Engineering the Durable Agentic Stack
Durable Execution First The industry is pivoting away from vibe-coding toward systems where state management and process persistence—via tools like Temporal and LangGraph—are mandatory for production reliability.\n> The Architecture Shift Performance gains are migrating from raw model weights to the harness—the middleware and local infrastructure that allow agents to reason recursively and recover from tool failures in real-time.\n> Long-Horizon Autonomy New patterns like Cognitive Accumulation and the Model Context Protocol (MCP) are enabling agents to maintain strategic intent over hundreds of steps, moving past simple one-off tasks.\n> Code-Centric Orchestration Developers are favoring smol libraries and code-as-action over complex JSON schemas, prioritizing precision on local hardware and vision-language models for robust GUI navigation.
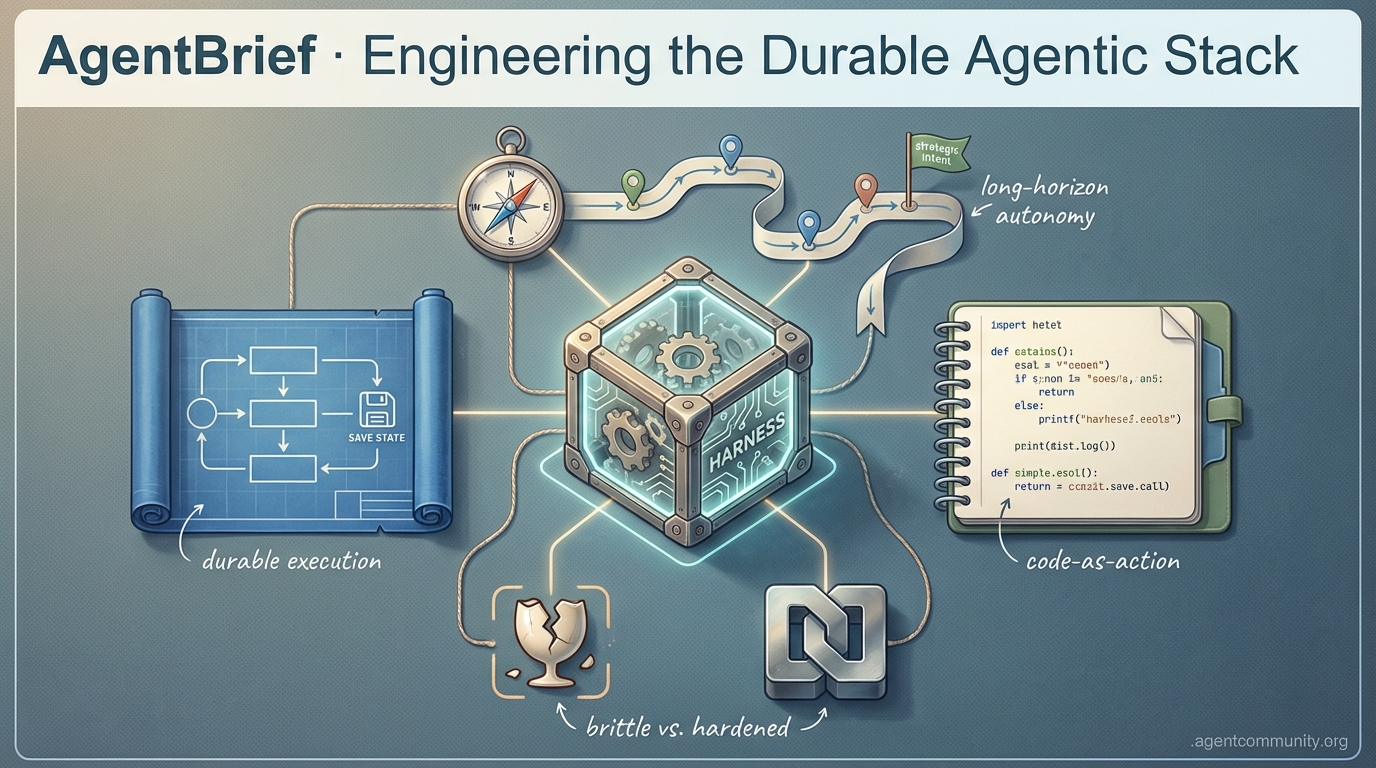
Brittle wrappers are out; hardened infrastructure and code-first execution are defining the next generation of autonomous systems.
AgentBrief for Jan 16, 2026
The X Intel
Forget chat bubbles; the future is hot-reloaded agentic skills and failure-informed training.
We are moving past the 'vibe coding' era and into the 'harness' era. It is no longer about just prompting; it is about the infrastructure that lets an agent live, fail, and fix itself in a sandbox. From Claude Code's hot-reloaded skills to models that treat tool-failure as a feature rather than a bug, the focus has shifted to the system around the model. If you are still treating agents as stateless chat bubbles, you are building for 2024. The 2026 stack is local, recursive, and brutally honest about its errors. This issue dives into the tooling and training patterns that make autonomous systems reliable enough to actually trust with your filesystem. We explore how hardware giants like AMD are pivoting to power 200B parameter models at the edge, while researchers at MIT are solving the 'context rot' that plagues long-horizon tasks. For agent builders, the message is clear: the model is the engine, but the harness is the vehicle. Let's look at the blueprints.
The Era of the Agent Harness is Here
The landscape of AI development is undergoing a profound transformation, moving from simple chat interfaces to sophisticated agent harnesses that redefine how developers interact with AI. Tools like Claude Code are evolving beyond static scripts into dynamic systems where skills can be hot-reloaded and executed without restarting sessions, as noted by @NickADobos. This capability enhances workflow continuity, turning 'vibe coding' into a structured, almost game-like experience for creating professional-grade mobile and web apps, as highlighted by @rileybrown. Developers are leveraging these sandboxed environments to push boundaries, with Claude Code acting as a central orchestrator via the Model Context Protocol (MCP), enabling seamless integration with external tools and data sources without local setup, according to @AnthropicAI. A key differentiator in this space is the competition between Claude Code and open-source alternatives like OpenCode. Claude Code excels in managing local state and tool execution through its agent harness, which wraps around the model to handle long-running tasks, prompt presets, and filesystem access, as described by @aakashgupta. In contrast, OpenCode offers a model-agnostic approach, allowing developers to sample across multiple models like Opus and Gemini, avoiding vendor lock-in, as noted by @dhh. This flexibility is crucial for builders seeking to customize their environments, with developers crafting MCP-powered components like Kanban boards to maintain control over autonomous agents, per @omarsar0. The race to build the ultimate developer experience for the agentic web is intensifying, with nuanced perspectives emerging. While Claude Code’s sandboxed environments are celebrated, some developers note the learning curve it imposes on 'vibe coders,' as pointed out by @innerline7. Meanwhile, OpenCode’s ability to deploy background agents in platforms like Slack provides a 'web experience' that some find more accessible, according to @PreslavMihaylov. This dichotomy suggests that the future of agent harnesses will hinge on how they balance usability with powerful orchestration in 2026 and beyond.
HardGen and RoboPhD: Pioneering Agent Self-Improvement Through Failure
Recent advancements in AI research are reshaping the landscape of agentic performance by emphasizing learning from errors over polished demonstrations. The 'HardGen' framework, as discussed by @rohanpaul_ai and further highlighted by @agentcommunity_, leverages tool-use failures as critical training data, enabling a 4B parameter model to rival much larger systems. This approach focuses on synthetic datasets that expose hidden failure modes, addressing the shortcomings of 'vibe-heavy' training data. Additionally, @ADarmouni praises HardGen's specialized tool integration, noting how it allows smaller models like Qwen3-4B to outperform frontier models on benchmarks such as BFCLv3 by focusing on error-driven learning. In a complementary stride, the 'RoboPhD' architecture is pushing the boundaries of self-improving agents, particularly in specialized tasks like text-to-SQL. According to @rohanpaul_ai and corroborated by @agentcommunity_, RoboPhD evolves both tools and prompts through feedback loops, splitting tasks into non-AI code scripts to achieve significant gains in accuracy. This framework allows agents to adapt dynamically without retraining, a critical step for handling complex, data-intensive tasks. Industry sentiment on X, such as from @IntuitMachine, underscores the transformative yet challenging nature of such iterative deployment. These breakthroughs are further contextualized by updates in related research, such as the expanded 86-page DeepSeek-R1 paper, which details reinforcement learning reward rules for correctness, empowering the open-source community to craft high-reasoning agents @rohanpaul_ai. This update, also noted by @jenzhuscott, provides deeper insights into training methodologies that avoid synthetic data contamination. Together, HardGen and RoboPhD signal a shift towards autonomous, failure-informed learning, with experts like @omarsar0 emphasizing the need for robust context engineering to prevent errors in long-horizon tasks.
AMD's Ryzen AI Halo Powers 200B Parameter Models Locally
At CES 2026, AMD CEO Lisa Su projected a 100x surge in AI capacity, with a strong emphasis on local processing for agentic workloads as reported by @FTayAI. The Ryzen AI Halo is engineered to run 200-billion-parameter models directly on consumer-grade desktops, a development that could redefine the economics of agentic web deployment by prioritizing personal compute sovereignty, according to @PranavPW. Industry voices like @beffjezos suggest that efficient hardware scaling is key to winning the AI race. Builders see this as a game-changer for privacy-first, low-latency agents, with @agentcommunity_ noting its potential to bypass subscription models through hardware equipped with 128 GB DRAM. However, some express cautious optimism about real-world performance, with @BadalXAI pointing out that benchmarks for these 60 TOPS NPUs are still pending. A counter-take from @kautiousCo highlights market skepticism despite the long-term promise of decentralized agentic infrastructure as noted by @WesRothMoney.
MIT's Recursive Language Models Redefine Infinite Context
MIT's research on Recursive Language Models (RLMs) is poised to revolutionize how agents handle vast data, moving beyond the 'context rot' that degrades reasoning in large windows. RLMs allow models to recursively process inputs of over 10 million tokens using Python interfaces, as highlighted by @a1zhang and @omarsar0. This strategy enables LLMs to interact with massive datasets as if they were variables in a REPL, maintaining reasoning quality across unprecedented input sizes, according to @raphaelmansuy. This shift is critical for agent builders managing long-horizon tasks without memory overload, a step forward noted by @askalphaxiv. Enthusiasts like @shawnchauhan1 report RLMs achieving 58% accuracy on tasks where frontier models score near zero. However, @femke_plantinga warns that overloading agents with info can slow processing, advocating for smarter memory management. Practical hacks like offloading history to file loops are gaining traction as interim solutions, as suggested by @jerryjliu0. These diverse reactions underscore that while RLMs mark an advancement, effective orchestration remains key as noted by @lateinteraction.
LMArena Secures $150M to Standardize Agent Benchmarking
LMArena has raised $150M at a $1.7B valuation to expand its crowdsourced model-comparison platform, underscoring the growing importance of standardized benchmarking in the agentic web, per @rohanpaul_ai. This funding reflects a strong investor belief in the need for reliable rankings as agent builders optimize performance for specialized tasks. The platform's focus on vision and web development tasks positions it as a critical 'source of truth' for developers navigating frontier models and SLMs, as noted by @rohanpaul_ai. Many celebrate the funding as a milestone for Establishing standardized metrics that agent builders desperately need, according to @FTayAI. However, some question if LMArena will shift toward enterprise demands for tailored SLMs over broad comparisons. A counter-take suggests that topping benchmarks does not guarantee market adoption, pointing to a disconnect between performance metrics and real-world utility as observed by @rohanpaul_ai. This underscores the platform's pivotal yet evolving role in evaluating autonomous systems.
Quick Hits
Agent Frameworks & Orchestration
- Google releases Antigravity for building projects via natural language requirements and AI agents @freeCodeCamp
- New framework for agents with self-learning capabilities released by @tom_doerr
Tool Use & Logic
- Pandada AI turns CSVs into compliance-ready reports in 30 seconds without SQL @hasantoxr
- Warden moves the wallet paradigm toward 'agentic wallets' for autonomous performance @wardenprotocol
Models for Agents
- Anthropic's Opus 4.5 described as 'Level 4 self-driving for code' @beffjezos
- DeepSeek-R1 paper expansion reveals 3 training checkpoints for reasoning gains @rohanpaul_ai
Agentic Infrastructure
- vLLM achieves 16k TPS for DeepResearch workloads on NVIDIA Blackwell @MaziyarPanahi
- Fused RMS norm kernel in vLLM shows 40% speedups for specific tasks @marksaroufim
Reddit Dev Debates
From framework fatigue to durable execution, the agentic stack is finally getting professional.
The 'vibe-check' era of agent development is officially ending. As builders move past the initial excitement of autonomous loops, they are hitting a wall of reality: standard frameworks are often too opaque, and 'toy agents' die the moment a server blinks. Today’s synthesis highlights a decisive pivot toward what we're calling the Durable Agentic Stack. Developers are rejecting black-box abstractions in favor of low-level infrastructure that treats state as a first-class citizen—using tools like Temporal.io and LangGraph to ensure agents survive process restarts. We are also seeing the Model Context Protocol (MCP) mature, though a frustrating 'sampling gap' in popular clients like Cursor is preventing the full recursive reasoning the spec intended. Security is the other major friction point; as we experiment with 'root access' for agents, the community is split between the convenience of desktop-acting assistants and the terrifying prospect of prompt-injection-led system compromise. Whether it is n8n solidifying its role in 'Agentic SEO' or Unsloth slashing VRAM requirements by 7x, the theme is clear: we are moving from thin wrappers to hardened, kernel-level agentic engineering. This issue breaks down the tools and architectures making that transition possible.
The Great Durability Pivot: Temporal vs. LangGraph r/AI_Agents
Shipping agents into real-world workflows is revealing a massive gap between 'demo mode' and production reliability. u/Interesting_Ride2443 argues that most current agents are 'fragile loops' that lose state and burn tokens if a server restarts. The industry is rapidly shifting toward durable execution where the agent's state is persisted at every step. This transition is defined by a choice between infrastructure-level engines like Temporal.io, which provides event-sourced reliability for long-running tasks, and AI-native frameworks like LangGraph. While LangGraph offers specialized 'checkpointers' for agentic reasoning cycles, Temporal is being hailed as the 'hardened' choice for enterprise-grade reliability, ensuring that a step 10 failure doesn't require a full restart.
This 'framework fatigue' stems from the repetitive need to build the same 6 architectural pillars—UI, API orchestration, credit tracking, webhooks, security, and persistence. Developers like u/AdditionalWeb107 are increasingly rejecting 'black box' abstractions. Observability platforms like Helicone and specialized libraries like PydanticAI are now being used to manage per-user quotas and prevent catastrophic 3 AM logic loops that can lead to runaway API bills. @skirano notes that the goal is moving toward an 'Agentic Kernel' where security and persistence are handled at the system level rather than the application layer.
MCP Ecosystem: SSH Management and the 'Sampling' Gap r/mcp
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is maturing into a robust infrastructure layer, recently bolstered by the release of an SSH MCP Server that grants agents the ability to manage remote environments via SFTP and command execution. This follows the trend of high-stakes domain adapters, such as the Japanese e-Gov Law server and arXiv research tools, which move LLMs from simple chat boxes to active system administrators u/shaneholloman. However, a significant technical gap exists in client-side implementation.
Developers like u/shitmoji report that major clients including Claude Desktop and Cursor still lack comprehensive support for Sampling Elicitation. This feature, defined in the MCP 1.0 spec, allows a server to request a completion back from the LLM—enabling the tool itself to ask the model for reasoning during a task. While Anthropic's @alexalbert_ has confirmed this is a core part of the protocol's evolution, current production clients are largely limited to one-way tool calling, which prevents the complex, recursive agentic loops required for true autonomous delegation.
The Root Access Dilemma and Zero-Trust Agents r/LocalLLaMA
The launch of desktop-acting agents like Claude Cowork has sparked a heated debate regarding security and the 'least-privilege' principle. u/PerformanceFine1228 warns that giving agents full system access by default is a 'disaster waiting to happen,' as researchers like @wunderwuzzi23 have demonstrated that indirect prompt injection can force agents to exfiltrate sensitive files.
To mitigate these risks, developers are shifting toward 'Zero-Trust' agent architectures. A prominent example is BlueMouse, an offline-first MCP server highlighted by u/Creative-Ad-8234 that provides a parasitic logic layer. By keeping basic system interactions local and requiring explicit gates for 'send' or 'delete' actions, BlueMouse ensures that even if a 'cloud brain' is compromised, the agent cannot perform arbitrary code execution. Security experts like @rez0__ argue that until agents move from 'vibes-based' security to kernel-level execution gates, enterprise adoption will remain stalled due to the 90% risk increase associated with unmonitored tool-calling.
Atomized RAG and the n8n Orchestration Layer r/LLMDevs
A technical divide is hardening between 'Standard RAG' and 'Agentic RAG.' u/OnyxProyectoUno argues that agentic systems require 'Atomized Chunks'—data decomposed into the smallest possible functional units—to allow agents to interpret complex hooks and dependencies. This is particularly critical for codebase mapping, where traditional truncation often breaks the logical flow required for autonomous debugging.
Meanwhile, low-code platform n8n is solidifying its position as the preferred orchestration layer for "Agentic SEO" and specialized HR automation. u/Safe_Flounder_4690 demonstrated this by automating a pipeline that generates 1,000+ optimized pages without manual oversight. The platform's competitive edge lies in its self-hosting capability, which allows developers to bypass the "SaaS tax" and implement complex logic like Redis-backed persistent memory. According to community discussions, the shift toward the native AI Agent node is enabling builders to create reliable agents that solve specific business pain points rather than chasing chaos-prone autonomous models.
VRAM Wars and the 7x Efficiency Breakthrough r/LocalLLM
The demand for running large local models is driving a surge in high-end hardware configurations. u/EmPips reports a 'thirst for VRAM' that quickly outpaces consumer-grade cards, leading many to dual RTX 3090 or A100 40GB setups. On the software side, Unsloth AI has released a breakthrough implementation of GRPO (Group Relative Policy Optimization) that achieves a 7x memory reduction, enabling 380K token context training on a single 192GB GPU with zero accuracy loss r/LocalLLM discussion.
In the model landscape, Black Forest Labs' release of FLUX.2 [klein] achieves 0.8s inference on consumer-grade hardware, making it the 'sweet spot' for local VRAM usage in agentic workflows. In the LLM frontier, the rollout of GPT 5.2 has introduced a clear split between 'Instant' and 'Thinking' modes, with @rowancheung reporting a 40% improvement in complex logic when using the 'Thinking' variant. However, u/W_32_FRH observes that model quality often drifts following major outages, creating friction for autonomous development loops.
Discord Power Users
As Grok and Hawk reshuffle the leaderboards, the real performance gains are moving from model weights to agentic architecture.
Today’s agentic landscape is defined by a growing tension: the gap between raw model intelligence and the 'harness' we build around it. While new entrants like Grok 4.20 and the mysterious Hawk Ultra are shredding the LMSYS leaderboards, developers are discovering that the middleware—the IDEs, the RAG pipelines, and the system prompts—is often what holds them back. This 'harness tax' is real, and it’s forcing a pivot toward architectural sparsity. Whether it’s n8n v2 enabling horizontal scaling for long-horizon tasks or the adoption of the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to break infinite loops, the focus is shifting from 'bigger models' to 'better systems.' We’re seeing a professionalization of the stack, where Q8 precision on local hardware and structured 'immune responses' to hallucinations are becoming the baseline for production. In this issue, we dive into why your IDE might be making your models dumber, how local infrastructure is evolving to handle VRAM-hungry MoEs, and the emerging economic divide between sustainable routers and high-burn research indices. The age of the 'raw prompt' is over; the age of the agentic architect has arrived.
The 'Harness Gap': Frontier Models vs. IDE Constraints
The LLM hierarchy is undergoing a volatile shift as 'theta-hat'—widely identified by the community as Grok 4.20—briefly dominated the LMSYS Coding leaderboard with an estimated 1345 ELO, outstripping both GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet @lmsysorg. Parallel to this, the mysterious Hawk Ultra has emerged as a formidable 'dark horse,' with early testers like @AiBattle_ reporting a 15% higher success rate in one-shot React component generation. However, a 'harness gap' remains a significant concern. As @swyx and aghs highlight, these frontier models often exhibit 'nerfed' reasoning when accessed through third-party IDE extensions due to aggressive system prompt constraints.
This 'harness tax' is increasingly attributed to the heavy system prompts used to ground models in codebase context. aghs contends that GitHub Copilot’s implementation of frontier models is 'consistently dumber' because its restrictive instructions and background RAG processes consume the model's reasoning budget. When system prompts exceed 2,500 tokens, logic begins to degrade. This has led to a 30% higher failure rate for complex refactoring tasks in request-based IDEs like Cursor compared to raw API calls. Developers are now moving toward standalone tools like Claude Code, which bypasses the IDE harness entirely to access the model's raw reasoning.
Join the discussion: https://discord.gg/anthropic
n8n v2: Horizontal Scaling for Long-Horizon Agents
The release of n8n v2 marks a paradigm shift with the introduction of multi-main instance support, allowing for true horizontal scaling of the orchestration layer. parintele_damaskin describes the complexity unlocked by this distributed architecture as 'alien,' effectively removing the single-instance bottleneck for high-concurrency agentic tasks. This update enables high-availability deployments where multiple main nodes share the load, ensuring that long-running autonomous systems remain resilient even if a primary node fails.
To improve reliability, developers are adopting the 'subworkflow-as-a-service' pattern. As explored by oi.11, this prevents models from 'lying' or hallucinating completion by forcing data to return through a structured schema. For developers on the edge, n8n v2 remains remarkably efficient; local Docker-based deployments can run effectively with as little as 700MB of RAM. The new Task Runner system further allows n8n to handle complex Python-based logic without the enterprise overhead typically associated with heavy automation platforms.
Join the discussion: https://discord.gg/n8n
Architectural Sparsity: MCP and Structured Memory Patterns
To combat performance degradation in massive context windows, developers are pivoting toward structured memory patterns and task decomposition. As highlighted in the VS Code Unified Agent Experience, the industry is moving toward a subagent architecture where specialized agents handle granular tasks, preventing the primary context from becoming bloated. This is complemented by the Model Context Protocol (MCP), which enables 'Ask Human' tools to break infinite agentic loops.
According to @alexalbert__, MCP provides a standardized way for agents to interact with external state and human supervisors. Community members like blindestgoose are also emphasizing 'agentic memory' through auto-injected markdown docs—like .cursorrules—to maintain environmental constraints across branched conversations. This shift from raw token count to architectural sparsity allows agents to maintain project state over weeks rather than minutes.
Join the discussion: https://discord.gg/anthropic
Engineering Immune Responses to Hallucination
Moving agents from demo to production requires a shift from passive filtering to engineering robust 'immune responses.' file333 argues that bias and hallucinations should be treated as signals to be managed. This aligns with the rise of automated verification frameworks like DeepEval, which provide unit testing for LLM outputs to catch hallucinations before they reach production @deepeval. For complex bug identification, sokoliem_04019 recommends forcing models to add verbose logging across the entire codebase before attempting a fix.
Reliability also extends to deployment safety. abhijithneilabraham is exploring the safety of Ollama for on-prem batch processing using Datatune to ensure row-level intelligence and deterministic data handling. Building 'battle-ready' code now requires agentic actions to be verifiable against pre-defined golden datasets, especially in high-stakes sectors like finance where a single hallucination has significant ROI impact.
Join the discussion: https://discord.gg/ollama
VRAM Thirst and the Q8 Precision Standard
The local LLM community's 'thirst for VRAM' is pivoting toward a 'precision-first' approach. electroglyph is championing Q8 quantization as the gold standard for CPU-based inference, arguing it provides the most consistent reasoning. While Q4 quantization dominates in raw speed—averaging 32-45 tokens per second (t/s) on high-end consumer CPUs—the Q8 standard offers a superior perplexity-to-performance ratio, maintaining a stable 14-20 t/s for reasoning-heavy tasks.
Efficiency is being redefined by IBM's Granite 4.0-h-tiny, a Mixture of Experts (MoE) model that allows for high-quality reasoning without massive compute. However, MoE still demands significant VRAM to keep all 'experts' resident in memory to avoid the massive latency of disk-swapping. This has driven a secondary market for A100 40GB and RTX 3090 setups, where developers prioritize memory bandwidth to prevent the 'expert-swapping' bottlenecks that cause agentic workflows to time out.
Join the discussion: https://discord.gg/localllm
The Profitability Paradox: Routing vs. Retrieval
The economic divide between AI aggregators and search-centric platforms is widening. OpenRouter has emerged as a favorite for sustainable infrastructure, with itzcrazykns noting its low-overhead routing model is likely already profitable. Unlike labs fronting billions for training, OpenRouter functions as a lean broker, avoiding the 'imaginary money' traps of high-burn research firms. Conversely, the search-index business model, typified by Perplexity AI, faces mounting skepticism regarding its unit economics.
While Perplexity has scaled its revenue through its $40/month Max tier, the cost of maintaining a live search index remains a significant drain on VC-funded reserves. Industry observers point out that routing services like OpenRouter benefit from a 'token-based' incentive structure that scales linearly with usage. For developers, the choice is becoming pragmatic: opting for providers with clear margins over those relying on perpetual funding rounds to subsidize inference costs.
Join the discussion: https://discord.gg/ollama
HuggingFace Research Hub
From multi-week scientific workflows to pixel-perfect GUI navigation, the agentic stack is moving from brittle JSON to robust code-first execution.
Today’s agentic landscape is shifting from one-off tasks to sustained strategic intent. We are seeing a dual movement: on one hand, researchers are tackling ultra-long-horizon autonomy with architectures like Cognitive Accumulation, which allows agents to maintain state across 500-plus steps. On the other, the developer community is aggressively shedding the weight of monolithic frameworks in favor of smol libraries that prioritize code-as-action over complex JSON schemas. This isn't just a trend; it is a fundamental maturation of the stack. Whether it is the Model Context Protocol (MCP) becoming the USB-C for tool interoperability or new Vision-Language Models (VLMs) optimized for Apple Silicon, the focus has moved toward reliability and latency. We are moving away from agents that hallucinate buttons and toward systems that can see pixels and think before they call a function. For builders, the message is clear: the future of agents is lightweight, code-centric, and capable of holding a thought for longer than a single API call. In this issue, we dive into the frameworks and benchmarks defining this new era of autonomous engineering.
Solving Ultra-Long-Horizon Autonomy in Science
The research paper Toward Ultra-Long-Horizon Agentic Science addresses the 'contextual drift' that typically causes AI agents to fail during multi-week experimental cycles. To solve this, the authors introduce the Cognitive Accumulation framework, which replaces simple memory buffers with a three-tier architecture: a Memory Stream for raw execution logs, a Cognitive State module that maintains high-level abstractions of progress, and an Action Engine that applies corrective logic. This structure allows agents to manage tasks spanning over 500 steps without losing strategic coherence. In practical evaluations, agents utilizing Cognitive Accumulation demonstrated a 2.4x improvement in success rates on the MLE-bench (Machine Learning Engineering Benchmark) compared to standard RAG-based architectures. Industry observers like @_akhaliq highlight that this framework enables agents to sustain 'strategic intent' across long-duration workflows, moving beyond isolated task execution toward true autonomous engineering.
The 'Code-First' Revolution in Agentic Orchestration
The Hugging Face Agents Course has ignited a massive wave of community interest, with the First_agent_template now surpassing 850 likes, reflecting a rapid adoption of the smolagents library. This library champions a 'code-as-action' paradigm, where the model writes raw Python code rather than generating complex JSON strings. @aymeric_roucher notes that this approach is significantly more robust for handling loops and error logic, as LLMs are natively better at writing code than following brittle JSON schemas. Unlike the heavy abstractions of LangChain, smolagents is designed to be extremely lightweight, often requiring less than 1,000 lines of total library code, which drastically reduces latency and simplifies the debugging process. Industry experts like @mervenoyann highlight that this shift effectively lowers the entry barrier for developers, moving the focus from managing framework-specific state machines to refining the agent's core execution logic.
From Pixels to Actions: The Rise of Reinforcement Learning in GUI Automation
The development of GUI agents is accelerating with a cluster of new research including GUI-Gym and ShowUI. These works mark a shift from simple API-based interaction to direct visual navigation. GUI-Gym specifically addresses the training bottleneck by providing a high-performance environment that supports 100+ FPS for reinforcement learning, allowing agents to learn from millions of interactions. This is a critical shift, as traditional LLM-based web agents often struggle with the 72.3% human baseline on OSWorld, where state-of-the-art models like GPT-4o initially scored only 12-15% @_akhaliq. To bridge this gap, ShowUI introduces a 'one-step' visual-to-action paradigm, treating the screen as a continuous coordinate space to predict click points directly from pixels, significantly reducing the 'hallucination of non-existent buttons' by grounding actions in visual context rather than text-based DOM descriptions.
The 'USB-C' of AI: MCP Standardizes Tool Interoperability
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is rapidly becoming the universal connector of the agentic web, as demonstrated by projects in the Agents-MCP-Hackathon/ecom_agent. This initiative highlights how MCP servers bridge the gap between LLMs and transactional services, enabling autonomous e-commerce navigation and structured data retrieval from external APIs. On the edge-computing front, the srswti/bodega-sharinganvlm-9b-mxfp4 model highlights the shift toward locally-hosted, tool-capable intelligence. Optimized with 4-bit quantization specifically for Apple Silicon, this model integrates native MCP support, allowing it to discover and interact with local tools without custom glue code. This synergy between the smolagents library's new MCP client and optimized VLM models like Sharingan is effectively slashing the latency and integration tax associated with cloud-based agentic orchestration.
Thinking-First Reward Models and Micro-Executors
Fine-tuning for tool use is entering a 'thinking-first' phase with the release of mradermacher/ToolRM-Gen-Qwen3-4B-Thinking. This reward model leverages the THUDM/ToolPref-Pairwise-30K dataset to evaluate and improve internal reasoning steps that precede tool execution. By rewarding trajectories that lead to successful multi-step function calls, these models effectively reduce the 'hallucination gap' in complex workflows. This is mirrored by the trend toward extreme efficiency in executors like Yaongi/HybriKo-117M-Exp6-FunctionCall, which demonstrates that even a 117M parameter architecture can be optimized for high-accuracy function calling, marking a shift toward a tiered architecture where small, specialized models handle high-frequency tool interaction.
Open-Source Deep Research: From Scholarly Papers to Codebases
The landscape of autonomous research is expanding through community-driven Spaces that prioritize transparent tool-use over black-box proprietary systems. miromind-ai exemplifies this by utilizing a multi-step planning loop powered by the Tavily Search API and DuckDuckGo for real-time web retrieval. Similarly, pdx97 focuses on the academic vertical, leveraging the Semantic Scholar API to automate literature reviews and synthesize scientific papers into structured reports. Beyond text, the cast42 Space demonstrates a specialized 'Deep Research' pattern for developers, using vector indexing to allow natural language queries across entire codebases, effectively democratizing the ability to extract deep insights from massive, unstructured datasets.