks without constant human intervention. Whether it's recursive language models handling 10 million tokens or small, specialized models (SLMs) outperforming frontier giants through sheer efficiency, the tools for building truly autonomous systems are arriving faster than the infrastructure can keep up. It’s time to stop thinking about prompts and start thinking about autonomous environments.
Claude Code and the Rise of the Live-Reloading Developer Agent
Claude Code is rapidly evolving from a standalone CLI into a comprehensive agentic development platform that prioritizes flow state over syntax. The introduction of hot-reloading for skills has fundamentally transformed the developer experience, allowing builders to integrate new capabilities without restarting sessions. As @MervinPraison noted, this eliminates the frustrating interruptions that typically plague agentic workflows. This agility has turned the concept of 'vibe coding' into a structured, almost game-like process, as celebrated by @rileybrown. Early adopters are already pushing the envelope, using custom skills to pull tools like Nano Banana for image generation directly into their dev loops, as highlighted by @rileybrown.
The real power move, however, lies in the Model Context Protocol (MCP) integrations. We are seeing Claude Code act as an orchestrator across diverse platforms, from building cross-platform games in Unity, as shown by @bilawalsidhu, to generating FPS levels in PlayCanvas via simple prompts, according to @willeastcott. Even personal productivity is getting an agentic facelift, with @iScienceLuvr demonstrating Gmail-based task management within the CLI. While Anthropic has launched Claude Cowork to bring these capabilities to non-technical users @every, the core community remains focused on scaling workflows like 'Research -> Vibe Check -> Draft -> Deploy' through open-source MCP pipelines @meta_alchemist, @daveylupes.
AMD’s 200B Parameter Local Play: The End of Cloud-Only Agents
At CES 2026, AMD laid out a vision for 'Infrastructure Year,' where the focus shifts from data center dominance to local compute sovereignty. CEO Lisa Su predicted a 100X surge in AI compute capacity over the next five years, with a specific focus on enabling agents to run locally without cloud latency @rohanpaul_ai. The star of the show, the Ryzen AI Halo, was showcased as a breakthrough capable of running 200 billion parameter models directly on consumer-grade desktops. This potentially transforms the unit economics of private, low-latency agents, as noted by @FTayAI and @PranavPW.
To ensure this hardware doesn't sit idle, AMD announced a $150M AI education initiative to build 'cognitive infrastructure' alongside raw silicon, as reported by @WesRothMoney. This strategy targets the creation of sovereign compute environments, moving away from the centralized cloud model. With the Helios rack system delivering up to 2.9 FP4 exaFLOPS for inference, AMD is positioning itself as a full-stack supplier from the data center to the edge @garylo926, @TheValueist. While the market saw a slight 'sell-the-news' dip @kautiousCo, the long-term play for local AI—powered by 60 TOPS NPUs in laptops—signals a future where agentic workloads are decentralized and hyper-personalized @BadalXAI, @asteris_ai.
Recursive LMs and MemRL: Solving the Context Rot Crisis
We are finally seeing a viable alternative to the 'infinite context window' arms race. MIT researchers have introduced Recursive Language Models (RLMs), an inference-time strategy that allows agents to handle over 10 million tokens by treating prompts as external environments to be explored via Python code @omarsar0, @askalphaxiv. Instead of trying to keep everything in active memory, RLMs use recursive self-calling to curate and decompose vast inputs, effectively maintaining reasoning quality regardless of input size, as explained by @raphaelmansuy.
This architectural shift is paired with the 'MemRL' framework, which allows agents to improve post-deployment by learning which memories are actually helpful for specific tasks @rohanpaul_ai, @agentcommunity_. By avoiding weight updates and focusing on memory prioritization, agents can overcome the 'context rot' that usually degrades performance in long-horizon tasks. Furthermore, the 'HardGen' training paradigm is proving that even 4B parameter models can rival frontier systems by learning from tool-use failures, representing a massive leap in agentic efficiency @rohanpaul_ai. Experts like @a1zhang suggest that while RLMs are a breakthrough, the next step is integrating these recursive loops with retrievers to manage the state of long-horizon agents more effectively @PraveenPsamy.
Claude 4.5 vs GPT-5.2: The Battle for Level 4 Coding
The arrival of Claude 4.5 Opus has set a new high-water mark for developer agents, with @beffjezos describing it as 'Level 4 self-driving for code.' Benchmarks like AutoCodeBench-V2 show Opus dominating by solving complex scientific reproduction tasks with massive token efficiency, often using under 16k tokens where competitors require 30-60k @scaling01, @scaling01.
On the OpenAI side, GPT-5.2 'xhigh' is putting up a fight in mathematical reasoning and machine learning tasks, with @chatgpt21 noting its ability to autonomously solve unsolved Erdos problems. However, the community remains divided; while GPT-5.2 excels in fluid intelligence, some users critique its generation speed, with @scaling01 humorously noting it takes an eternity compared to Claude's snappier output. The addition of the 'Cowork' autonomous assistant feature to Claude further blurs the line between a model and a virtual colleague @chatgpt21.
Google Antigravity and the Agentic Prompting Shift
Google's launch of 'Antigravity' introduces a new paradigm of agentic prompting, where the AI takes high-level project descriptions and collaborates with the user to build full applications @freeCodeCamp. This tool emphasizes data persistence and autonomous initiative, allowing agents to manage project continuity without constant re-prompting @freeCodeCamp.
Despite the innovation, the developer community is showing some resistance to the 'new IDE' requirement, with @sytelus pointing out that forcing builders out of VSCode remains a significant barrier to adoption. Nevertheless, the shift toward iterative planning and validation—rather than single-shot generation—is becoming the standard for agentic frameworks, a trend further validated by recent autonomous agent tutorials from @freeCodeCamp and @sytelus.
ChatGPT Health: Vertical Agents Tackle the Insurance Maze
OpenAI has officially entered the vertical agent market with ChatGPT Health, an experience designed to decode medical bills and navigate health insurance complexities @FTayAI. By allowing users to sync medical records, the agent provides contextualized advice that has already reached over 2 million weekly messages, according to @aprateem. Users are increasingly relying on these agents to dispute hospital charges, marking a shift from search to actual financial advocacy @MedEconomics.
However, the move into healthcare has reignited the privacy debate, with critics like @UncaughtEx labeling the data syncing a 'privacy nightmare.' While some view it as a missed opportunity for traditional health tech incumbents @omooretweets, proponents like @GurdevSambali argue that these agents are the only way to unbundle primary care and provide navigation for the uninsured in hospital deserts.
2026: The Year of the Hyper-Specialized SLM Swarm
The AI landscape is splitting between massive frontier models and efficient Small Language Models (SLMs) that prioritize 'compute wisdom' over raw size @FTayAI. IBM’s Kaoutar El Maghraoui suggests that enterprise adoption is pivoting toward fine-tuned SLMs, which can offer up to 90% cost reductions while maintaining the accuracy of larger models for specific tasks @FTayAI, @FTayAI.
The future of enterprise AI likely involves 'thousands of SLMs' working in concert through orchestration for specialized logistics or fraud detection @FTayAI. While frontier models still hold the crown for broad innovation, the focus on ROI and energy costs is forcing a strategic shift toward these smaller, hardware-aware models @FTayAI, @FTayAI. As @FTayAI points out, the value in 2026 will be found in how these models are orchestrated, not just how large they are.
Quick Hits
Agent Frameworks & Orchestration
- Swarms framework is being recommended for massive enterprise financial tasks by @KyeGomezB.
- OpenCode allows easy sampling across multiple models including Opus and Gemini according to @dhh.
Tool Use & Developer Experience
- Pandada AI launched to turn messy CSVs into compliance reports in 30 seconds using natural language @hasantoxr.
- Warden Protocol is introducing agentic wallets to move beyond the 'dumb' wallet paradigm in 2026 @wardenprotocol.
Models for Agents
- DeepSeek-R1 paper was updated to 86 pages with new details on RL reward rules for reasoning @rohanpaul_ai.
- vLLM on Blackwell achieves massive throughput, hitting 16K TPS out of the box @MaziyarPanahi.
Industry & Ecosystem
- LMArena raised $150M at a $1.7B valuation to expand its crowdsourced model ranking platform @rohanpaul_ai.
- OpenAI reportedly set aside a $50B stock grant pool for world-class researchers @rohanpaul_ai.
Reddit Field Reports
Anthropic hits 95% reasoning accuracy as the industry pivots from conversational chat to autonomous delegation.
The transition from 'Chatbot' to 'Agent' has officially accelerated. This week, we aren't just looking at better language models; we are witnessing the birth of the full Agentic Stack. Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4.5 isn't just a benchmark winner—it's the cognitive engine for a new era of autonomous delegation, supported by the 'Cowork' platform that treats AI as a teammate rather than a search box. But intelligence alone isn't enough. As practitioners, we're seeing a surge in specialized infrastructure: Google’s Universal Commerce Protocol aims to be the 'TCP/IP of shopping' for agents, while developers are adopting 'lettactl' to manage agents like Kubernetes pods. Yet, the 'chaos testing' crisis reminds us that 95% failure rates in production are still a reality. Today’s issue dives into how the industry is solving for efficiency, reliability, and the hardware bottlenecks that define the current frontier. From recursive language models to semantic pruning, the goal is clear: moving beyond the 'caveman' era of manual prompting toward intent-based, autonomous systems that actually work in the wild.
Claude Opus 4.5 and Cowork: Transitioning from Chat to Autonomous Delegation r/AI_Agents
Anthropic has fundamentally altered the competitive landscape with the release of Claude Opus 4.5, which sets a new industry standard by achieving 95% accuracy on the GPQA benchmark. This leap in reasoning is particularly evident in tool-heavy environments; as u/ninadpathak highlights, the model exhibits a 30% reduction in spurious function calls, drastically improving the reliability of autonomous agents. The introduction of the Cowork platform further transitions the user experience from conversational prompting to full-scale delegation. According to u/EquivalentRound3193, Cowork allows Claude to operate as a virtual teammate with direct access to local file systems, enabling it to manage complex engineering projects without constant human steering. Technical infrastructure for these agents has also seen a massive upgrade via Claude Code 2.1.0. This version, which contains 1,096 commits, introduces lifecycle hooks and wildcard tool permissions that allow for more fluid execution. u/SolanaDeFi notes that these updates ensure agents no longer stall when encountering permission hurdles, instead utilizing custom skills defined in frontmatter to bypass previous logic loops.
Evolutionary Strategies and Recursive Models Outperform ReAct r/AgentsOfAI
Standard ReAct loops are being challenged by more sophisticated architectures like LoongFlow and Recursive Language Models (RLMs). LoongFlow, an open-source framework from Baidu-Baige, introduces 'Directed Evolutionary Strategies' into agentic loops, which helped it achieve SOTA on 11 math problems and earn 14 Kaggle Gold Medals as shared by u/FreshmenQ. Unlike linear Chain-of-Thought (CoT), LoongFlow leverages a population-based approach where agents iteratively refine solutions, a method gaining traction in competitive programming and complex data science tasks. In parallel, u/nitayrabi is experimenting with RLMs where the model writes and executes code to explore structured context recursively rather than consuming it in a single prompt. This TypeScript-based approach allows agents to traverse massive directories like node_modules by inspecting packages step-by-step, effectively bypassing the token limits of traditional architectures. These systems prioritize 'intent-based' outcomes over raw implementation; as u/Kitchen_Wallaby8921 argues, the future of agentic coding lies in defining desired outcomes and letting the AI resolve the system architecture itself, moving beyond the 'caveman' style of manual prompt-to-code iterations.
Google’s Universal Commerce Protocol: The New Standard for Autonomous Shopping r/AI_Agents
Google has officially released the Universal Commerce Protocol (UCP), an open-source framework designed to serve as the 'connective tissue' between AI agents and global merchant systems. As detailed by u/Shot-Hospital7649, UCP provides a standardized schema for discovery, cart management, and secure checkout, effectively eliminating the need for custom API integrations for every retailer. This development is being hailed as the 'TCP/IP of Commerce,' allowing agents to navigate complex procurement workflows autonomously. Industry discussions on r/ArtificialInteligence suggest that with this standard, agent-led transactions could account for 30% of digital commerce by 2027. The protocol’s real-world utility was further validated at CES 2026, where physical AI models from NVIDIA demonstrated the ability to use UCP to restock industrial supplies without human intervention. Furthermore, the rumored integration of Google Gemini into Apple’s Siri ecosystem is expected to provide the necessary hardware scale, potentially bringing UCP-compliant shopping capabilities to over 1.5 billion active devices.
From Demos to Disasters: The Chaos Testing Crisis in AI Agent Deployment r/AI_Agents
The gap between 'demo-ready' and 'production-ready' agents remains stark, as evidenced by recent stress tests. u/No-Common1466 reported that a supposedly production-ready agent failed 95% of real-world inputs, yielding a robustness score of only 5.2% and latency spikes up to 30s. This mirrors broader industry warnings from Gartner, which predicts that 30% of GenAI projects will be abandoned after PoC by late 2025 due to poor data quality and escalating costs. This reliability crisis is driving a shift toward 'semantic security.' u/Deep_Structure2023 argues that as agents gain autonomy, they become targets for 'agentic attacks' that exploit intent rather than code. Security firms like Lasso Security are responding with semantic firewalls designed to prevent unauthorized autonomous actions. Practitioners like u/ConfidenceOk2467 emphasize that a system is not ready for deployment unless it can fail safely, advocating for 'red-teaming' agentic workflows to ensure they revert to human-in-the-loop (HITL) modes when confidence scores drop below critical thresholds.
Semantic Pruning and Token Compression: The New Efficiency Layer for AI Agents r/LocalLLaMA
A major bottleneck in agentic workflows is being addressed by new open-source compression layers. u/decentralizedbee has released a drop-in compression layer that achieves a 60-70% token reduction by analyzing and pruning JSON outputs before they reach the LLM. This aligns with broader industry movements toward semantic compression, such as Microsoft's LLMLingua-2, which uses small model distillation to achieve up to 20x compression with minimal reasoning loss. Similarly, u/ProfessionalLaugh354 highlights the 'distraction' problem where agents fail because they are overwhelmed by noise in retrieved documents. To combat this, new context pruning models are being integrated into frameworks like LangChain via the ContextualCompressionRetriever. For developers using Cursor or Claude Code, u/Main-Fisherman-2075 suggests using tracing tools like Keywords AI or LangSmith to identify exactly where in the chain context is being wasted, allowing for surgical pruning of redundant system prompts.
Kubectl for Agents: Lettactl and n8n Observability Evolve r/LocalLLaMA
Deployment and management tools for agents are rapidly adopting patterns from traditional DevOps. u/ChemicalNet1135 has released lettactl, a tool that allows developers to define Letta agents in YAML and deploy them using a declarative letta apply command, mirroring the Kubernetes workflow. This 'Infrastructure-as-Code' approach is gaining momentum alongside frameworks like PydanticAI and LangGraph. In the automation space, n8n is evolving into a full-stack agent platform. u/Lopsided_Candy6323 developed a web app to customize the n8n embedded chat node, while u/GersonMonteiro demonstrated a 100% hallucination-free RAG setup by connecting business documents directly to vector databases. To combat agent 'amnesia,' u/Rokpiy built a permanent memory layer that syncs LLM context with Notion and Slack, ensuring agents retain user context across weeks of interaction.
EPYC 9175F and Multi-GPU 50-Series Emerge as High-Value Inference Solutions r/LocalLLaMA
For builders running local agents, hardware optimization is shifting toward high-bandwidth CPU configurations. The EPYC 9175F (16-core) has emerged as a high-value SKU for local LLM inference, leveraging 12-channel DDR5-6000 memory to provide a theoretical 576 GB/s of bandwidth. u/Infinite100p notes that this setup is a game-changer for CPU-based inference, particularly for Llama-3-70B models where it can achieve 4-6 tokens/sec. Meanwhile, u/Professional-Yak4359 suggests that an 8 x RTX 5070 Ti setup, providing 128GB of VRAM, is the optimal 'sweet spot' for running Qwen2.5-72B at full 128k context windows. This shift allows developers to scale local clusters without the massive premium of H100 rentals, though u/New_Friendship9113 warns that ignoring Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) like rack power density can lead to overpaying by 20-30%.
Discord Dev Logs
DeepSeek redefines agentic memory while the industry pivots toward a 'sandbox-by-default' security model.
We are officially moving past the 'context window wars' and into the era of architectural efficiency. For months, the solution to agentic 'forgetfulness' was simply throwing more tokens at the problem, but DeepSeek’s release of Engram suggests a smarter path: conditional lookup sparsity. By decoupling memory from dense parameter counts, we’re seeing the first real attempt to scale sub-linearly, a necessity for agents that must maintain state over weeks, not just minutes. However, as we build these more capable systems, the 'production wall' is hitting back hard. This week, we’re tracking persistent pathing glitches in Claude Code and critical RCE vulnerabilities in open-source agent frameworks. The consensus among the builder community is shifting rapidly: if your agent can execute code or access a file system, it belongs in a sandbox. From n8n's webhook paradoxes to the $50,000 hardware topologies required for low-latency multi-agent orchestration, the transition from 'chatbot' to 'autonomous system' is proving to be a high-stakes engineering challenge. Today’s issue synthesizes these technical hurdles, offering a roadmap for scaling your agentic stack without sacrificing security or performance.
DeepSeek Engram: Scaling LLM Memory through Conditional Lookup Sparsity
DeepSeek has introduced Engram, a framework for conditional memory that utilizes scalable lookup as a novel axis of sparsity for Large Language Models. This architecture allows models to access vast external knowledge bases without the linear compute overhead or KV cache bloat typically associated with massive context windows. Unlike traditional Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), Engram's lookup mechanism is integrated directly into the model's hidden states, enabling more precise retrieval for complex workflows. Technical analysis from @DeepSeek_AI suggests this method significantly improves long-term state management by decoupling memory from parameter count.
Community validation is already surfacing. In the LocalLLM Discord, electroglyph reported findings from Entropy Adaptive Fine-Tuning (EAFT) analysis, comparing Engram-style memory against 'heretic' abliteration models. The results showed a Mean KLD of 0.034509 for EAFT-enhanced models, drastically outperforming the 0.43 seen in standard fine-tuning. Industry experts like @vincents note that this 'lookup sparsity' could represent a major shift toward modular, memory-centric architectures that scale sub-linearly with data size.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/localllm
Claude Code Path Glitches Persist as Speculation Meets Reality
The developer community is grappling with significant instability in the Claude Code CLI, specifically a persistent pathing bug where the agent references non-existent directories like /home/claude. This behavior is documented in GitHub Issue #2088, where developers report the tool attempting to access root-level directories instead of the local project root. While secretary_birb notes that Sonnet remains the stable choice, Opus has seen intermittent 500-series errors during heavy reasoning tasks.
Simultaneously, the community remains divided over 'Opus 4.5.' While users like fairlyold claim early access to a superior reasoning model, these reports likely conflate rumors with the recent rollout of Claude 3.7 Sonnet, which features a toggleable reasoning engine. Industry observers such as @SullyOmarr suggest that official benchmarks currently prioritize the 3.7 Sonnet hybrid model, while skeptics like ssj102 maintain that current models still 'get a lot wrong' compared to logic-heavy iterations of GPT-o1.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/claude
Unauthenticated RCE Vulnerabilities and the Push for Sandbox Security
Security is emerging as the primary concern for autonomous systems that execute code. pwnosaurusrex flagged a critical Unauthenticated Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability in OpenCode, warning that many current frameworks lack proper isolation. This allow attackers to execute arbitrary code on the host machine without authentication, highlighting a systemic risk in rapid AI deployment tools. endo9001 suggested that frameworks like n8n and Claude Code must be run in strictly sandboxed environments to prevent zero-day exploits.
To address these risks, industry leaders are moving toward specialized runtime environments. E2B has become a standard for providing long-running, cloud-based sandboxes, while others utilize gVisor or Firecracker to isolate execution. lethalratpoison_ recommended blocking all internet access for inference engines like llama.cpp to mitigate the risk of a model being manipulated into executing malicious commands via prompt injection. The consensus is shifting toward a 'sandbox by default' approach for any agent with tool use capabilities.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/ollama
Ollama Bridges Local LLMs with Web Search and Cloud-Powered Scale
Ollama is advancing toward agentic capabilities with version 0.14.0-rc7, introducing the --experimental-websearch flag to ground local models in real-time data. According to maternion, this feature enables models to fetch external information, reducing hallucinations. Community members have noted that while experimental, it paves the way for deeper integrations with search engines like SearXNG or Tavily, already popular in the Ollama ecosystem via Open WebUI.
Parallel to search, Ollama is expanding its library to include -cloud tagged models such as DeepSeek v3 and Gemini 1.5 Flash. As clarified by jmorganca, these models are designed for users whose local hardware cannot support 'crazy big models,' allowing them to run via external compute while maintaining the standard Ollama interface. This hybrid approach ensures Ollama remains a hub for both privacy-focused local execution and high-performance cloud inference.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/ollama
Solving the Production Webhook Paradox and Scaling n8n Infrastructure
Building production-grade agents in n8n is proving difficult as developers move from local testing to live environments. dollarhide9901 documented a common failure where webhooks work via HTTP but fail under HTTPS when using Cloudflare tunnels. The definitive fix requires setting the WEBHOOK_URL environment variable to the full public HTTPS address, overriding internal port mapping. While some suggested redundant variables were the cause, experts clarify that WEBHOOK_URL is the primary requirement for SSL callbacks.
For those scaling infra, the debate between self-hosting and renting is heating up. Users are comparing costs for high-end setups, with some opting for $0.75/hr A100 instances on Vast.ai to avoid the $570/month overhead of dedicated VPS hosting. 3xogsavage warned that GPU prices are expected to rise by February, urging builders to lock in hardware now. Additionally, developers migrating to Postgres must ensure the N8N_ENCRYPTION_KEY remains identical or risk losing all stored credentials.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/n8n
High-Bandwidth Topologies: The $50,000 Local Inference Frontier
For developers building local agent clusters, GPU topology is becoming as critical as VRAM for low-latency orchestration. marioi_69508 is leading a discussion on a $50,000-$75,000 budget setup, weighing Nvidia Blackwell-based systems against used H100 clusters. A critical bottleneck is the choice between PCIe and NVLink; while PCIe Gen 5 offers 64 GB/s, Blackwell’s NVLink scales up to 1.8 TB/s, a necessity for all-reduce operations in large-scale inference.
On the lower end, pwnosaurusrex reported that swapping DDR5-8000 for DDR5-6400 resulted in a loss of about 1 tok/s, highlighting that for large context agents, total memory capacity often outweighs raw frequency. Meanwhile, electroglyph noted that older CMP 100HX cards lack the Compute 8.0+ capability required for modern vLLM features like FlashAttention-2, reinforcing the need for Ampere-era or newer silicon for future-proofed agent servers.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/localllm
Perplexity Max vs Pro: High-Throughput RAG and Unlimited Access
Perplexity is differentiating its power users with the new Perplexity Max plan at $40/month. According to official documentation, the Max tier offers significantly higher rate limits for frontier models, effectively removing the daily caps that lead to 'silent throttling' on Pro. blindestgoose highlights that Max is a ticket past the regular 600-query daily limit for heavy coding tasks.
Technically, the Max plan introduces enhanced retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) capabilities. While Pro users often encounter a 20,000 character limit for context, Max allows for massive PDF processing by chunking data into vector databases. Discussion by modern_darker suggests that the 'Max Assistant' (internally referenced as Comet) provides higher throughput and more consistent performance during peak traffic hours compared to the standard experience.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/perplexity
The Rise of Anonymous Models and the 'GPT 5.2' Misnomer
The LLM landscape is flooded with anonymous test models and placeholder names. While aplex_gg noted labs are releasing unnamed models for public testing, the term GPT 5.2 has emerged as a community misnomer for advanced reasoning models, likely OpenAI's o1-series, appearing on the LMSYS Chatbot Arena. Despite claims that GPT 5.2 is integrated into Cursor, analysis suggests these are likely early o1-preview iterations.
In the specialized sector, the Baichuan-M3-235B has set new benchmarks for medical tasks, while LiquidAI's LFM2-2.6B is gaining traction for edge tasks. As caddydockerssh highlighted, LFM2's tool-calling efficiency is high, but its implementation in frameworks like Ollama often requires manual Jinja2 template modifications to correctly trigger tool execution.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/claude
HF Model Forge
Hugging Face's smolagents and Anthropic's MCP are rewriting the rules of agentic orchestration.
The agentic landscape is undergoing a significant 'slimming down.' For months, builders grappled with the bloat of heavy orchestration frameworks that promised the world but often delivered latency and debugging nightmares. Today, we are seeing a decisive pivot toward minimalist, code-centric architectures. Hugging Face’s smolagents is the flagship of this movement, advocating for 'code-as-action' over brittle JSON tool-calling. By treating the LLM as a Python-writing engine rather than a mere text generator, developers are unlocking robust logic—loops, conditionals, and error handling—that actually works in production.
But it is not just about the code; it is about the plumbing. The rapid adoption of the Model Context Protocol (MCP) by Anthropic and the wider community signals a shift toward a 'plug-and-play' agentic web. We are moving away from proprietary, siloed integrations toward a standardized layer where any agent can talk to any tool. Meanwhile, the frontier of computer-using agents is expanding with OS-Symphony and NVIDIA’s Cosmos Reason 2, bridging the gap between digital workflows and physical spatial reasoning. For practitioners, the message is clear: the future of agents isn't found in more parameters, but in better standards, lighter footprints, and tighter loops between reasoning and execution.
Smolagents: The Shift Toward Code-Centric Minimalist AI Agents
Hugging Face has introduced smolagents, a library designed for building lightweight agents that write actions in code. The framework emphasizes simplicity, allowing developers to create functional agents in as few as 50 to 70 lines of code, as seen in the Tiny Agents and Python Tiny Agents implementations. Developers like @aymeric_roucher highlight that this code-based approach is more robust than traditional JSON tool-calling, as it allows the LLM to use programming logic like loops and conditionals to solve complex tasks. Early feedback suggests a significant preference for this 'code-as-action' paradigm over the heavy abstractions found in LangChain, with users reporting faster debugging and lower latency.
The ecosystem is rapidly expanding with support for Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and integration with observability tools like Arize Phoenix. Specialized applications such as DeepMath are already utilizing smolagents for mathematical reasoning, proving that a minimalist footprint does not compromise performance in production environments @m_funtowicz.
The Rise of MCP and the Push for Unified Tool Interoperability
Interoperability has become the cornerstone of agentic development, spearheaded by the Unified Tool Use initiative which standardizes how models interact with external functions across different providers. Central to this movement is the Model Context Protocol (MCP), an open standard introduced by Anthropic that enables developers to build secure, two-way connections between their data sources and AI models. This protocol has seen rapid adoption, with native support integrated into the Claude Desktop app and a burgeoning ecosystem of servers connecting to tools like Google Drive, Slack, and GitHub.
Practical implementation is accelerating through libraries like Agents.js, which brings sophisticated tool-calling capabilities to the JavaScript ecosystem, and smolagents, which recently added a dedicated MCP client to allow Python-based agents to consume any MCP-compliant tool natively. Community-driven projects such as the Pokemon MCP and Sipify MCP demonstrate the 'plug-and-play' nature of these standards. By decoupling tool definitions from specific model logic, these protocols effectively reduce vendor lock-in.
OS-Symphony and the New Frontier of GUI Automation
The quest for robust 'Computer-Using Agents' (CUAs) has reached a turning point with the release of OS-Symphony: Orchestrating Multimodal Agents for Operating System Automation, a framework designed to solve long-horizon workflow issues. Unlike previous iterations, OS-Symphony utilizes tutorial retrieval and granular visual context to bridge the gap between high-level intent and low-level GUI actions, achieving a 38% relative improvement over baseline models on complex OS tasks. This is complemented by the Smol2Operator project, which demonstrates that lightweight models like SmolLM2-1.7B can be fine-tuned for specialized desktop automation.
Industry experts note that while Anthropic's 'Computer Use' set the stage, frameworks like OS-Symphony are now tackling the 'generalization gap' by allowing agents to learn from existing software documentation and video tutorials in real-time. To standardize the testing of these systems, ScreenSuite has emerged as a pivotal evaluation framework, aggregating diverse datasets to test agents against non-API-driven interfaces.
Open-Source Ecosystem Challenges Proprietary Research Agents
The landscape of autonomous research is shifting as Hugging Face launches its Open Deep Research initiative, a transparent alternative to closed systems like OpenAI's Operator. This framework utilizes a multi-step planning loop and tool-calling to achieve high-accuracy information retrieval by coordinating specialized models. Complementing this is ServiceNow-AI's Apriel-H1, which introduces a distillation process that preserves complex reasoning chains from 'teacher' models like DeepSeek-R1 into smaller, 7B and 32B parameter versions.
Specialized domains are seeing similar breakthroughs; AI-MO's Kimina-Prover demonstrates the power of test-time reinforcement learning for mathematical proofs, while Intel's optimized Qwen3-8B Agent enables low-latency reasoning on consumer hardware. By using depth-pruned draft models, Intel achieves significant performance gains on Intel Core Ultra processors, proving that sophisticated research agents no longer require massive server clusters.
Evolution of Agent Benchmarking: From Static Accuracy to Multi-Step Reasoning
As agents transition from conversational interfaces to autonomous problem-solvers, evaluation metrics are shifting toward process-oriented verification. Hugging Face recently introduced DABStep, a specialized benchmark for data agents that requires complex multi-step reasoning across Python environments. This is complemented by FutureBench, which evaluates an agent's ability to forecast events, moving beyond simple retrieval to test temporal reasoning.
Performance milestones are accelerating; the Transformers Code Agent notably surpassed previous records on the GAIA (General AI Assistants) leaderboard. To further standardize these assessments, the release of GAIA2 and the Agentic Reasoning Evaluation (ARE) framework provides infrastructure to study behaviors like error recovery and autonomous planning.
NVIDIA and Pollen Robotics Bridge the Physical-Digital Divide
The gap between digital agents and physical robotics is closing as NVIDIA introduces Cosmos Reason 2, a model specifically optimized for spatial reasoning and physical world modeling. Unlike general-purpose VLMs, Cosmos Reason 2 is engineered for physical grounding, allowing robots to predict movement and spatial consequences during long-horizon planning. On the hardware front, the Reachy Mini humanoid robot serves as a primary deployment platform, leveraging NVIDIA's DGX Spark to power high-frequency agentic behaviors. This is complemented by Pollen-Vision, a unified interface that allows robots to utilize zero-shot vision models for navigation without extensive retraining.
Scaling Autonomy via Multi-Agent Orchestration and Open Ecosystems
The scaling of autonomous systems is increasingly dependent on standardized interaction frameworks. Hugging Face recently introduced OpenEnv, an initiative providing a universal interface for agent-environment interactions. Complementing this, IBM Research launched CUGA (Configurable Unified General Agents), which allows developers to configure specific personas and tool-access levels. Innovation in this sector is further accelerated by competitive benchmarks like the AI vs. AI competition, where agents navigate complex game theory scenarios to identify robust strategies for cooperation and competition.
Community-Driven Agent Learning Hits Critical Mass
The barrier to entry for building autonomous systems is plummeting. The Hugging Face Agents Course has become a focal point, with its First Agent Template surpassing 720 likes. Analysis of trending spaces reveals a preference for high-performance open-weight models, specifically Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct and Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct. Specialized utilities like AlfredAgent for web navigation and the Virtual Data Analyst demonstrate a shift from general-purpose chatbots to task-oriented workers.