The Agentic Reliability Revolution
Developers are ditching brittle JSON for code-executing subagents and local-first hardware clusters.
-
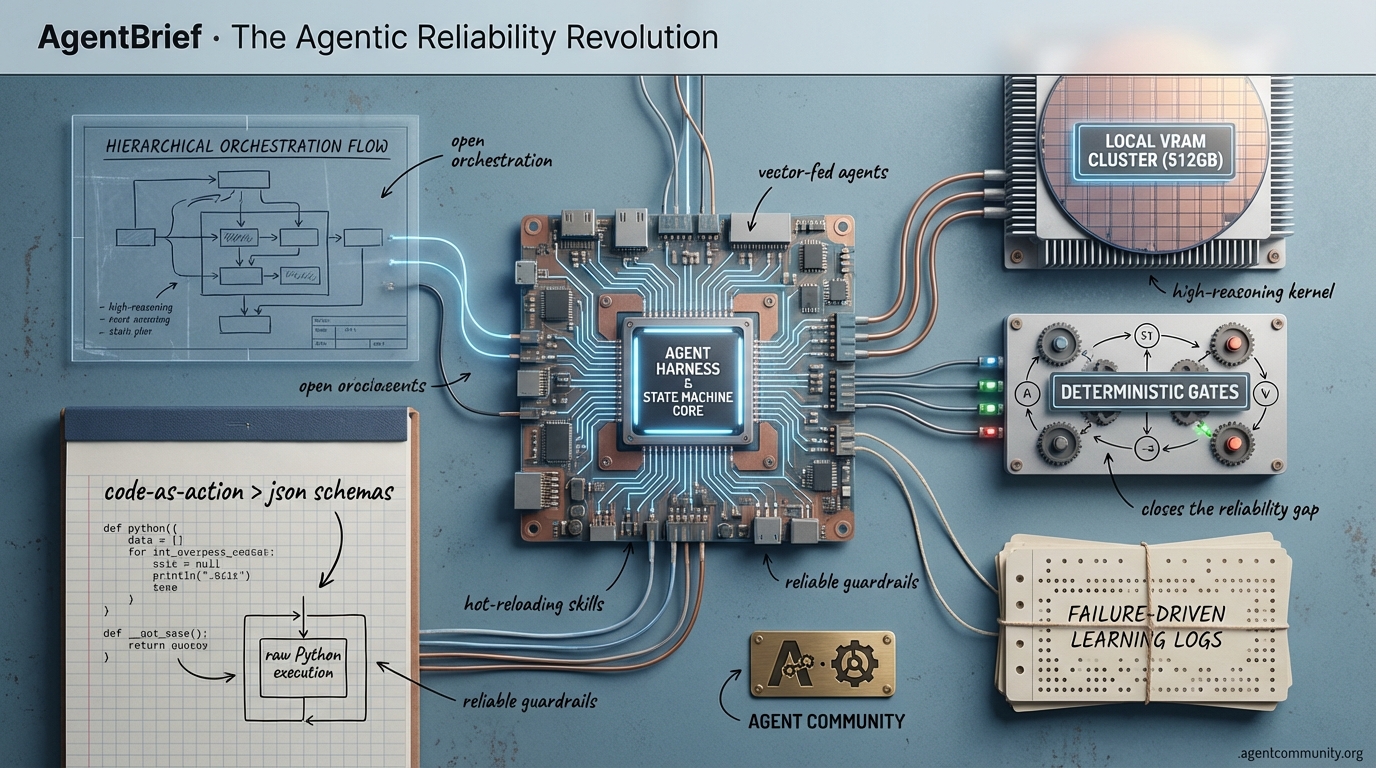
- Code-as-Action Dominance The industry is pivoting from fragile JSON schemas to raw Python execution, with frameworks like smolagents delivering massive gains in reasoning and tool-use reliability.
-
- The VRAM Arms Race Building production-grade agents now requires substantial local compute, with practitioners moving toward 512GB Mac Studios and custom AMD MI50 clusters to support high-reasoning kernels.
-
- Hierarchical Agent Frameworks We are moving beyond single-agent prompts into complex ecosystems where tools like Claude Code and MCP allow autonomous subagents to manage technical debt and complex orchestration loops.
-
- Deterministic State Machines To close the 'Reliability Gap,' builders are implementing finite state machines and 'Deterministic Gates' to ensure agents remain within operational guardrails rather than relying on open-ended chat prompts.
X Intel & Local Labs
Stop chasing context windows and start building local-first recursive agent environments.
The transition from prompt engineering to agentic orchestration is no longer a theoretical shift—it is the reality of the 2026 stack. We are moving away from the fragile 'chat-with-a-PDF' era into a world of robust agent harnesses where the IDE becomes an autonomous command center. As we see with the rise of tools like Claude Code and the MIT research into Recursive Language Models, the focus has shifted from the size of the model to the sophistication of the environment it inhabits. For those of us building the agentic web, the 'vibe coding' trend isn't just about speed; it's about reducing the friction between intent and execution through hot-reloading skills and local 200B parameter inference. We are entering a phase where agents don't just follow instructions—they learn from their own tool-use failures and manage their own memory via recursive loops. This issue explores how local hardware breakthroughs like AMD's Ryzen AI Halo are finally making sovereign, low-latency agents a production reality, while frameworks like HardGen are proving that smaller, smarter models can out-reason the giants when trained on the right signals. It's time to stop building chatbots and start building ecosystems.
The Rise of Agent Harnesses and Hot-Reloading Skills
The era of agent harnesses has officially arrived, transforming AI development from basic chat interfaces to advanced orchestration layers that empower developers to create highly customized environments. As previously noted by @omarsar0, developers are 'vibe coding' their own versions of tools like Cursor using Claude Code and MCP-powered Kanban boards for task management. This shift is gaining significant traction, with @aakashgupta describing agent harnesses as a 'full development team inside an IDE,' capable of managing prompt presets, human-in-the-loop tool calls, and direct filesystem access for long-running tasks. A standout feature accelerating this evolution is automatic skill hot-reloading, which allows new agent capabilities to be integrated instantly without session restarts, a productivity boost confirmed by @NickADobos and further emphasized in the latest Claude Code 2.1.0 update by @bcherny, noting specific support for hot-reload and custom agent integration with zero setup. Building on this momentum, platforms like VibeCode are providing safe sandboxes for developers to build professional mobile and web applications using Claude Code, complete with API integrations and custom command creation, as highlighted by @rileybrown. The community is also contributing to open-source alternatives, with @jarrodwatts open-sourcing a comprehensive Claude Code configuration repository that includes agents, commands, hooks, rules, skills, and plugins. While Claude Code excels with features like skill hot-reloading, as noted by @hotwire09 with a new library boasting 100+ pre-made agents, OpenCode offers greater flexibility for developers seeking less fragility, as argued by @ScriptedAlchemy. This dynamic landscape suggests that while Claude Code remains a leader in developer experience, OpenCode's open standards are fostering a growing user base, pushing the boundaries of agent harness frameworks in 2026.
Recursive Language Models and MemRL Redefine Infinite Context
As the AI industry pivots from the race for larger context windows to innovative architectures, MIT's Recursive Language Models (RLMs) are emerging as a groundbreaking solution to the 'context rot' problem. RLMs employ a novel inference-time strategy that treats input prompts as variables in an external Python REPL environment, allowing the model to programmatically decompose and recursively process data snippets of over 10 million tokens without memory overload @a1zhang. This architecture achieves 20-30% higher accuracy at ~30% lower cost compared to traditional long-context LLMs, as noted by @innoworkspro. However, challenges persist, with @BoWang87 cautioning that high information density can still pose architectural issues for frontier models. On the memory enhancement front, MemRL offers a framework that allows agents with frozen LLMs to improve post-deployment by selectively reusing episodic memories tied to successful task outcomes @rohanpaul_ai. This approach creates a self-improving loop without the need for expensive retraining, addressing issues like catastrophic forgetting, as highlighted by @dair_ai. While specific performance benchmarks for MemRL in agentic tasks are emerging, its ability to enhance problem-solving through runtime reinforcement learning has been praised @JagersbergKnut. Rounding out the agentic memory evolution, practical hacks involve offloading history to file systems, allowing agents to loop through data using file-system tools instead of overloading context windows @jerryjliu0. Together, these innovations signal a shift toward smarter, more sustainable memory management for the next generation of autonomous systems.
Local 200B Parameter Execution and Compute Surges with Ryzen AI Halo
The infrastructure supporting agentic systems is experiencing a groundbreaking shift towards local compute capabilities. At CES 2026, AMD's CEO Lisa Su forecasted a staggering 100x surge in AI compute capacity over the next five years, a vision echoed by industry observers who stress the urgent need for hardware scaling @rohanpaul_ai. The Ryzen AI Halo platform, highlighted by @FTayAI, is central to this transformation, designed to run 200 billion parameter models locally on consumer-grade hardware. This platform boasts 128 GB of unified high-bandwidth memory, enabling powerful local inference with 60 TOPS NPU performance, potentially redefining agent economics by eliminating cloud dependencies and reducing latency @agentcommunity_. On the software front, the 'Chronicals' framework, as noted by @rohanpaul_ai, accelerates LLM fine-tuning by 3.51x on A100 GPUs through optimized data handling. While specific benchmarks comparing Ryzen AI Halo’s local inference against cloud-based solutions remain limited, posts on X suggest that local compute could offer significant advantages in privacy and low-latency for agent tasks, with AMD’s hardware providing a viable path to sovereign agents @BradWardFight. However, skepticism persists regarding real-world performance, with @BadalXAI urging caution until comprehensive benchmarks for these high-TOPS NPUs are available. The synergy of powerful local hardware and optimized software frameworks points to a future where agents operate with greater autonomy, independent of centralized data centers.
vLLM Achieves Record 19K TPS on NVIDIA Blackwell for Agentic Workloads
The landscape of real-time agent inference is undergoing a dramatic transformation with NVIDIA's Blackwell architecture pushing the boundaries of performance. Recent reports from @MaziyarPanahi highlight that vLLM has shattered previous benchmarks by achieving up to 19,000 tokens per second (TPS) on Blackwell B200 GPUs, surpassing the earlier reported 16,000 TPS mark. This performance is particularly impactful for high-throughput agentic workloads such as medical dataset generation, as noted by @MaziyarPanahi, who observed consistent TPS fluctuations between 18,000 and 20,000 over extended runs. Complementing this hardware leap, software optimizations like the 'Oink!' kernel deliver a 40% speedup over existing implementations, according to @marksaroufim, further enhancing inference efficiency for agent builders requiring rapid response times. However, some voices urge caution; while the raw performance is undeniable, @BadalXAI emphasizes that real-world benchmarks for sustained workloads are still pending. These insights underscore that while vLLM on Blackwell sets a new standard, scaling this power to the broader agentic community remains a critical hurdle for 2026.
HardGen Framework: Revolutionizing Agent Training with Failure-Driven Learning
The 'HardGen' framework is redefining how agentic systems are trained by emphasizing learning from tool-use failures rather than relying solely on perfect demonstrations. As detailed by @rohanpaul_ai, HardGen transforms errors into critical training data, enabling a 4B parameter Small Language Model (SLM) to rival much larger frontier models on complex benchmarks like BFCLv3, a claim reinforced by @ADarmouni. This failure-informed approach specifically targets hidden traps in API interactions and incorrect tool selections, areas often overlooked in standard synthetic datasets, according to @agentcommunity_. While the HardGen framework garners optimism, it is not without challenges. @IntuitMachine cautions about the long-term control and ethical considerations of iterative learning from mistakes, suggesting that unchecked failure loops could introduce unforeseen behaviors. A counter-take from @christian_tail argues that while SLMs excel in specific scenarios, they may still struggle with complex orchestration compared to larger models, indicating that success might be context-dependent. These varied perspectives underscore the need for a balanced approach to agent training, blending failure-informed learning with robust oversight.
Healthcare and Finance Agents Accelerate Toward Production in 2026
The evolution of AI agents from generic chatbots to specialized vertical solutions is accelerating in healthcare and finance. In healthcare, recent deployments are capable of analyzing years of clinical data to detect cognitive concerns, with small models matching the performance of GPT-4o on critical benchmarks, as noted by @rohanpaul_ai. This aligns with reports from @omooretweets on specialized healthcare agent capabilities, while @FTayAI adds that 60% of US adults are already using AI for insurance navigation. In the finance sector, vertical AI agents are automating intricate processes with remarkable efficiency. @hasantoxr introduced Pandada AI, a tool that transforms messy CSVs into compliance-ready executive reports in 30 seconds, showcasing the power of specialized orchestration. This is complemented by innovations like virtual financial advisors highlighted by @AITECHio. However, @aakashgupta cautions that vertical agent startups must integrate unique data feeds to differentiate from broader coding agents, suggesting a competitive challenge ahead for builders in 2026.
Google's Antigravity Platform Redefines Agentic Development
Google's Antigravity platform is revolutionizing the developer experience by enabling seamless collaboration between developers and AI agents through agentic prompting. This tool, highlighted by @freeCodeCamp, allows developers to define projects in natural language, persisting data and managing tasks like reminders within applications. Insights from @GoogleCloudTech reveal that Antigravity integrates with Gemini 3 and AI Studio, offering a workflow that transitions from cloud prototyping to local IDE environments via the Agent Manager. This aligns with Google's broader push for autonomous operations, as noted by @kevinhou22, who emphasizes its use of Gemini 3 Pro for terminal and browser-based tasks. Community reactions provide a mix of enthusiasm and critical perspectives; @ai_for_success praises the collaborative experience, but concerns about integration persist. @sytelus questioned the necessity of switching IDEs to fully leverage Antigravity's capabilities, while @JulianGoldieSEO advocates for sandboxed environments to mitigate risks associated with terminal commands in such collaborative setups.
Quick Hits
Agent Frameworks & Orchestration
- Google's Antigravity lets you work with agents to build projects from requirements, as highlighted by @freeCodeCamp.
- The Swarms framework is recommended for complex agent coordination tasks by @KyeGomezB.
- OpenCode provides a model-agnostic alternative for users facing geographic blocks, per @Rasmic.
Tool Use & Engineering
- RoboPhD uses LLMs to self-improve text-to-SQL capabilities by evolving tools and prompts based on feedback, notes @rohanpaul_ai.
- Gemini can now power intelligent software testing toolkits to detect UI anomalies via natural language, reports @GoogleCloudTech.
Models & Infrastructure
- DeepSeek-R1’s training paper was expanded to 86 pages, adding detail on its 3-checkpoint RL setup, per @rohanpaul_ai.
- Cerebras Chocolate is described as a 'thick' hardware advancement in AI compute by @dylan522p.
- Microsoft's new data center proposal in Michigan has been revealed, according to @CNBC.
Reddit Reliability Check
Developers are ditching 'vibes-based' loops for deterministic state machines as the reliability gap hits home.
The gap between CEO-level optimism and engineer-level debugging has become the defining story of the agentic web. While Anthropic’s Dario Amodei suggests AI could handle the bulk of software engineering within a year, practitioners on the ground are wrestling with a persistent 'Reliability Gap.' We are moving past the 'just prompt it' phase and into a high-stakes engineering era where the bottleneck has shifted from raw reasoning to data hygiene and orchestration logic. This issue explores how the community is hardening the agentic stack. From the rise of the Model Context Protocol (MCP) as a universal driver to the adoption of 'Deterministic Gates' and Finite State Machines, builders are realizing that agents work best when they are treated as workers within a rigid framework, rather than open-ended managers. We also dive into the hardware arms race, where 512GB Mac Studios are becoming the new baseline for local high-reasoning kernels. The agentic web isn't just about models anymore; it's about the infrastructure that keeps them from hallucinating in production. Let's get into the technicals.
The Great Disconnect: Agent Hype vs. Production Reality r/AI_Agents
The tension between corporate optimism and engineering reality has reached a boiling point. While Anthropic’s Dario Amodei suggested that AI could handle the bulk of software engineering within 6-12 months @darioamodei, production data reveals a persistent 'Reliability Gap.' On the SWE-bench Verified benchmark, top-tier models still struggle to surpass 50% accuracy on real-world GitHub issues, far below the 90%+ reliability required for autonomous deployment. Practitioners like u/ugon report that agents frequently fail at basic state-tracking in live environments, leading to what experts call the 'Long-Tail of Agentic Failure,' where the final 20% of edge cases consume 80% of development time @karpathy.
The bottleneck has shifted from raw reasoning to 'Data Hygiene.' As u/According-Site9848 notes, project stalls are rarely due to model intelligence but rather messy data silos and unstructured indexing, which cause RAG-based agents to hallucinate even with perfect logic. This is corroborated by recent industry reports indicating that while 75% of enterprises have agentic pilots, only 12% have reached full production scale. Current observability stacks remain 'passive,' providing failure alerts but no automated recovery paths, leaving developers trapped in manual debugging loops, as observed by u/OneTurnover3432.
MCP Becomes the Agentic Software Primitive r/OpenAI
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is rapidly evolving from a niche integration detail into a standard primitive for the agentic web. u/Bogong_Moth describes MCP-native apps as a new 'default interface,' where applications act as a 'universal driver' for LLM reasoning @alexalbert__. This shift is supported by new developer utilities like murl, a curl-like CLI for MCP servers built by u/turlockmike, which allows for deterministic testing of remote toolsets without a full agentic loop.
Efficiency remains a primary friction point as tool counts grow. u/dinkinflika0 highlights how exposing hundreds of tool definitions can cause token usage to explode, often consuming 30-40% of the context window. Their 'Code Mode' approach reportedly cuts token usage by 50% by allowing the LLM to write a script that executes multiple tool calls locally. To further combat bloat, developers are adopting 'Hierarchical MCP' structures. As noted by @skirano, 'Router Servers' that only expose top-level capabilities until requested can reduce initial handshake tokens by up to 80%, ensuring agents remain responsive even when connected to massive enterprise data lakes.
Claude Code Dominates as Gemini CLI Challenges the 'Token Tax' r/claude
Claude Code and the Opus 4.5 model continue to set the bar for agentic coding, with users reporting 'eureka moments' where the model identifies architectural flaws before they are even coded. Developers like u/karun012 are reporting successful full-app builds, but the ecosystem is diversifying. Google's Gemini CLI is gaining traction by offering a 2-million token context window, allowing it to ingest entire repositories without the aggressive context-thinning that sometimes plagues Claude-based sessions.
Cost remains a significant friction point for high-end agent IDEs. A recent alert from u/puppabite warned that the MiniMax Agent IDE consumed 10,000 credits in just 3 hours for basic refactoring, highlighting the 'runaway loop' risks inherent in autonomous systems. This has accelerated the shift toward 'local-first' agents. u/tammamtech has popularized a method for running Claude Code with GLM-4.7 Flash via llama.cpp, providing a 90% cost reduction while maintaining high success rates in structured data extraction.
Deterministic Gates: The Rise of Pivot Protocols and FSM Leashes r/AI_Agents
To combat the unpredictability of LLMs, developers are returning to deterministic orchestration patterns, moving away from 'vibes-based' loops. u/cloudairyhq has introduced the Pivot Protocol, which replaces standard retry logic with a strategy switch that forces agents to change tactics upon failure. Early benchmarks suggest this approach can reduce 'stuck' loops by 45% by breaking the repetition cycle.
This is complemented by a 'State Machine Leash,' a pattern advocated by u/AgentsOfAI to ensure business logic remains deterministic. Safety and control are being formalized through libraries like Faramesh, released by u/Trick-Position-5101, which provides one-line wrappers to prevent agents from executing high-risk commands without human approval. As noted by @skirano, the goal is to shift orchestration from 'LLM-as-the-manager' to 'LLM-as-the-worker' within a rigid framework.
Local Power: Qwen3-Coder and the 512GB Unified Memory Frontier r/LocalLLaMA
The hardware requirements for local agentic workflows are hitting a theoretical ceiling. u/BitXorBit reports that running Qwen3-Coder-480B on a Mac Studio M3 Ultra with 512GB of Unified Memory yields a usable 2.4 tokens per second, effectively bringing Opus-level reasoning to a local desktop. While this lags behind enterprise clusters, @tech_benchmarks notes the 90% reduction in power consumption makes it the gold standard for private kernels.
For mid-tier deployments, the 'VRAM vs. Speed' debate is intensifying. u/m31317015 highlights that a 3x RTX 3090 setup remains superior for long-context agentic loops compared to dual 4080 Supers. Efficiency gains are also appearing in the 30B class; GLM-4.7-Flash has surpassed 124,000 downloads on Hugging Face, with @llm_optimist noting its 350ms TTFT makes it ideal for real-time tool-calling.
Legal Agents Struggle with Messy PDFs: The Rise of OCR-Native RAG r/ArtificialInteligence
Specialized agents in the legal sector are hitting a 'data ceiling' when processing historical archives. u/DangerousBedroom8413 highlights that standard RAG pipelines frequently hallucinate on scanned court records where low-quality OCR fails. As noted by @vince_ai, 'OCR is the silent killer of legal RAG,' often requiring multi-stage extraction to prevent a 30-40% drop in precision.
Retrieval failures persist even in modern local stacks. u/Haya-xxx reports that semantic search often misses nuanced legal relationships. To combat this, the industry is pivoting toward hybrid search architectures—combining BM25 keyword matching with vector similarity. The focus has shifted toward 'high-fidelity' extraction that can handle the complex table structures typical of legal filings, eliminating the 'garbage-in' problem at the ingestion layer.
Discord Dev Dispatches
Subagents are spawning within Claude Code while developers build 256GB VRAM clusters to keep up.
The era of the 'single agent' is effectively over. We are moving into a recursive reality where agents are now managers, spawning subagents to handle the technical debt they themselves create. Today’s lead story on Claude Code’s 'Composer 1' subagents highlights this shift: we aren't just prompting anymore; we are orchestrating hierarchies. But this complexity comes with a 'harness tax.' Between token buffers that won't clear and the desperate need for massive VRAM—exemplified by the $880 AMD MI50 'budget' clusters—the infrastructure is struggling to keep pace with the software's ambition. Meanwhile, the 'Uncanny Valley' in voice is being bridged not just by faster models like ElevenLabs V3, but by the intentional injection of background noise. It is a fascinating paradox: to make agents more reliable, we are adding noise; to make them smarter, we are adding layers. Whether you are debugging GLM 4.7 templates in Ollama or benchmarking ModernBERT, the message is clear: the Agentic Web is getting noisier, heavier, and far more sophisticated. Let’s dive in.
Claude Code Spawns Autonomous Subagents; Context 'Autocompact' Struggles to Clear 77k Token Buffers
Developers are identifying a shift toward hierarchical autonomy within the Claude ecosystem, with the CLI tool now capable of spawning 'Composer 1' subagents to manage segmented refactoring tasks. As reported by eden881, these subagents are triggered automatically during high-complexity logic flows, effectively acting as worker nodes to prevent primary context pollution. However, this orchestration layer introduces significant overhead; users like chintz.eth report that even after clearing history, persistent memory buffers remain at 22% to 38.5% (approximately 77.0k tokens), scaling rapidly to 65% during subagent handoffs.
To mitigate this, practitioners are leveraging the newly discovered 'autocompact' routine, which uses recursive self-calls to compress architectural state. While @alexalbert__ confirms that these features are part of the 'long-horizon' roadmap, @swyx warns that the 'harness tax' of managing multiple subagents can lead to reasoning drift if the compacting logic thins out critical dependencies in large-scale builds. This aligns with official documentation regarding sub-context management, which suggests that the agent's internal 'scratchpad' is now a primary bottleneck for project-wide autonomy.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/cursor
GLM 4.7 Flash Faces Ollama Template Issues
The technical rollout of GLM 4.7 Flash has encountered friction due to Jinja-to-Go template translation errors within Ollama. theyruinedelise identified that the Q8_0 quants yield inconsistent results compared to raw llama.cpp implementations, a discrepancy traced to how Ollama's Go-based engine handles complex Jinja2 logic. To stabilize output, starsupernova has popularized a Modelfile 'one-liner' that manually overrides the system by setting the RENDERER and PARSER to 'glm-4.7'. This fix is critical for maintaining structured reasoning, as @unslothai previously noted that incorrect gating weights in early GGUF quants could lead to infinite repetition loops.
Simultaneously, the edge-AI community is pivoting toward specialized audio agents with the release of LiquidAI's LFM2-Audio-1.5B. pwnosaurusrex confirmed its successful integration into llama.cpp, highlighting its efficiency for audio-to-audio tasks that require low-latency agentic processing. Meanwhile, Qwen 2.5 remains the 'gold standard' for local coding; outlandishmink reports that the 14B variant offers the best performance-to-VRAM ratio for generating complex PyTorch scripts. This is supported by benchmarks from @vllm_project, which show the Qwen 2.5 family achieving a 92% success rate in structured JSON intent generation.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/ollama
Structured Output and Secure Scaling: The New n8n Production Standard
Reliably extracting structured data remains a primary friction point in agentic automation. While n8n has introduced a 'Structured Output' toggle in its AI Agent nodes, practitioners like oi.11 and @jan_oberhauser emphasize that this often requires a secondary Output Parser node or strict JSON Schema enforcement to guarantee valid responses. Without these deterministic guardrails, agents frequently default to 'agentic sycophancy,' hallucinating successful data extraction to satisfy the prompt. To achieve 99.9% reliability, developers are shifting toward 'neuro-symbolic' workflows where the LLM proposes a structure that is immediately validated by a code-based schema checker.
Security for scaled agent fleets is also evolving toward decentralized credential management. queryqueryquitecontrary_57153 highlights the necessity of using Postgres with PGCrypt and SSL to store and inject dynamic credentials at runtime. Furthermore, for teams operating in sensitive regions, local PII redaction has become a prerequisite. Microsoft Presidio, when paired with spaCy's specialized models for Russian and Turkish, provides a high-performance, local-first solution for data masking, ensuring compliance with local regulations like KVKK and GDPR without the latency of cloud-based API calls.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/n8n
The Latency War: Retell AI and ElevenLabs V3 Redefine Multilingual Voice
In the battle for production-grade voice agents, the focus is shifting from simple speech synthesis to low-latency orchestration. odin7m advocates for Retell AI in high-stakes environments, citing its superior handling of conversational fillers and sub-800ms end-to-end latency. While Retell provides the full 'harness' for turn-taking, ElevenLabs V3 has emerged as the dominant 'black box' for raw TTS, with parintele_damaskin noting its ability to scale to 2.4k outbound calls daily via WebSockets.
According to @elevenlabsio, the V3 Turbo model offers a 30% reduction in latency for Spanish and Italian, finally matching English-language performance levels. However, the 'human-likeness' gap is narrowing. Developers are increasingly using Vapi.ai as a middle-tier orchestrator to combine ElevenLabs' emotional prosody with custom LLM logic. As noted by @vapi_ai, the key to bypassing the 'uncanny valley' in non-English languages isn't just the voice, but the injection of 'ambient realism' via layered white noise to mask digital artifacts.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/n8n
The 256GB VRAM Budget King: AMD MI50 Clusters and the NPU Support Gap
The 'poor man's VRAM' meta has shifted toward massive AMD MI50 clusters, where developers like TrentBot are leveraging 8x GPU arrays to secure 256GB of HBM2 VRAM for roughly $880. Recent benchmarks demonstrate these legacy clusters can achieve 26.8 tok/s on MiniMax-M2.1 and 15.6 tok/s on GLM 4.7. However, software friction persists; as @ROCm_Expert notes, the Vega 20 architecture requires specific ROCm v5.7 or v6.1 patches to maintain stability in vLLM environments without performance degradation.
On the ultra-portable front, Tiiny AI has unveiled the AI Pocket Lab featuring a 12-core ARM CPU and an integrated NPU. Community feedback from jimmyate highlights that Ollama still lacks native NPU orchestration for many ARM-based chips, forcing users to rely on Vulkan-based offloading which can incur a 20-30% performance penalty. Despite this, the push for local autonomy is driving a new wave of Unified Memory Access (UMA) optimizations to better leverage shared RAM on these compact agentic nodes.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/ollama
ModernBERT and EmbeddingGemma: The New Efficiency Frontier in Retrieval
In the search for more efficient RAG pipelines, developers are benchmarking new embedding models against established favorites. electroglyph reported that ModernBERT-base and EmbeddingGemma are significantly outperforming Nomic's v1.5 MoE model in technical retrieval tasks. This is corroborated by MTEB leaderboard data where ModernBERT-base (149M params) achieves state-of-the-art performance for its size @answerdotai.
For local RAG, nicholas_the_furious vouches for EmbeddingGemma's performance on a 40k example retrieval benchmark. While llama.cpp is the standard for generative inference, community experts like @Nils_Reimers suggest that 'sentence-transformers' remains faster and more ergonomic for managing embedding models, offering superior throughput for batch processing. Developers are increasingly moving toward these models—with ModernBERT-small weighing in at just 22MB—to handle 'hard negatives' in specialized datasets.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/localllm
HuggingFace Open Research
Hugging Face’s smolagents and the Model Context Protocol are killing brittle JSON schemas in favor of raw code execution.
We are witnessing a fundamental architectural shift in how agents operate. For the last year, developers have been forcing LLMs to output structured JSON to trigger tools—a method that is increasingly seen as a brittle relic of the 'chatbot' era. Today’s issue highlights the rise of the 'code-as-action' paradigm, championed by Hugging Face’s smolagents. By allowing agents to write and execute raw Python, we are seeing massive performance gains on benchmarks like GAIA, because Python inherently handles logic loops and error recovery better than any static schema ever could. This isn't just a theoretical win; the performance delta is nearly 20% over traditional methods. But it’s not just about the code; it’s about the plumbing. The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is rapidly becoming the universal connector, allowing these 'tiny agents' to interact with local environments and desktop tools with minimal friction. From ServiceNow’s 'hindsight reasoning' to open-source Deep Research loops that outperform proprietary giants, the trend is clear: we are moving away from monolithic, black-box assistants toward modular, verifiable, and highly specialized autonomous workers. If you are still building agents by parsing strings, today’s stories are your signal to refactor for the Agentic Web.
Hugging Face’s smolagents: The 1,000-Line Framework Outperforming Heavyweight Orchestrators
Hugging Face has disrupted the agentic landscape with smolagents, a minimalist library of under 1,000 lines of code that prioritizes a 'code-as-action' paradigm. By allowing models to write and execute raw Python rather than parsing brittle JSON schemas, the framework enables agents to handle complex logic like loops and error recovery with significantly higher reliability. This approach is empirically validated by Hugging Face results on the GAIA benchmark, where the CodeAgent architecture achieved a state-of-the-art 53.3% on the validation set. As noted by @aymeric_roucher, this represents a definitive pivot toward raw Python as the superior language for planning and error recovery.
The performance delta is significant: while traditional JSON-based orchestration frameworks have historically struggled to maintain accuracy on multi-step reasoning, smolagents demonstrates a ~15-20% performance lead over standard prompt-based tool-calling agents on the GAIA validation set. The ecosystem's reach is further extended through multimodal support, enabling agents to 'see' by processing visual inputs through Vision-Language Models (VLMs). For developers seeking production-grade reliability, the Arize Phoenix integration provides a robust observability layer, which @arizeai describes as essential for tracing nested tool calls and Python code execution in real-time.
MCP Protocol Powers the Next Generation of Tiny Agents
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) has rapidly transitioned from a niche standard to the 'USB-C for AI,' effectively slashing the 'integration tax' for developers. New implementations like Tiny Agents in Python demonstrate that fully functional, tool-capable agents can be built in as little as 70 lines of code, following a minimalist 50-line proof-of-concept in Tiny Agents. This modularity allows developers to decouple tool logic from model logic, enabling a single MCP server to support multiple frameworks simultaneously.
As noted by @aymeric_roucher, this approach is significantly more robust than traditional JSON-based tool calling because it treats tools as standardized, reusable servers rather than brittle, model-specific schemas. To manage the complexity of these interactions, the community has introduced tools like the Gradio Agent Inspector, which provides real-time visualization of protocol-compliant tool calls. However, local execution via MCP introduces specific security considerations. Since MCP servers often run as local processes via stdio or SSE, experts like @mervenoyann emphasize that transparency and debuggability are paramount. While the protocol itself provides a secure transport layer, the 'code-as-action' paradigm requires robust sandboxing—especially when agents are granted filesystem or shell access.
Open Source Deep Research: Scaling Autonomous Fact-Checking
The 'Deep Research' movement is shifting toward open-source transparency with the Open-source DeepResearch project, providing a code-first alternative to proprietary, black-box research assistants. Built on the smolagents library, the architecture utilizes a recursive reasoning loop—Plan, Search, Read, and Review—enabling agents to execute hundreds of concurrent search queries for synthesizing comprehensive reports. This method significantly mitigates hallucinations; as @aymeric_roucher notes, the 'code-as-action' paradigm allows agents to handle complex loops more reliably than JSON schemas.
Community-led implementations like MiroMind-Open-Source-Deep-Research are already demonstrating these capabilities in action, integrating the Tavily Search API and DuckDuckGo for real-time retrieval. Experts such as @mervenoyann emphasize that moving these workflows into the open domain not only reduces reliance on closed APIs—potentially cutting costs by over 50% for complex tasks—but also makes the agent's planning fully visible and debuggable.
Beyond the Browser: ScreenSuite and Holo1 Standardize Cross-OS Computer Use
The frontier of computer-use agents is rapidly shifting from brittle web-scraping to full-stack desktop automation, anchored by the release of ScreenEnv and the ScreenSuite evaluation framework. Spanning 3,500+ tasks across 9 domains, ScreenSuite has identified inference latency and fine-grained coordinate precision as the primary bottlenecks preventing agents from achieving human-like fluid control. To address these gaps, Smol2Operator introduces post-training techniques that optimize models for tactical GUI execution.
On the model side, the Hcompany/Holo1 family of 4.5B parameter VLMs is setting a new state-of-the-art with a 62.4% success rate on the ScreenSpot subset, significantly outperforming GPT-4V's 55.4%. As noted by @_akhaliq, these local, specialized models are increasingly capable of challenging proprietary APIs by prioritizing tactical execution over general-purpose reasoning. This collective push toward standardized sandboxes aims to solve the 'environment drift' problem and provide a verifiable path toward autonomous digital workers.
Strategic Distillation and Test-Time Scaling Unlock High-Performance Reasoning
The push for high-fidelity reasoning in compact footprints is accelerating through specialized distillation and inference-time scaling techniques. ServiceNow AI has introduced Apriel-H1, an 8B parameter model that achieves performance parity with Llama 3.1 70B on complex agentic benchmarks. According to @ServiceNow, the breakthrough stems from 'Hindsight Reasoning,' a distillation method where the model learns to refine its planning by analyzing past execution errors.
Simultaneously, the frontier of verifiable logic is expanding via test-time scaling. AI-MO has released Kimina-Prover, a formal reasoning model that applies test-time RL search to solve intricate mathematical proofs within the Lean system. As noted by @_akhaliq, this approach allows models to scale compute during inference to explore and verify logical paths, effectively 'thinking longer' to ensure accuracy. These developments are critical for deploying autonomous agents in resource-constrained environments where hallucination is not an option.
DABStep and FutureBench Set New Evaluation Standards for Multi-Step Autonomy
As agents transition from conversationalists to autonomous executors, evaluation frameworks are shifting toward complex, long-horizon behavior. Hugging Face has introduced DABStep, a Data Agent Benchmark that moves beyond single-turn tasks to evaluate multi-step reasoning workflows. While GAIA focuses on general tool-use, DABStep specifically targets data science tasks and identifies critical failure modes such as 'plan-act' misalignment, a phenomenon where agents fail to follow their own generated logic during execution.
Pushing the boundaries of temporal reasoning, FutureBench evaluates agents on their ability to forecast future events, measuring prediction accuracy through Brier Scores. For industrial applications, IBM Research has launched AssetOpsBench to bridge the gap between academic benchmarks and industrial reality. This framework evaluates how agents handle real-world operational tasks, providing a necessary quantification of reliability for autonomous systems in high-stakes environments, a development highlighted by @_akhaliq as a key step toward long-horizon autonomy.