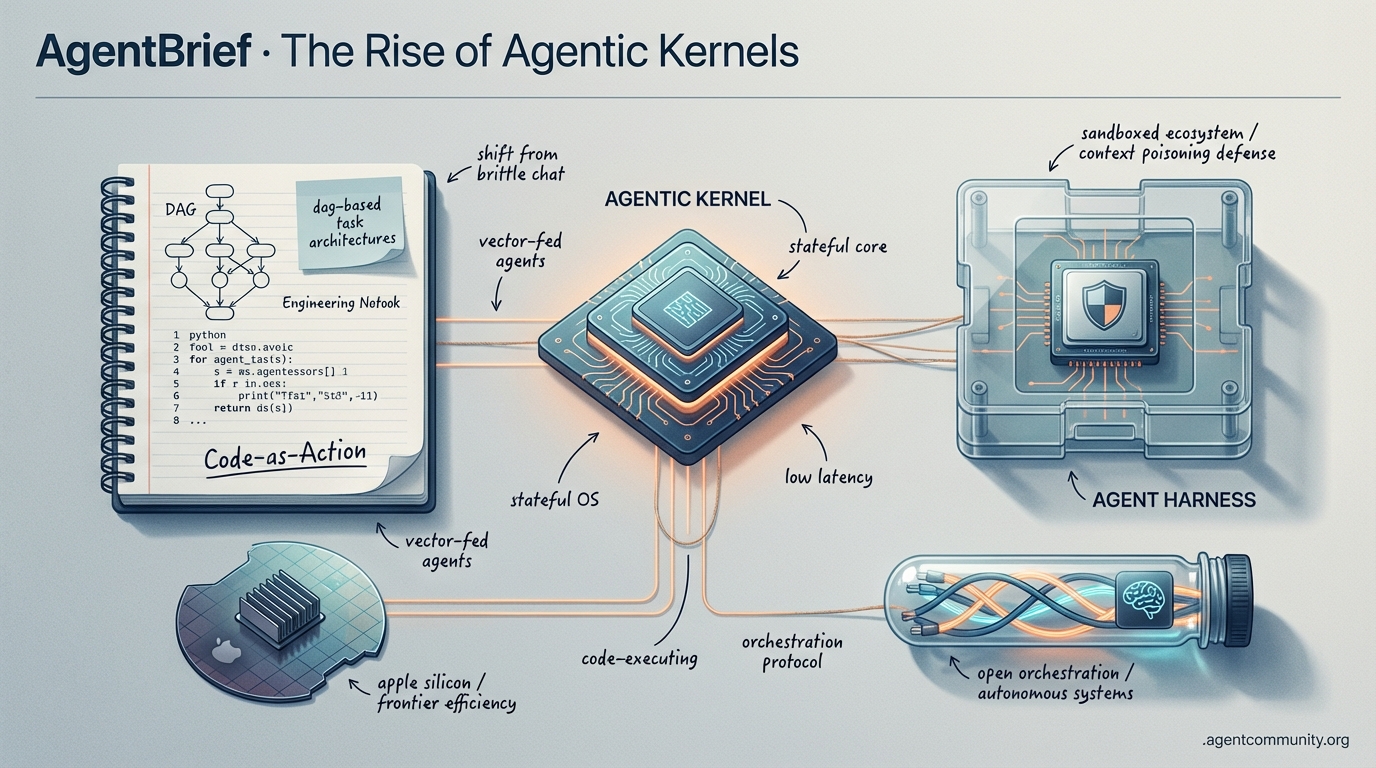
The Rise of Agentic Kernels
The industry is shifting from brittle chat interfaces to stateful, code-executing agent environments.
-
- From Chat to Kernels The paradigm is shifting from simple ReAct loops to "agentic kernels" and DAG-based task architectures, treating agents as stateful operating systems rather than conversational bots.
-
- Code-as-Action Dominance New frameworks like smolagents and Transformers Agents 2.0 are proving that agents writing raw Python outperform traditional JSON-based tool calls, significantly raising the bar for autonomous reasoning.
-
- Environment Engineering Builders are focusing on "agent harnesses" and sandboxed ecosystems to mitigate context poisoning and manage hierarchical orchestration within complex, real-world repositories.
-
- Hardware and Efficiency As DeepSeek slashes frontier reasoning costs and local-first developers lean on Apple Silicon’s unified memory, the infrastructure for low-latency, autonomous systems is finally maturing.
The X Intelligence Loop
Stop building chatbots and start building environments where agents actually ship.
We are witnessing the death of the 'chat box' as the primary interface for AI. For agent builders, the frontier has shifted from prompt engineering to environment engineering. We’re moving into the age of the 'agent harness'—structured, sandboxed ecosystems like Claude Code where agents don't just suggest code; they live in it. This isn't just about better models; it's about better scaffolding. Whether it's HardGen training models to learn from their own tool-use failures or AMD pushing 200B parameter models to the edge, the infrastructure for true autonomy is finally here. If you're still relying on naive ReAct loops, you're building for 2024. Today's winners are building persistent memory systems and self-correcting logic that evolves during runtime. In this issue, we dive into the rise of MCP-driven autonomy and the hardware shifts making local, low-latency agents a reality. It’s time to stop talking to AI and start orchestrating it. The agentic web isn't coming; it's being compiled right now.
Claude Code and the Rise of the Agent Harness
The developer ecosystem is undergoing a profound shift from raw chat interfaces to sophisticated 'agent harnesses' that provide structured environments for autonomous operation. As @omarsar0 noted, the era of the harness has arrived, empowering developers to craft custom environments akin to Cursor or specialized Claude Code plugins. This transformation is fueled by tools like VibeCode, which @rileybrown describes as a way to gamify coding through sandboxed environments where agents autonomously develop skills. The latest Claude Code updates take this further with automatic skill hot-reloads, allowing agents to evolve capabilities on the fly without session restarts, a feature highlighted by @NickADobos.
Developers are increasingly leveraging the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to push Claude Code beyond traditional coding into broader automation. @meta_alchemist emphasizes that connecting via MCPs is a key strategy for enhancing agent functionality. For instance, @rileybrown showcased this potential by creating a 'Nano Banana' skill, allowing an agent to autonomously manage public images via API gateways. This turns Claude Code into a comprehensive development team within an IDE with full filesystem access, as @aakashgupta describes. While @shteremberg suggests that agents can sometimes bypass formal MCP setups by generating interfaces directly, @GTrushevskiy notes that MCPs effectively turn Claude into an 'AI operating system' for orchestrating entire workflows.
HardGen and MemRL: Engineering the Self-Correcting Agent
New research is addressing the fragility of agentic workflows by shifting from simplistic tool loops to sophisticated learning frameworks. @jerryjliu0 advocates for offloading long context to file system loops, urging builders to move beyond the 'naive ReAct' model. The 'HardGen' framework is a breakthrough here, with @rohanpaul_ai describing how it trains 4B-parameter models to rival larger systems by learning from tool-use failures. @ADarmouni confirms its effectiveness, noting it outperforms frontier models on benchmarks like BFCLv3 by targeting hidden error modes.
Significant advancements in memory persistence are also arriving via MemRL. As detailed by @rohanpaul_ai, MemRL empowers agents to selectively reuse episodic memories of success, improving performance without retraining. This addresses catastrophic forgetting, a benefit emphasized by @dair_ai, while @VentureBeat underscores its separation of stable reasoning from dynamic memory. Recent benchmarks from @Atulkumarzz reveal MemRL hitting a 93.05% score on LoCoMo and 83.00% on LongMemEval-S. While @christian_tail warns that small models still face orchestration hurdles, the runtime reinforcement learning praised by @JagersbergKnut represents a paradigm shift toward truly adaptive agents.
DeepSeek-R1 Paper Expands with RL Training Insights
The DeepSeek-R1 paper has expanded to 86 pages, offering an unprecedented look into the reinforcement learning (RL) methodologies behind advanced reasoning models, as highlighted by @rohanpaul_ai. This update provides a roadmap for builders aiming to replicate 'reasoning-first' agents in open-source settings, with @agentcommunity_ echoing the immense value of this documentation for local development.
Further insights from @rohanpaul_ai emphasize how pure RL with answer-only rewards can cultivate genuine reasoning without human step-by-step traces. However, @jenzhuscott stresses that the real challenge remains scaling these insights to diverse agentic tasks while avoiding synthetic data contamination.
LMArena Secures $150M to Standardize Agent Benchmarking
LMArena has secured $150M in Series A funding at a $1.7B valuation, as announced by @lmarena.ai. This funding, supported by @istoica05, aims to provide the independent, transparent evaluation frameworks necessary for builders to trust autonomous systems.
With over 35 million users, the platform is becoming a 'source of truth' for model performance, a sentiment reinforced by @GrowthLists. However, @ml_angelopoulos notes that the focus must remain on real-world utility as the industry shifts toward Small Language Models (SLMs) for specific agentic sub-tasks.
AMD's CES 2026 Vision: 200B Parameter Models on the Edge
AMD CEO Lisa Su unveiled the Ryzen AI Halo platform, designed to run 200-billion-parameter models locally on consumer-grade hardware, as reported by @FTayAI. This move toward edge compute is essential for private, low-latency agent workloads, a point reinforced by @AMDRyzen.
While @FractalFactor notes that 128 GB of unified memory will revolutionize multi-agent orchestration, @BadalXAI urges caution until we see real-world benchmarks for the 60 TOPS NPUs. Nevertheless, @bwjbuild argues that this architecture could finally eliminate the latency issues inherent in cloud-based agents.
Nvidia Blackwell and vLLM Smash Records with 19K TPS
Nvidia’s Blackwell B200 GPUs, optimized with vLLM, have achieved an unprecedented 19,000 tokens per second (TPS), as highlighted by @MaziyarPanahi. This massive throughput supports roughly 350 requests per second, making it the new gold standard for high-concurrency agentic workloads and deep research, according to @MaziyarPanahi.
Software optimizations like the 'Oink!' kernel are delivering 40% speedups to vLLM operations, as noted by @marksaroufim. Despite this, @BadalXAI emphasizes that sustained production benchmarks are still needed to confirm these gains for diverse agentic use cases.
Quick Hits
Agent Frameworks & Orchestration
- Google releases 'Antigravity' for building projects via agentic prompting @freeCodeCamp
- Warden Protocol debuts 'agentic wallets' for autonomous MFA and transactions @wardenprotocol
- Swarms framework moves into high-stakes predictive market use cases @KyeGomezB
Tool Use & Function Calling
- RoboPhD framework enables LLMs to self-evolve text-to-SQL capabilities @rohanpaul_ai
- Pandada AI automates financial compliance from CSVs in <30 seconds @hasantoxr
Models for Agents
- Opus 4.5 hailed as 'Level 4 self-driving for code' by early testers @beffjezos
- Recursive Language Models from MIT may solve 'context rot' for 10M+ tokens @IntuitMachine
- Hunyuan3D 3.1 lets agents generate rigged 3D models from 2D images @deedydas
Agentic Infrastructure
- Nvidia requires full upfront payment for Chinese H200 shipments due to regulation @Reuters
- Cloudflare serverless stack recommended for low-cost persistent agent backends @freeCodeCamp
Reddit's Technical Deep-Dive
Anthropic moves to DAG-based tasks while DeepSeek slashes frontier reasoning costs by 10x.
We are witnessing the death of the 'chatbot' and the birth of the 'Agentic Kernel.' Anthropic’s pivot from simple 'Todos' to a DAG-based 'Tasks' architecture signals a fundamental shift: agents are no longer just conversational interfaces; they are becoming stateful operating systems. This transition is messy. We are seeing 'state drift' in distributed workflows and a 90% increase in attack surfaces via indirect prompt injections. Yet, the ecosystem is hardening. From 'digital shields' like Hipocap to DeepSeek V3.2’s staggering efficiency—matching GPT-5 reasoning levels at 10x lower costs—the infrastructure for autonomous systems is maturing at a breakneck pace. For builders, the message is clear: the model is just the engine, but the kernel—the persistent state, the security gates, and the observability layer—is where the real value is being built. Today’s issue dives into the hardware required to run these beasts locally, the protocols securing them, and why the 'long-tail' of agentic failure still requires a Minimum Viable World Model to solve.
Claude Code Transitions to Dependency-Aware Tasks r/ClaudeAI
Anthropic has formalized the 'Agentic Kernel' by replacing the legacy 'Todos' system in Claude Code with a sophisticated 'Tasks' architecture. This system utilizes a directed acyclic graph (DAG) to manage explicit dependencies, allowing Claude to execute multi-step operations with a structured understanding of cause-and-effect u/BuildwithVignesh. These tasks are persisted locally, facilitating shared state across sessions but introducing new synchronization hurdles. Experts like @skirano argue that this shift moves Claude from a simple executor to a stateful orchestrator capable of managing long-horizon developer workflows. Simultaneously, the 'Cowork' research preview has expanded Claude's reach to direct desktop and file system manipulation r/claude discussion. However, technical friction persists; early testers report that 'code restore' features frequently break when sub-agents modify the file system outside the primary agent's context u/Flamesilver_0. This 'state drift' remains a critical bottleneck, as current sandboxes lack the granular zero-trust execution gates required to prevent sub-agents from creating 'agentic technical debt' during complex refactors, a risk highlighted by security researchers like @wunderwuzzi23.
DeepSeek V3.2 and the Efficiency Revolution r/LocalLLaMA
The open-source landscape has reached a parity inflection point with the release of DeepSeek-V3.2, which utilizes Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) to match GPT-5 reasoning levels at 10x lower operational costs ($0.028/million tokens) @DeepSeek_AI. As noted by u/EchoOfOppenheimer, the Chinese lab achieved this frontier performance with a training budget of only $5.5M. The architecture's 'Sparse Attention' is powered by MLA's ability to compress the KV cache by a factor of 4-5x, paired with an auxiliary-loss-free Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) that activates only 37B of its 671B parameters per token, effectively avoiding the routing collapse that plagues standard MoE designs @bindureddy. This efficiency is being further optimized for local devices via REAP 2.5 pruning on models like GLM-4.7-Flash u/ilzrvch, though researchers like @maximelabonne caution against potential 'knowledge lobotomies' during aggressive compression.
Custom MCP Servers and Digital Shields Redefine Utility r/mcp
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) ecosystem is maturing as developers move from generic wrappers to specialized, high-performance servers. A new alternative Jira MCP server u/Open_Variation1438 addresses context exhaustion, while a Google Sheets server u/Fresh-Cheetah8945 now provides 27 distinct tools. Observability is also being integrated directly via langfuse-mcp u/gabrielknight1410, enabling agents to perform 'self-debugging' by querying their own traces, acting as a 'universal driver' for LLM reasoning @alexalbert__. However, security remains a massive concern. Researchers have demonstrated that agents can be manipulated via hidden prompts in emails u/ConsiderationDry7581, leading to unauthorized tool execution. To counter these indirect prompt injections, the community is developing 'digital shields' like Hipocap and Faramesh u/Trick-Position-5101, providing human-in-the-loop wrappers to mitigate the 90% increase in attack surface created by autonomous agents @skirano.
The Reliability Ceiling: Why Frontier Models Still Loop r/aiagents
A recent architectural evaluation shared by u/404NotAFish reveals a 'Model Upgrade Paradox': simply swapping in stronger reasoning kernels does not resolve fundamental agentic failure modes. In long-horizon task benchmarks, frontier models still exhibit a 40-60% failure rate due to 'hypothesis commitment errors,' where agents lock into incorrect paths and enter loops. This confirms observations by @karpathy that the 'long-tail' of edge cases consumes 80% of development time. Builders are responding with hardened failover infrastructure like the Bifrost project, which routes around provider outages in under 50ms u/dinkinflika0. The consensus is shifting toward the necessity of a 'Minimum Viable World Model' u/mynameisyahiabakour—a persistent state layer that provides just-in-time context to ground reasoning and prevent logic drift.
Workstation Builds Reach 160GB VRAM Peak r/LocalLLaMA
Practitioners are pushing consumer hardware to the edge to support local agentic workflows. u/sloptimizer showcased a quiet Threadripper build featuring 768GB DDR5 and 160GB VRAM by combining an RTX 5090 with four R9700 GPUs, requiring dual power supplies to handle the compute load. While the RTX 5090 is expected to offer a 32GB VRAM floor, early leaks suggest a 600W TDP, making high-density multi-GPU setups a significant thermal challenge @kopite7kimi. For enterprise-grade silicon on a budget, NVIDIA Grace Hopper GH200 superchips are appearing for under $15,000 u/fairydreaming, though finding compatible MGX-standard baseboards remains a 'prohibitive hurdle' @RyanShrout. The trend toward local compute is accelerating as OpenAI CFO Sarah Friar hints at 'outcome-based pricing' u/distalx, which could increase the cost of iterative debugging by 5-10x by charging for successful completions rather than tokens.
n8n Multi-Agent Marketing Orchestrators Emerge r/n8n
Low-code platform n8n is evolving from simple linear chains to complex multi-agent systems. u/emrahdemirkoc is architecting a 'Multi-Agent Marketing Orchestrator' that splits tasks between specialized Researcher and Copywriter agents using n8n’s new AI Agent node. This modularity is bolstered by n8n Data Tables, which practitioners are using as a 'Memory MVP' to store structured state externally, effectively creating a durable kernel that survives workflow crashes u/Specialist-Ad-241. However, as utility scales, users are hitting a 'Pricing Wall.' u/General_Maize_7636 argues that n8n's execution-based model is less efficient for high-volume tasks than Gumloop, which utilizes a usage-based credit system better suited for agents performing thousands of web-scraping micro-steps.
Discord Dev Discussions
As Claude Code and Cursor push the limits of hierarchical autonomy, developers are battling context poisoning and a global RAM shortage.
Today’s issue marks a pivot point in the Agentic Web: the transition from the single-agent paradigm to complex, hierarchical orchestration. We are seeing tools like Claude Code and Cursor move beyond simple completions to spawning sub-agents that manage discrete logic modules. This architecture is a direct response to the context poisoning that occurs when massive repositories overwhelm even the largest context windows. But this autonomy isn't free. Between the harness tax of increased token usage and the aggressive history compacting that can thin out architectural dependencies, practitioners are discovering that managing a fleet of agents requires a new kind of engineering discipline. Meanwhile, the infrastructure supporting these agents is under pressure. Local-first developers are hitting context walls on models like GLM-4.7, while the hardware market faces an HBM3e shortage that is making Apple Silicon’s unified memory look like the most viable path for high-bandwidth local AI. From the maturity of the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to the precision of Qwen 3 VL in document logic, the tools are ready. The challenge now is orchestrating them without crashing the engine or the budget.
Hierarchical Orchestration: How Claude Code’s Sub-agents Defeat Context Poisoning
Developers are increasingly adopting hierarchical autonomy within Claude Code, utilizing a sophisticated orchestrator-sub-agent pattern to maintain logic density across massive repositories. As documented by sweattypalms, the CLI tool spawns 'Composer' sub-agents to summarize discrete modules, returning only high-level structured data to the primary agent. This mechanism prevents the 200k context window from being 'poisoned' by redundant boilerplate, enabling 'flawless' planning on projects that would otherwise exceed token limits. Anthropic's @alexalbert__ has signaled that these autonomous worker nodes are central to the tool's long-horizon capabilities, though they contribute to the 'harness tax' of increased token consumption during handoffs. However, state management remains a primary friction point for power users. The 'compacting chat' feature, which uses recursive self-calls to compress history, is being criticized for summarizing too aggressively; vixi_vs reports that critical architectural dependencies can be 'thinned out' during active refactoring. Furthermore, while the $100/mo and $200/mo Pro tiers provide the high-volume quotas needed for these agentic loops, developers like @swyx note that the community is pivoting from wanting more messages to demanding direct context window expansions to 500k+ tokens to avoid the reasoning drift associated with aggressive compacting.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/anthropic
Cursor Scales to 14 Sub-agents Amidst 'Auto Mode' Billing Debate
Cursor is pushing the boundaries of multi-agent orchestration, with reports from avincor showing users managing up to 14 concurrent sub-agents for large-scale refactors. This mirrors the hierarchical autonomy recently seen in Claude Code but operates within a more integrated IDE environment. However, this power comes at a steep price; codex1609 and other power users highlight that 'auto' mode is frequently billed at $6 per million tokens, reflecting the high 'thinking' overhead required to maintain state across multiple files. This pricing has led to comparisons with Anthropic's 'harness tax,' as developers weigh the cost of autonomous planning against raw token efficiency. Stability remains a friction point as the platform evolves. The latest 2.4.21 release has triggered reports of crashes specifically when the agent attempts to generate .md plan files in 'plan mode,' a feature designed to provide a 'scratchpad' for complex logic. While the team at Anysphere continues to optimize these 'high thinking' models, developers are finding that Cursor's UI-driven orchestration is often more context-heavy than the terminal-based 'autocompact' routines found in Claude Code, leading to faster token depletion during project-wide edits.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/cursor
New Tooling Bridges Remote MCP Server Gaps as OAuth Friction Mounts
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) ecosystem is maturing with the release of murl, a 'curl-like' CLI tool for interacting with remote MCP servers. Developed by turlockmike, it allows developers to inspect and debug MCP server resources, prompts, and tools via a standard terminal interface, effectively acting as a diagnostic layer for the 'agentic harness.' This complements the expansion of local-first clients like the mcp-client-for-ollama, which enables Ollama-based models to invoke the same standardized tools as Claude. Meanwhile, containerization remains a priority for maintaining tool consistency; coding_a_app highlighted a setup using MCP-GATEWAY in Docker to bridge tools across Cursor and VS Code, reducing the 30-minute setup time typically required for multi-IDE sync. Despite this growth, OAuth stability for MCP servers has become a critical pain point as Anthropic tightens security boundaries. Developers report that previously working OAuth flows for Google Drive and Slack MCP servers have begun failing with redirect URI mismatches following recent Claude Desktop updates. As noted by @mcp_dev, these 'silent breaking changes' occur when the host application modifies how it handles tool-initiated browser redirects. To combat this, the community is shifting toward standardized Docker-based auth proxies that handle credential rotation outside the primary agent context, ensuring 99.9% uptime for authenticated tool loops.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/anthropic
Qwen 3 VL and DeepSeek-VL2 Shatter the Proprietary OCR Ceiling
The 'agentic vision' gap is closing as local models transition from descriptive imagery to high-precision document logic. While practitioners like sv.agi note that cloud giants like Gemini 1.5 Pro still 'suck' at the deterministic rigors of structured OCR, Qwen 3 VL has emerged as the new benchmark leader in the 8B-parameter class. According to recent technical evaluations, Qwen 3 VL achieves a 94.8% accuracy rate on complex form extraction, significantly outperforming GPT-4o in multi-column ledger parsing. This shift is driven by its native support for dynamic resolution, allowing the model to 'zoom' into micro-text without losing global context @alibabacloud. DeepSeek-VL2 is providing the primary counterweight, leveraging a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture to maintain efficiency during high-resolution scans. Developers are increasingly utilizing the DeepSeek-OCR-WebUI to bypass the 'vibecoding' failures of probability-based inference. As @deepseek_ai highlights, the integration of spatial coordinate tokens allows these models to return text with pixel-perfect bounding boxes, a prerequisite for the autonomous navigation of legacy enterprise software. For production fleets, the recommendation is shifting: use Qwen for surgical precision in structured forms and DeepSeek for high-throughput batch processing of messy, non-standardized documents.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/ollama
Ollama Leverages MLX for Local Diffusion as GLM-4.7 Hits the 128k Context Wall
Ollama is aggressively expanding its local-first capabilities by integrating the MLX backend for high-speed image generation on macOS, effectively enabling local diffusion workflows that rival cloud performance. While Apple Silicon users benefit from this first-class integration, the community remains in a holding pattern for equivalent Vulkan or NPU optimizations on AMD and Intel hardware. A critical bottleneck has emerged with the rollout of GLM-4.7-Flash; users like maternion report massive memory spikes up to 123.4 GiB when attempting to utilize the full 128k context window on models that theoretically require only 32GB of VRAM. These spikes frequently trigger 'Internal Server Errors' during the offloading process, exposing the current limits of Ollama's Go-based memory management. To bypass these 'context walls,' developers are pivoting to optimized GGUF releases from Unsloth, which @unslothai claims are 1.5x faster due to recent llama.cpp gating fixes. Current best practices for stability on consumer GPUs involve manually capping context to 32k and using the Modelfile 'one-liner' popularized by starsupernova to force the correct renderer and parser settings for the GLM-4.7 architecture.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/ollama
Batching Strategies and V2 Task Runners: Solving n8n’s Memory Wall
Practitioners building production agents in n8n are hitting wall-clock and memory limits when processing multi-page documents. aiautomationfirstclient_27667 reports that 12-14 page invoices frequently trigger 4k token output overflows, while 45k row datasets cause terminal memory crashes. To bypass these 'harness' boundaries, developers are adopting a 4-page sliding window batching strategy, extracting structured JSON at each step to maintain context. @jan_oberhauser has confirmed that the v2 Task Runner is the architectural fix for these high-concurrency loops, providing the isolation needed for 99.9% system reliability. However, the v2 transition is plagued by 'prototype mutation' errors—a security guardrail in the new runner that prevents sandbox escapes. akindeleisrael_ notes that libraries like docxtemplater fail unless they are explicitly injected into the runner's environment. According to n8n community documentation, successful scaling now requires configuring the N8N_TASKS_RUNNER_EXTERNAL_SOURCES variable to map local node_modules, ensuring that agentic nodes can resolve dependencies without crashing the primary orchestration engine.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/n8n
RAM Price Apocalypse Favors Apple Silicon as HBM3e Shortages Bite
A 'RAM Apocalypse' is fundamentally shifting the economics of local AI. As manufacturers like SK Hynix and Micron report that HBM3e production is sold out through 2025 to satisfy data center demand for Nvidia's Blackwell architecture, the resulting capacity crunch is spilling over into consumer markets. kerunix highlights that skyrocketing DDR5 prices have made the 'Apple Premium' almost non-existent, with the Mac Mini M4 Pro—boasting 273 GB/s memory bandwidth—becoming a highly competitive option for scaling out 64GB+ AI workloads. As manufacturers prioritize high-margin HBM, consumer RAM prices have surged, making 32GB upgrades cost as much as 300€ in some regions. In the GPU market, the 'owning vs. renting' debate is intensifying. While 24GB GPU rentals are available for $60/mo, users like bigstormai argue that local hardware like dual Blackwell (RTX 5090) setups pay for themselves within 2 months through API credit savings. However, the 'software edge' gap remains a significant hurdle. Although Intel's IPEX-LLM benchmarks show the Arc A770 (16GB) can efficiently run Llama-3-8B, many developers stick to Nvidia despite a 40% higher price tag to avoid the 'trainwreck' of unoptimized drivers and to leverage the maturity of the CUDA ecosystem.
Join the discussion: discord.gg/anthropic
HuggingFace Open-Source Pulse
Hugging Face’s new frameworks prove raw Python beats brittle JSON for real-world autonomy.
We are witnessing the end of the 'JSON era' for AI agents. For the past year, we’ve forced models to communicate with tools via brittle schemas—a chat-centric compromise that often broke under the pressure of multi-step reasoning. Today, the shift toward 'code-as-action' is official. With Hugging Face’s release of smolagents and Transformers Agents 2.0, the industry is pivoting to a paradigm where agents write and execute raw Python to navigate the world. This isn't just a developer preference; it’s a performance necessity. The 53.3% score on GAIA proves that execution-centric logic handles the 'integration tax' far better than structured strings ever could. But the evolution doesn't stop at the terminal. We’re seeing this same drive for precision move into GUI interaction with local VLMs like Holo1 and into the physical world via NVIDIA’s Cosmos architecture. The common thread? Agents are being given the tools to act directly on their environment—whether that’s a sandbox, a browser, or a robotic arm. For builders, the message is clear: the most capable agents aren't just talking; they're coding, clicking, and grasping. This issue explores the frameworks, benchmarks, and physical platforms making this transition possible.
Code-as-Action: The Death of Brittle JSON Schemas
Hugging Face is fundamentally shifting the agentic landscape toward a 'code-as-action' paradigm with the release of smolagents and Transformers Agents 2.0. Unlike traditional frameworks that rely on brittle JSON-based tool calling—which often fails during multi-step reasoning—these libraries allow agents to write and execute raw Python. This approach is empirically superior, as demonstrated by the CodeAgent achieving a state-of-the-art 53.3% on the GAIA benchmark Hugging Face. Experts like @aymeric_roucher note that while JSON is 'chat-centric,' code is 'execution-centric,' enabling agents to handle complex logic loops and self-correct execution errors without hitting token limits or schema hallucinations.
In production, this shift introduces a trade-off between reasoning depth and execution latency. While JSON tool-calling is faster for single-turn API interactions, code-writing agents reduce the 'integration tax' by managing their own logic, though they require secure sandboxing environments to mitigate security risks @mervenoyann. To bridge the observability gap, the Arize Phoenix integration now enables developers to trace nested Python calls and tool executions in real-time, ensuring that the ~15-20% performance lead observed in benchmarks translates to reliable, debuggable autonomous workflows.
Open Deep Research Democratizes Agentic Search
The release of Open-source DeepResearch marks a significant milestone in freeing search agents from proprietary silos. By combining a recursive Plan, Search, Read, and Review reasoning loop, these agents can execute hundreds of concurrent search queries to synthesize comprehensive reports. According to @aymeric_roucher, the framework's 'code-as-action' paradigm—built on the smolagents library—significantly mitigates hallucinations by allowing agents to handle complex logic loops more reliably than traditional JSON schemas. High-reasoning models like Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct are currently performing as the primary orchestrators for these long-horizon retrieval tasks.
These developments represent a shift toward 'planning' as the core pillar of the agentic stack. Innovative techniques like AI-MO/Kimina-Prover are applying test-time RL search to formal reasoning, enabling models to 'think longer' and verify logical paths within systems like Lean. Simultaneously, ServiceNow-AI/Apriel-H1 has demonstrated that an 8B parameter model can achieve performance parity with Llama 3.1 70B on agentic benchmarks through 'Hindsight Reasoning,' a distillation method where models learn from past execution errors. Specialized tools are further narrowing the gap; Jupyter-Agent-2 is training models to reason within computational notebooks, while Intel/DeepMath provides a lightweight solution for mathematical reasoning, with specialized models increasingly hitting 90%+ accuracy on targeted reasoning benchmarks as noted by @_akhaliq.
Small Models, Big Pixels: The Open-Source GUI Revolution
The race for 'Computer Use' is shifting from monolithic APIs to specialized, local executors. Hcompany/Holo1, a lean 4.5B parameter VLM, has set a new open-source benchmark with a 62.4% success rate on the ScreenSpot subset, notably outperforming GPT-4V's 55.4%. This specialized architecture powers the Surfer-H agent, which handles fine-grained coordinate precision that often stumps larger, general-purpose models. To address the evaluation gap, Hugging Face/ScreenSuite provides a massive testing ground of 3,500+ tasks across 9 domains, identifying inference latency and pixel-level accuracy as the next major hurdles for autonomous digital workers. Efficiency is the primary driver for models like Hugging Face/Smol2Operator, which uses post-training to optimize small models for tactical GUI interactions. Compared to Anthropic’s Computer Use, which relies on the high-parameter Claude 3.5 Sonnet, these local models offer a significant advantage in token efficiency and latency by avoiding the overhead of massive general-reasoning loops for simple UI tasks. This shift is supported by Hugging Face/ScreenEnv, a sandbox for full-stack desktop OS deployment, and research highlighted in the GUI-Gym paper, which supports reinforcement learning at over 100 FPS.
Physical AI: Bridging Visual Reasoning and Robotic Action
NVIDIA is closing the 'physicality gap' with Cosmos Reason 2, a visual-thinking architecture that enables long-horizon planning and spatial reasoning, such as predicting object stability before a grasp. As noted by @DrJimFan, this intelligence is physically grounded by the Reachy Mini platform, a compact humanoid powered by the NVIDIA DGX Spark which delivers 275 TOPS of edge compute necessary for real-time inference. While high-level reasoning handles complex logic, real-time manipulation requires low-latency perception; @pollen_robotics highlights that their Pollen-Vision interface simplifies this by providing 'vision-as-a-service,' integrating zero-shot models like Grounding DINO and SAM to help agents interact with novel objects without prior training. The transition from 'see-and-react' to 'reason-and-act' is further supported by the LeRobot Community Datasets, which aim to become the 'ImageNet of robotics' by standardizing open-source data for embodied AI. Experts like @_akhaliq observe that these advancements are moving agents from controlled labs into dynamic environments, suggesting the Agentic Web is evolving into a physical layer where standardized robotic interfaces allow for seamless deployment in homes and offices.
Browser-Native Agency and the Modular Tooling Standard
Agent infrastructure is pivoting toward browser-native execution with the introduction of Agents.js, a library that enables developers to provide LLMs with direct tool access within JavaScript environments. This shift allows for low-latency, client-side automation, though it introduces a new security perimeter; developers must implement robust sandboxing to prevent prompt injection from triggering unauthorized local function calls. The modularity of this ecosystem is further anchored by the Model Context Protocol (MCP), which has been proven to power fully functional agents in as little as 50 to 70 lines of code, effectively standardizing how agents discover and interact with external data sources across both Python and JS stacks.
To simplify enterprise adoption, the Hugging Face x LangChain partner package now provides a streamlined interface for using ChatHuggingFace and HuggingFaceEndpoint within existing LangChain workflows. This is complemented by IBM Research's CUGA (Configurable Universal Graph-based Agent), which offers a high-level orchestration platform for democratizing complex agentic behaviors. To ensure these systems remain interoperable and reproducible, the OpenEnv initiative is establishing a shared ecosystem for agent environments, specifically designed to mitigate 'environment drift' and prevent vendor lock-in across diverse deployment targets.
Closing the Gap: New Benchmarks Target Forecasting and Industrial Autonomy
As agents move beyond simple conversationalists, evaluation is shifting toward multi-step reasoning and predictive accuracy. FutureBench introduces a framework for evaluating agents on their ability to forecast future events using Brier Scores (where 0 is a perfect prediction). Current results indicate a significant 'forecasting gap'; while top-tier models like GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet are being benchmarked, they generally lag behind human superforecasters who consistently achieve lower Brier scores on complex geopolitical and financial queries. This benchmark is critical for strategic agents that must move beyond retrieval to active anticipation.
Simultaneously, the DABStep (Data Agent Benchmark) has identified a critical failure mode known as 'plan-act' misalignment, where agents generate a correct logical plan but fail to follow it during execution. To address industrial readiness, IBM Research/AssetOpsBench bridges the gap between lab environments and operational reality, testing agents on their ability to manage assets and maintenance tasks. These metrics are essential as the community transitions to GAIA 2.0, which raises the bar for general-purpose autonomy by introducing more dynamic, multi-modal tasks that require agents to maintain state over long, non-linear workflows.